Question: matrix_proc.c code: /* * ch14/speed_multiprcs_vs_multithrd_simple/matrixmul/prcs_matrixmul.c *************************************************************** * This program is part of the source code released for the book * Hands-on System Programming with Linux



matrix_proc.c code:
/* * ch14/speed_multiprcs_vs_multithrd_simple/matrixmul/prcs_matrixmul.c *************************************************************** * This program is part of the source code released for the book * "Hands-on System Programming with Linux" * (c) Author: Kaiwan N Billimoria * Publisher: Packt * * From: Ch 14 : Multithreading Part I - The Essentials **************************************************************** * Brief Description: * A quick test: matrix multiplication via: * - process model (this program); operations done in sequence; * - threaded model; operations done in parallel. * * For details, please refer the book, Ch 14. */ #include#include //#include "common.h" #define N 1024 //32 // number of rows/columns int a[N][N], b[N][N], c[N][N]; int main(void) { int i, j, k; // Initialize the matrices 'a' and 'b' for (i = 0; i
matrix_threads.c code:
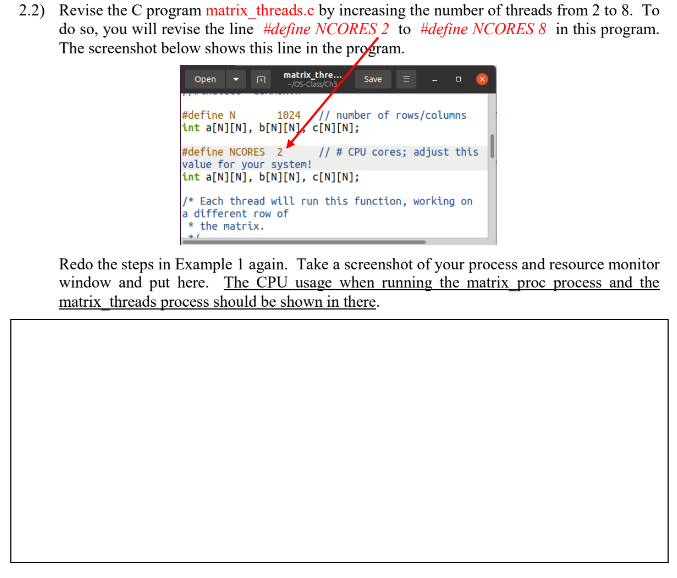
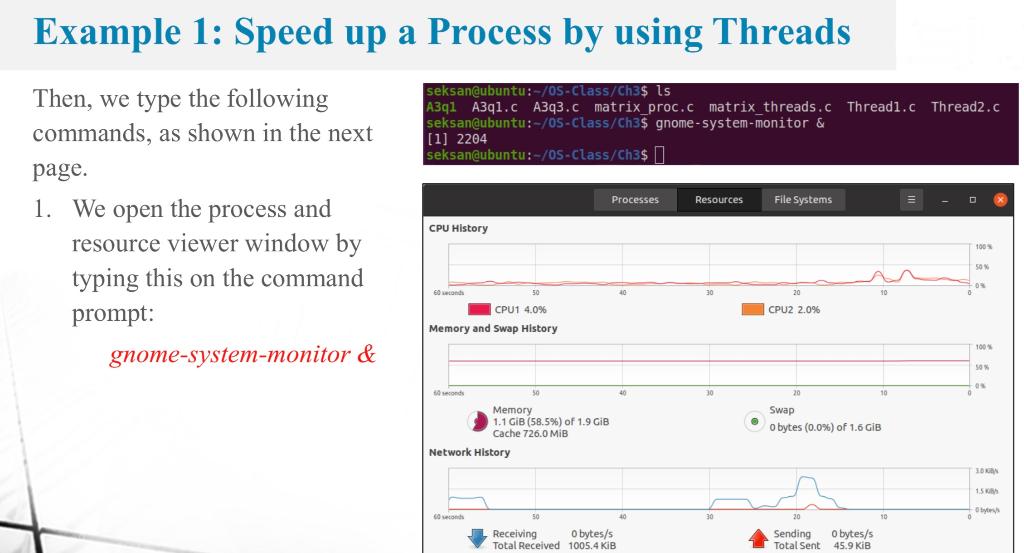
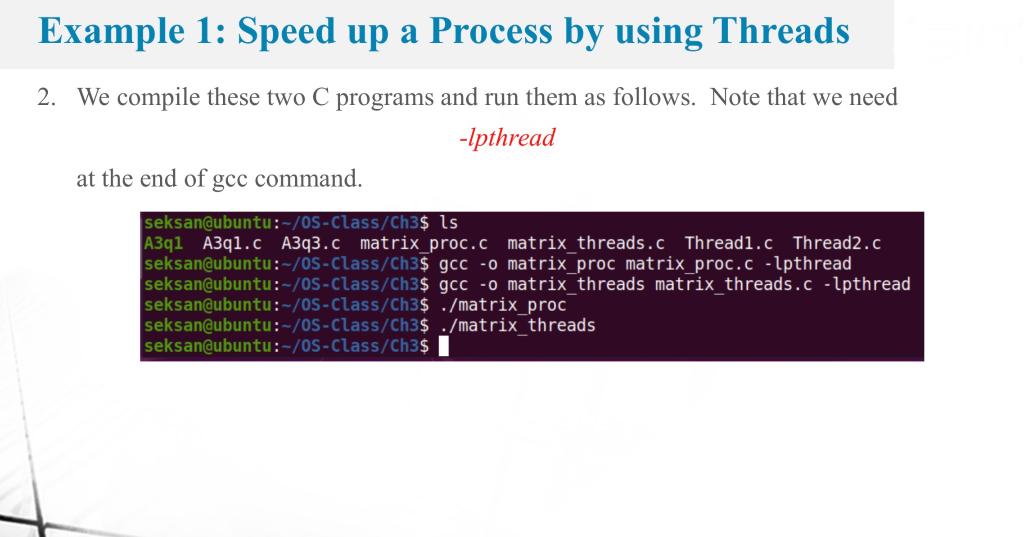
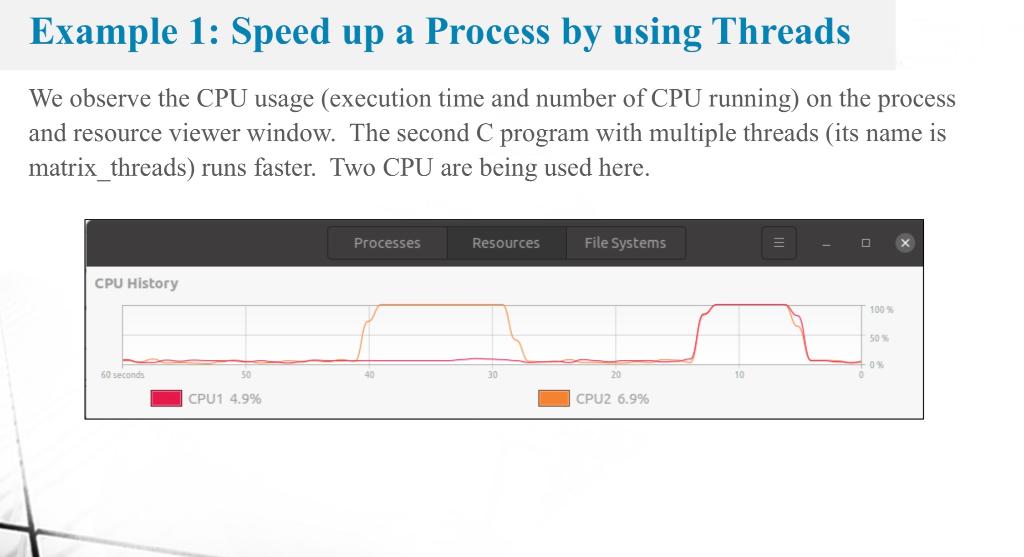
/* * ch14/speed_multiprcs_vs_multithrd_simple/matrixmul/thrd_matrixmul.c *************************************************************** * This program is part of the source code released for the book * "Hands-on System Programming with Linux" * (c) Author: Kaiwan N Billimoria * Publisher: Packt * * From: Ch 14 : Multithreading Part I - The Essentials **************************************************************** * Brief Description: * A quick test: matrix multiplication via: * - process model; operations done