Question: ME1 V . E = P Eo ME 2 V . B= 0 OB ME3 V X E = - at OE ME4 VX B
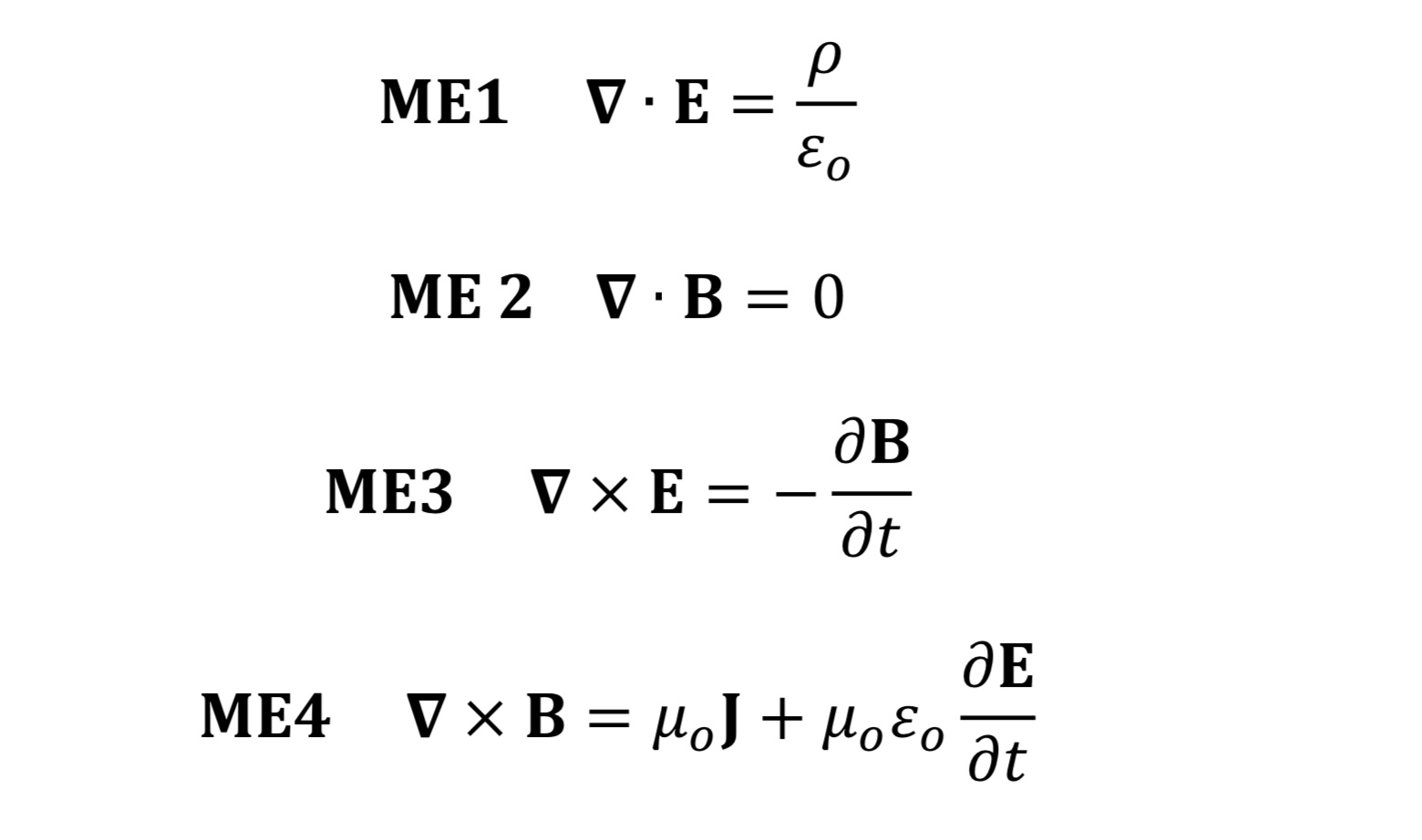



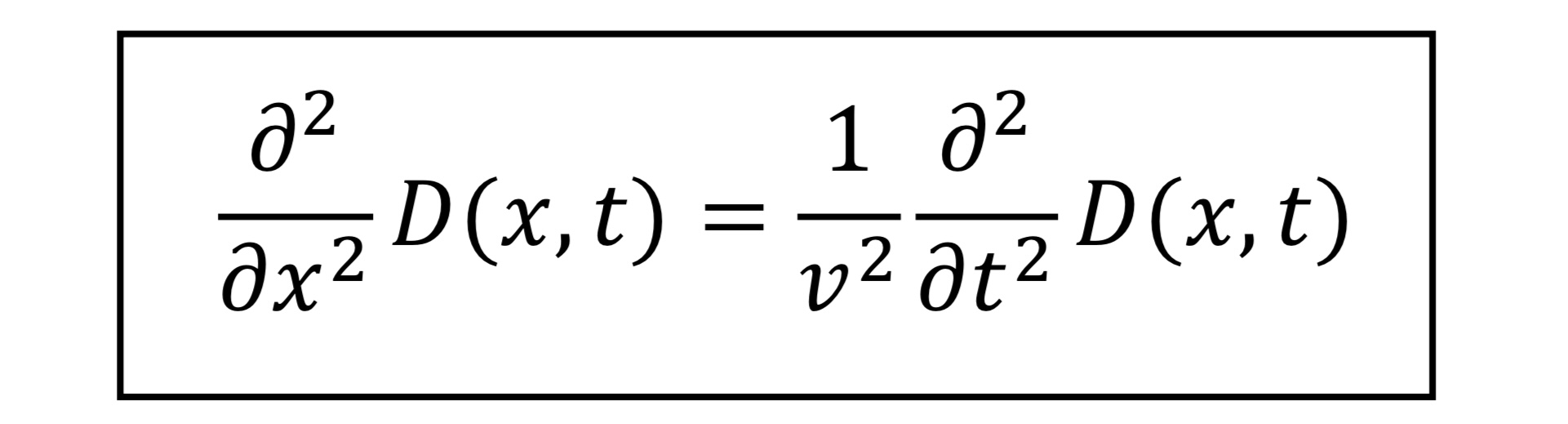
ME1 V . E = P Eo ME 2 V . B= 0 OB ME3 V X E = - at OE ME4 VX B = MoJ + Moco atFrom Maxwell's equations to a wave equation Maxwell applied these equations to free space (i.e. empty space) where there are no charges or currents (p = 0 and J = 0). 1. Rewrite Maxwell's equations for free space (i.e. letting p = 0 and J = 0). ME1) ME3) ME2) ME4) Equations 3 and 4 are now saying "changing magnetic fields cause changing electric fields" and "changing electric fields cause changing magnetic fields".2. Operate on both sides of equation ME3 by V x . On the left side use the identity V x (V x F) = V(V -F) VZF . You can V2 with 62/6x2 since our wave is traveling in the x direction. On the right side, use ME4 to substitute V x B with yosan/at. We now have 62E/6x2 on the left side and azE/at2 on the right side. The result is a differential equation for a wave (see the boxed equation on page 11). In fact, it is the differential equation for an electric eld wave. 3. What is the velocity of this wave? (See the boxed equation on page 11). Use 60 = 8.854 >
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


