Question: Model 4: Splitting in Double Bonds Double bonds have unique splitting patterns, because the hydrogens can be non-equivalent. Questions 6. a.) Is the circled H
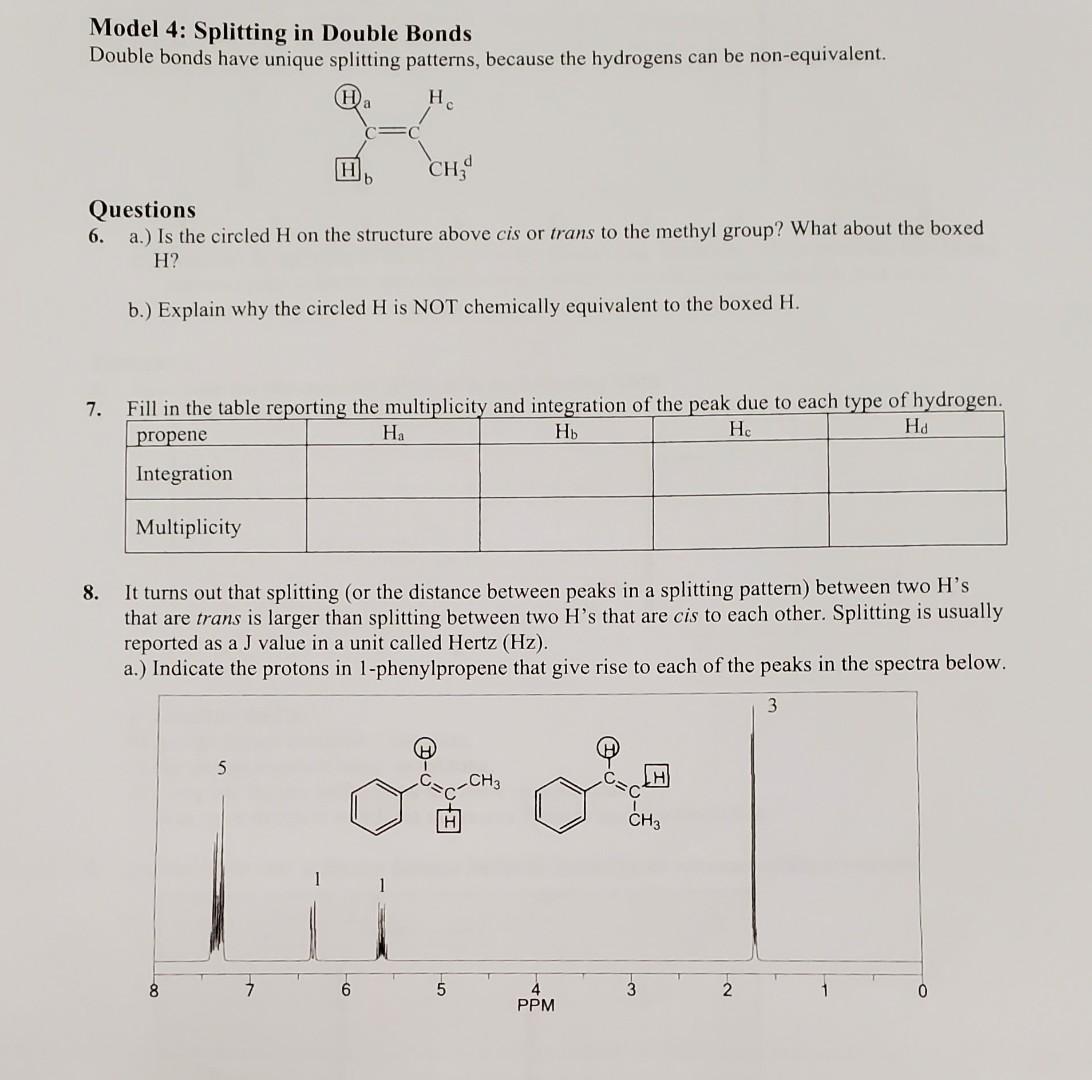

Model 4: Splitting in Double Bonds Double bonds have unique splitting patterns, because the hydrogens can be non-equivalent. Questions 6. a.) Is the circled H on the structure above cis or trans to the methyl group? What about the boxed H ? b.) Explain why the circled H is NOT chemically equivalent to the boxed H. 7. Fill in the tahle renortino the multinlicitv and integration of the peak due to each type of hydrogen. 8. It turns out that splitting (or the distance between peaks in a splitting pattern) between two H's that are trans is larger than splitting between two H's that are cis to each other. Splitting is usually reported as a J value in a unit called Hertz(Hz). a.) Indicate the protons in 1-phenylpropene that give rise to each of the peaks in the spectra below. based on the splitting of the CH next to the phenyl ring, determine which spectrum (above and previous page is for the trans molecule and which is for the cis molecule (i.e. look at the spacing of the peaks in the doublet at 6.4 ). Label them accordingly
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


