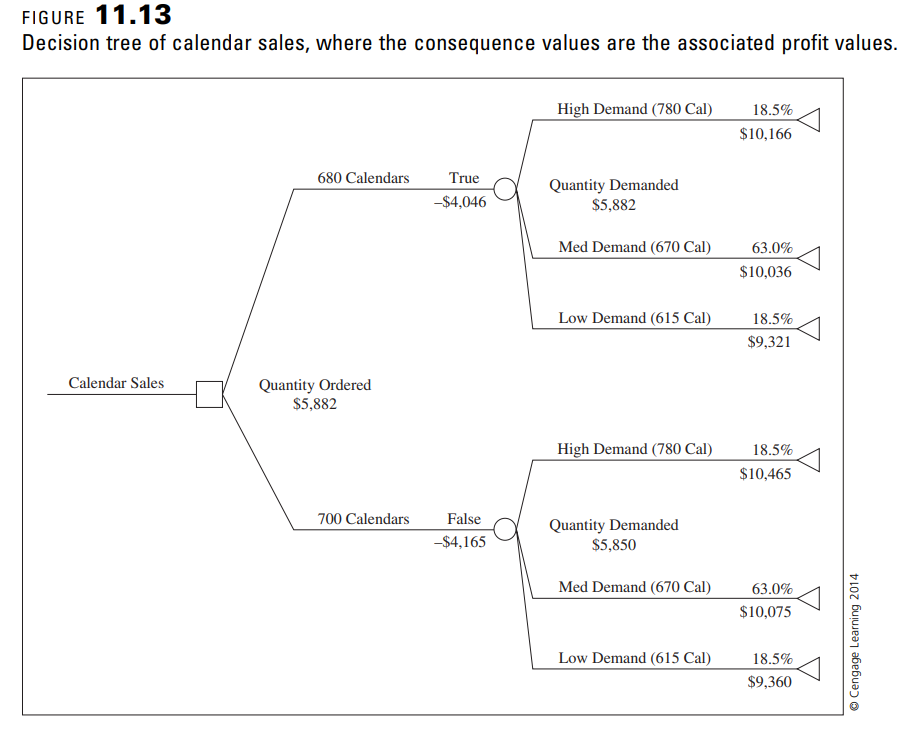
Question: Modify the decision-tree model in Figure 11.13 to use the extended Swanson-Megill (ES-M) approximation for demand instead of the EPT approximation. a. Use your ES-M
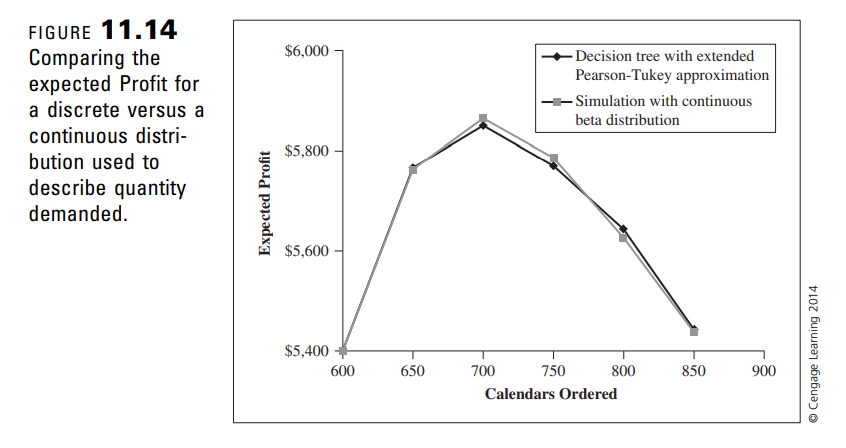
Modify the decision-tree model in Figure 11.13 to use the extended Swanson-Megill (ES-M) approximation for demand instead of the EPT approximation. a. Use your ES-M model to calculate expected profit for Order Quantity values 600, 650, 700, 750, and 800. How do your results compare to those in Figure 11.14?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


