Question: Matrix Multiplication Programming. Implement two types of algorithms for multiplying two n x n matrices. Assume n is a power of 2. 1. The straight-forward
Matrix Multiplication Programming.
Implement two types of algorithms for multiplying two n x n matrices.
Assume n is a power of 2.
1. The straight-forward O(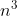 ) matrix multiplication algorithm.
) matrix multiplication algorithm.
2. Strassen's matrix multiplication algoritm.
Evaluate your different algorithms, and write a short report. Create test matrices for different values
of n(4, 16, 512 and 1024). Generate matrices using random numbers.
Do you expect the two algorithms to have the same output when using doubles?
Compute the running time of your algorithms.
Sample Test Class.
public class MatrixMultiplicationTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // create two double 2-D arrays double[][] a double[][] b Matrix m1 = new Matrix(a); Matrix m2 = new Matrix(b); System.out.println(m1); Matrix productStrassen=m1.multiplyStrassen(m2); Matrix productRegular=m1.multiply(m2); System.out.println("Are matrices the same? "+productStrassen.equals(productRegular)); System.out.println(productStrassen); } }
public class Matrix { private double[][] matrix; public Matrix(double[][] matrix) { this.matrix = matrix; } /** * Compute matrix multiplication using regular method O(n3) solution. * This method should return product matrix. * * @param matrixB * @return */ public double[][] productRegular(double matrixB[][]) { // Implement your algorithm here. } /** * Compute matrix multiplication using Strassen's method. * This method should return product matrix. * * @param matrixB * @return */ public double[][] productStrassen(double matrixB[][]) { // Implement your algorithm here. } } Note: To count the time use system.currentTimeMillis(). Every time you compare a pair of numbers increase an appropriate counter. The first programming assignment is basically to learn JUnit testing.
- Do not use any fancy libraries. We should be able to compile it under standard installs. Include a readme file on how to you compile the project.
/*
sample JUnit tests for checking and comparing the result of
regular O(n^3) matrix multiplication algorithm with Strassen
multiplication algorithm.
*/
import static org.junit.Assert.assertArrayEquals;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* The main JUnit Test class to test regular multiplication
* and Strassen multiplication method.
*
*
*/
public class MatrixTest extends TestCase {
private Matrix A, B; //input matrices
private Matrix productRegularResult, productStrassenResult; // Matrices for storing the results
private int N; // size of the NXN matrix
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception
{
N = 4; // size of the matrix
double[][] array1 = new double[N][N];
double[][] array2 = new double[N][N];
A = new Matrix(array1);
B = new Matrix(array2);
productRegularResult = new Matrix(N);
productStrassenResult = new Matrix(N);
} // setUp()
/* compare result matrices of regular multiplication method and Strassen multiplication method:
*/
@Test
public void testProductCompare() {
//run user defined random() method to generate the matrices
A = A.random();
B = B.random();
// run productRegular()
productRegularResult = A.productRegular(B);
// run productStrassen()
productStrassenResult = A.productStrassen(B);
for (int i = 0; i
assertArrayEquals(productRegularResult.data[i], productStrassenResult.data[i], 0.0001 ); // data[][] is a data member for storing matrix values in class Matrix.
}
}
/* multiplying a 2D array using the regular method:
*/
@Test
public void testProductRegular() {
//expected output
double[][] expected = {{96.0,94.0,81.0,128.0},{144.0,117.0,112.0,162.0},{132.0,112.0,101.0,152.0},{112.0,86.0,87.0,130.0}};
// input 2D arrain
double[][] array1 = {{2.0,4.0,5.0,7.0},{6.0,7.0,2.0,8.0},{4.0,6.0,3.0,9.0},{8.0,4.0,1.0,5.0}};
double[][] array2 = {{6.0,4.0,5.0,8.0},{8.0,7.0,8.0,8.0},{2.0,6.0,5.0,9.0},{6.0,4.0,2.0,5.0}};
Matrix m1 = new Matrix(array1);
Matrix m2 = new Matrix(array2);
// run productRegular()
productRegularResult = m1.productRegular(m2);
for (int i = 0; i
assertArrayEquals(expected[i],productRegularResult.data[i], 0.0); // data[][] is a data member for storing matrix values in class Matrix.
}
}
/* multiplying a 2D array using the Strassen method:
*/
@Test
public void testProductStrassen() {
//expected output
double[][] expected = {{96.0,94.0,81.0,128.0},{144.0,117.0,112.0,162.0},{132.0,112.0,101.0,152.0},{112.0,86.0,87.0,130.0}};
// input 2D array
double[][] array1 = {{2.0,4.0,5.0,7.0},{6.0,7.0,2.0,8.0},{4.0,6.0,3.0,9.0},{8.0,4.0,1.0,5.0}};
double[][] array2 = {{6.0,4.0,5.0,8.0},{8.0,7.0,8.0,8.0},{2.0,6.0,5.0,9.0},{6.0,4.0,2.0,5.0}};
Matrix m1 = new Matrix(array1);
Matrix m2 = new Matrix(array2);
// run productRegular()
productStrassenResult= m1.productStrassen(m2);
for (int i = 0; i
assertArrayEquals(expected[i],productStrassenResult.data[i], 0.0); // data[][] is a data member for storing matrix values in class Matrix.
}
}
} // class MatrixTest
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