in sequence; * - threaded model (this program); operations done in parallel. * * For details, please refer the book, Ch 14. */ #include#include #include //#include "common.h" #define N 1024 // number of rows/columns int a[N][N], b[N][N], c[N][N]; #define NCORES 2 // # CPU cores; adjust this value for your system! int a[N][N], b[N][N], c[N][N]; /* Each thread will run this function, working on a different row of * the matrix. */ void *threadfun(void *data_arg) { int *p = (int *)data_arg; int i, j, k; for (i = *p; i In this exercise, we will observe and compare the process's execution time and CPU usage when we use more threads in a process. We follow the steps as shown in Example 1 in Lecture Note 3 , where matrix multiplication is considered. The following two programs are from Chapter 14 of this book: K. N. Billimoria, Hands-On System Programming with Linux, Packt Publishing, 2018. We have the C programs matrix proc.c and matrix_threads.c. They are in the Google Classroom. Follow the steps shown in Example 1 in Lecture Note 3 and answer the following questions. 2.1) Take a screenshot of your process and resource monitor window and put here (similar to that shown in Example 1). The CPU usage when running the matrix proc process and the matrix threads process should be shown in there. 2.2) Revise the C program matrix_threads.c by increasing the number of threads from 2 to 8 . To do so, you will revise the line \#define NCORES 2 to \#define NCORES 8 in this program. The screenshot below shows this line in the program. Redo the steps in Example 1 again. Take a screenshot of your process and resource monitor window and put here. The CPU usage when running the matrix proc process and the matrix threads process should be shown in there. 