Question: MODULE 2 WORKSHEET Comparing Means Purpose: You will be able to demonstrate a general understanding of interpreting statistical output to compare group means. Instructions: Answer
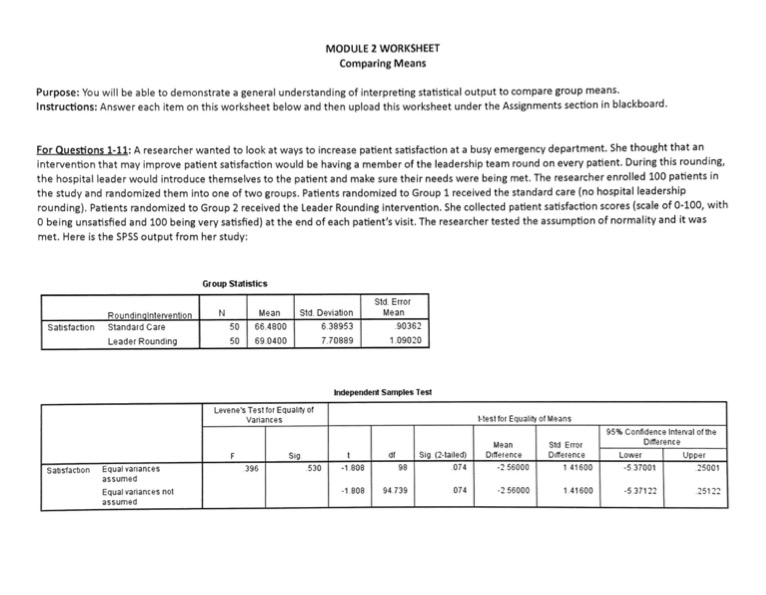

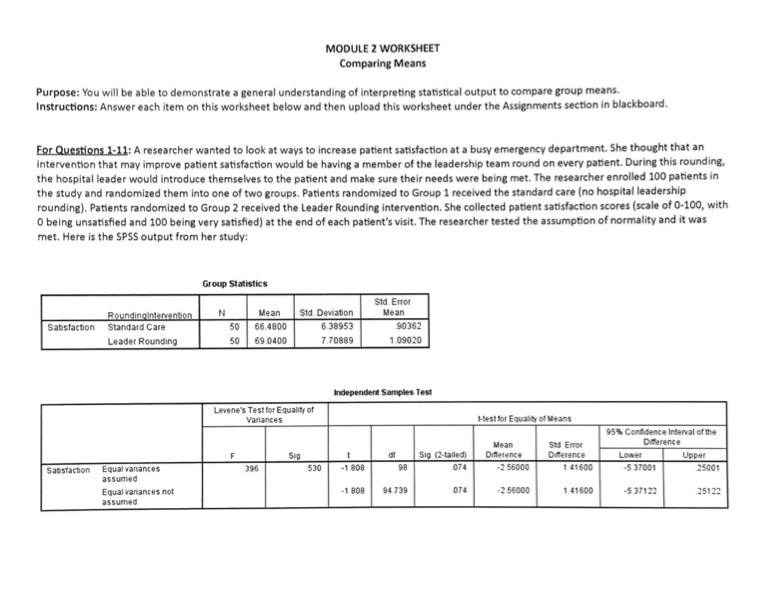

MODULE 2 WORKSHEET Comparing Means Purpose: You will be able to demonstrate a general understanding of interpreting statistical output to compare group means. Instructions: Answer each item on this worksheet below and then upload this worksheet under the Assignments section in blackboard. For Questions 1-11: A researcher wanted to look at ways to increase patient satisfaction at a busy emergency department. She thought that an Intervention that may improve patient satisfaction would be having a member of the leadership team round on every patient. During this rounding, the hospital leader would introduce themselves to the patient and make sure their needs were being met. The researcher enrolled 100 patients in the study and randomized them into one of two groups. Patients randomized to Group 1 received the standard care (no hospital leadership rounding). Patients randomized to Group 2 received the Leader Rounding intervention. She collected patient satisfaction scores (scale of 0-100, with O being unsatisfied and 100 being very satisfied) at the end of each patient's visit. The researcher tested the assumption of normality and it was met. Here is the SPSS output from her study: Group Statistics Sid. Error Roundingintervention N Mean Sid. Deviation Mean Satisfaction Standard Care 50 66.4800 6.38953 90362 Leader Rounding 50 69.0400 7.70889 1 09020 Independent Samples Test Levene's Test for Equality of Variances 1-best for Equality of Means 95% Confidence Interval of the Mean Dearence Sig (2-tailed) Difference Difference Lower Upper Shostaction Equal vanances 396 530 1808 074 2 56000 1 41600 -$ 37001 25001 assumed Equal variances not -1 808 94 739 OTA -256000 1 41600 -5 37122 25123 assumed1. What is the independent variable? (2 points) 2. What is the dependent variable? (2 points) 3. What is the null hypothesis being tested? (2 points) 4. What was the mean satisfaction score of the patients who received standard care? (2 points) 5. What was the mean satisfaction score of the patients who received the Leader Rounding intervention? (2 points) 6. What is the Levene's test p value? (5 points) 7. What does the Levene's test p value tell you (why is it important to look at this value)? (5 points) 8. What is the t value from this analysis? (5 points) 9. What is the p value from the t-test analysis? (5 points) 10. Would you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? (5 points) 11. What conclusion would you make? (5 points) For Questions 12-17: A researcher is interested in reducing the rate of inpatient falls in acute care hospitals. He conducted a multi-site study and enrolled 100 hospitals. Hospitals were randomly assigned a new intervention to implement with all patients who scored as a fall risk: Unit 1 - Patients scored as a fall risk wore yellow non-slip socks Unit 2 - Patients scored as a fall risk had bed alarms installed that notified staff when patient was attempting to get out of bed Unit 3 - Patients scored as a fall risk had telesitters placed in the room and a staff member watched the monitors and could communicate with the patient if they began rising from bed
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


