Question: MIPS ASCII Decimal to 2SC Program Specification Functionality The functionality of your program will be as follows: 1. Read two program arguments: signed decimal numbers
MIPS ASCII Decimal to 2SC Program
Specification
Functionality
The functionality of your program will be as follows:
1.
Read two program arguments: signed decimal numbers [-64, 63].
2.
Print the user inputs.
3.
Convert the ASCII strings into two sign-extended integer values.
a.
Convert the first program argument to a 32-bit twos complement number,
stored in register $s1.
b.
Convert the second program argument to a 32-bit twos complement number,
stored in register $s2.
4.
Add the two integer values, store the sum in $s0.
5.
Print the sum as a decimal to the console.
6.
Print the sum as 32-bit twos complement binary number to the console.
7.
(Extra credit) Print the sum as a decimal number expressed in Morse code.
a.
Use a period (ASCII code 0x2E) for dots and a hyphen (ASCII code 0x2D)
for dashes.
b.
Insert a space (ASCII code 0x20) between characters.
c.
Dont forget to print the Morse code for a minus sign if the number is
negative!
Registers $s1 and $s2 shall contain the two 32-bit twos complement integers entered
by the user. Register $s0 shall be used to store the 32-bit twos complement sum.
You should try to use as few registers as possible. Try to only use $zero, $v0, $a0,
$s0-$s2, and the temporary registers, $t0-$t9. If you run out of registers, you may
use $s3-$s8.
Syscalls
When printing the integer values, you may use syscall system services 4 (print
string) and 11 (print character). You
may not use syscall system service 1 (print
integer) or syscall system service 35 (print integer as binary).
Input
In this lab you will obtain two user inputs, not using a syscall, but by using
program arguments. The user will enter two integer values between -64 and 63. These
numbers will be sign-extended to 32 bits and stored in $s1 and $s2. Turn on program
arguments from the Settings menu as shown below.
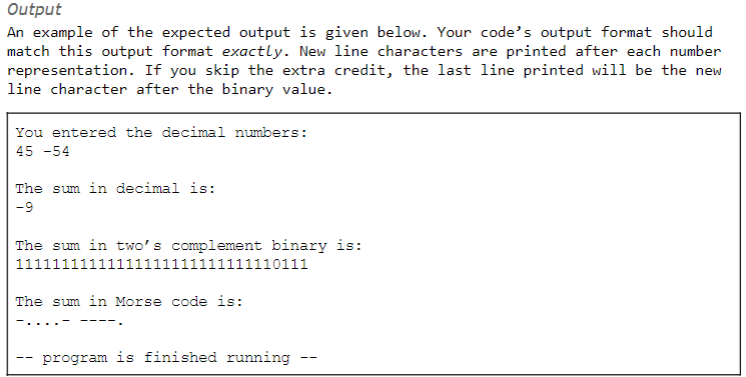
Output An example of the expected output is given below. Your code's output format should match this output format exactly. New line characters are printed after each number representation. If you skip the extra credit, the last line printed will be the new line character after the binary value. You entered the decimal numbers: 45-54 The sum in decimal is: -9 The sum in two's complement binary is: The sum in Morse code is: -program is finished running Output An example of the expected output is given below. Your code's output format should match this output format exactly. New line characters are printed after each number representation. If you skip the extra credit, the last line printed will be the new line character after the binary value. You entered the decimal numbers: 45-54 The sum in decimal is: -9 The sum in two's complement binary is: The sum in Morse code is: -program is finished running
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