2.3) Compare the CPU execution times between running maxtix threads in 2.1 and running matrix_threads in 2.2. Discuss why they are the same or different. The answer might differ from case to case. In this example (which is Exercise 2 in Assignment 3), we compare two C programs which do the same jobs - compute an inner product of two matrix whose size is 10241024. - The first C program is a single-threaded process: matrix proc.c. - The second C program is a multi-threaded process (one main thread and four worker threads helping computing the inner product): matrix_threads.c. The C programs are from Chapter 14 of this book: K. N. Billimoria, Hands-On System Programming with Linux, Packt Publishing, 2018. These C programs are also available in https://github.com/PacktPublishing/Hands-on-System-Programming-with-Linux Example 1: Speed up a Process by using Threads Then, we type the following commands, as shown in the next page. 1. We open the process and resource viewer window by typing this on the command prompt: gnome-system-monitor \& Example 1: Speed up a Process by using Threads 2. We compile these two C programs and run them as follows. Note that we need -lpthread at the end of gcc command. seksan@ubuntu: /0 S-Class/Ch3\$ ls A3q1 A3q1.c A3q3.C matrix proc.c matrix_threads.c Thread1.c Thread2.c seksaneubuntu: / /0S-Class/Ch3s gcc -o matrix_proc matrix_proc.c -lpthread seksaneubuntu: / /0S-Class/Ch3s gcc 0 matrix-threads matrix_threads.c -lpthread seksaneubuntu: /0S-Class/Ch3\$./ matrix_proc seksan@ubuntu: /0S-Class/Ch3\$\$./matrix_threads seksan@ubuntu:-/0S-Class/Ch3\$\$ Example 1: Speed up a Process by using Threads We observe the CPU usage (execution time and number of CPU running) on the process and resource viewer window. The second C program with multiple threads (its name is matrix_threads) runs faster. Two CPU are being used here
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


