Question: Modify the code below to run the non-deterministic finite automata (NFA) in python with the given graph below. - initialize `current_states` - define `x` -
Modify the code below to run the non-deterministic finite automata (NFA) in python with the given graph below.
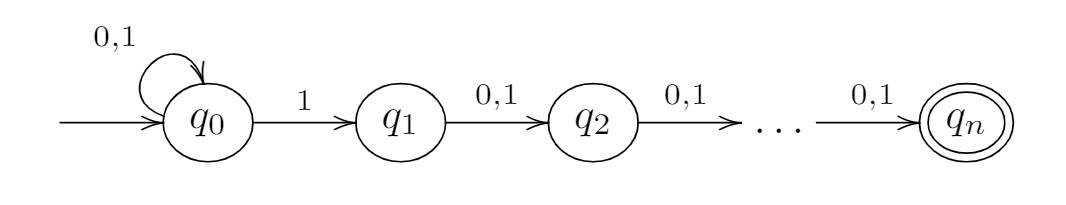
- initialize `current_states`
- define `x`
- define the NFA given above by edit nfa1
- The function must return accept with input (000001010110100100011010000) and reject input (01010101111111111001010000111110000000)
Code: (Only modify the section "code here")
```
class FA:
def __init__(self, alphabet, states, transition, accepting_states):
self.alphabet = alphabet
self.states = states
self.transition = transition
self.accepting_states = accepting_states
def DFA(input_string, dfa):
# set current_state to initial state
current_state = dfa.states[0]
# run through the input string
for symbol in input_string:
i = dfa.states.index(current_state)
j = dfa.alphabet.index(symbol)
current_state = dfa.transition[i][j]
return current_state
def NFA(input_string, nfa):
# set current_state to initial state
current_states = nfa.states[code here]
# run through the input string
for symbol in input_string:
x = set()
for state in current_states:
i = nfa.states.index(state)
j = nfa.alphabet.index(symbol)
x = code here
current_states = x
return current_states
def main():
# Read in the input_string
input_string = input()
# Define a DFA
dfa1 = FA(['0','1'],['q','r'],[['r','q'],['q','r']],{'q'})
nfa1 = code here
# Run the DFA on the input string
# final_state = DFA(input_string, dfa1)
# if final_state in dfa1.accepting_states:
# print("Accept")
# else:
# print("Reject")
# Run the NFA on the input string
final_states = NFA(input_string, nfa1)
if set(final_states) & set(nfa1.accepting_states):
print("Accept")
else:
print("Reject")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
```
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


