Question: MATLAB The method of False Position (Linear Interpolation) is another iterative method that we can use to find the root (s) of a non-linear function
MATLAB


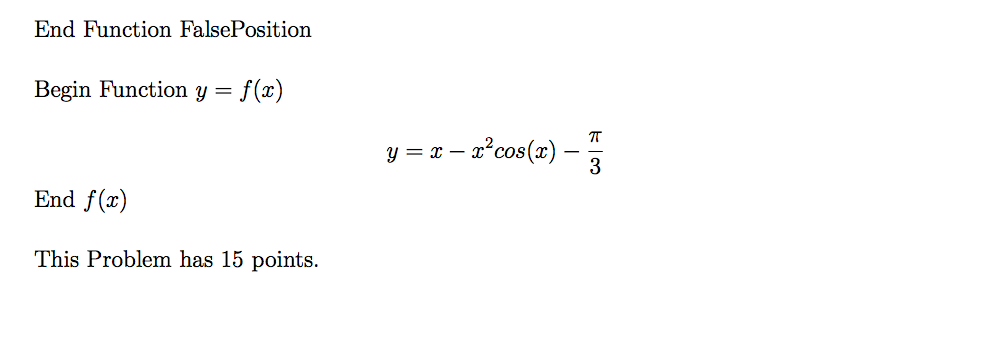
The method of False Position (Linear Interpolation) is another iterative method that we can use to find the root (s) of a non-linear function f(r). Let us assume that the values of the function f(r1) and f(r2) at two points T1 and r2 have different signs. If we know that the function is continuous between r1 and T2, there should be at least one point between r1 and z2 for which the value of the function is zero. The method of False Position works when there is only one root between r1 and r2. In other words, if there is more than one point between a and r2 at which the function f(z) intersects the z-axis, the method of False Position might fail to find those points. Now, just for simplicity, lets us assume that the f(z1) 0 and f(z2) 0. The equation of the line that passes (r1. f(r1)) and (r2, f(r2)) is y(T) mr c where m and c are f(r2) f (r1) T2 T1 mr let us find the point a3 at which y (r) intersect the r-axis: y (ra) T2 Now we calculate the value of f(r3). If f(z3) 0, the root of f (ar) is now between z3 and T2. So, we have got a little bit closer to the root! Similarly, if the f(z3) 0 it means that the root is now between z1 and z3. Let us assume that f(T3) 0, then we can find the next guess by repeating the method above this time for the line that passes (z1, f(r1) and (r3, f(a 3)): T4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


