Question: Module 3: RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION Provide the missing data in the table: Suppose you are to toss 3 coins simultaneously. Let X be

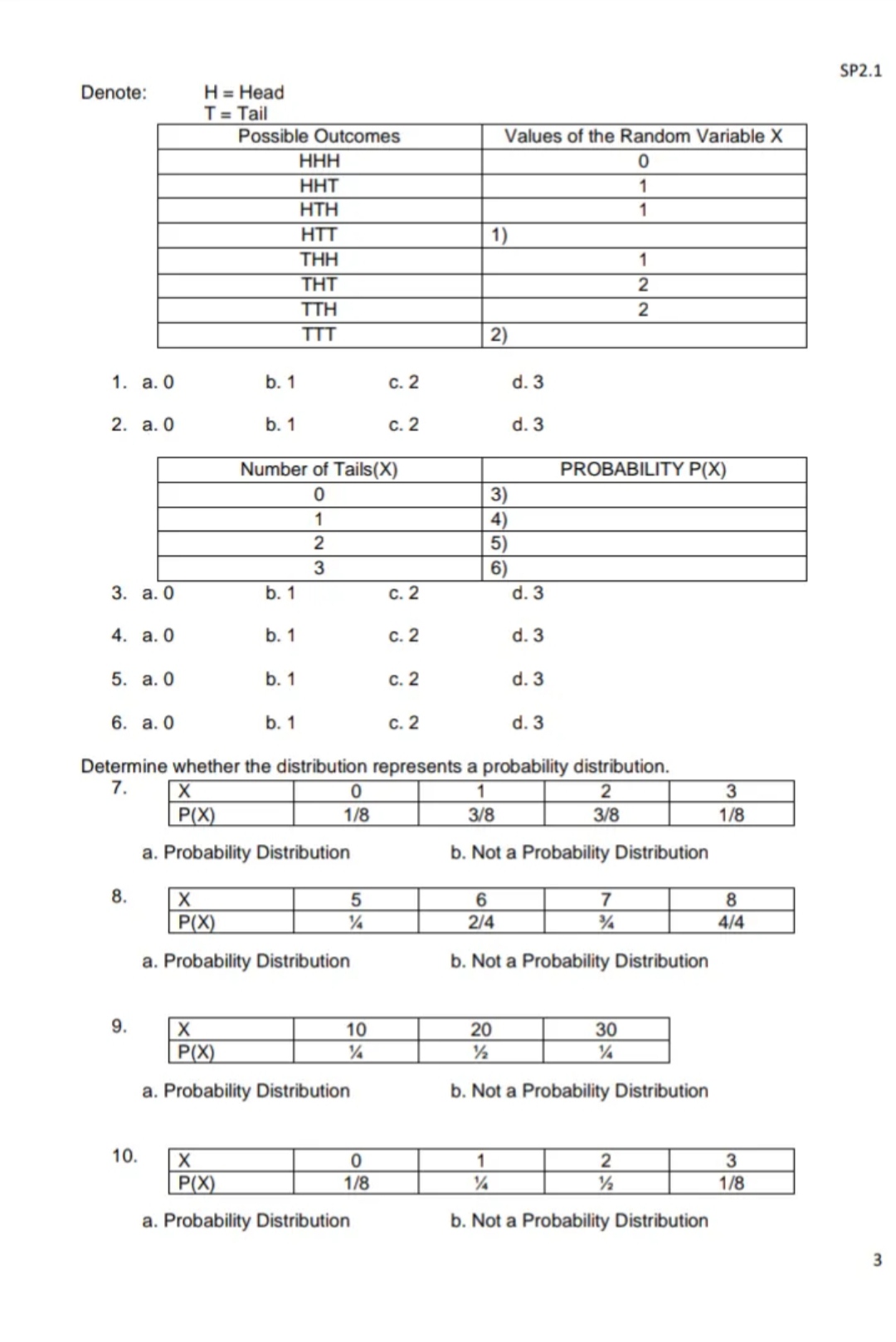



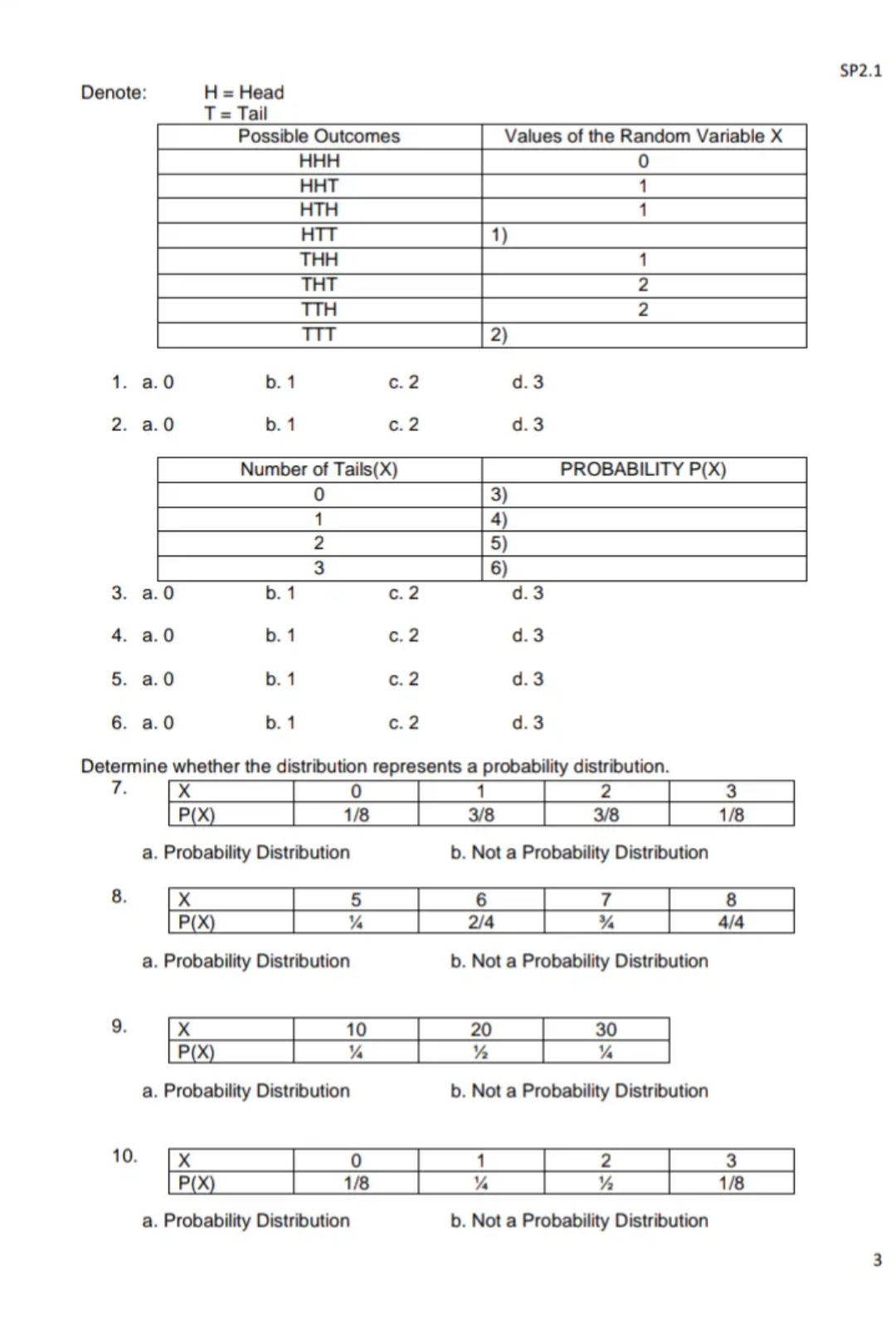


Module 3: RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION Provide the missing data in the table: Suppose you are to toss 3 coins simultaneously. Let X be the random variable representing the number of tails that occurred. Find the values of the random variable X and its corresponding probability 2SP2.1 Denote: H = Head T = Tail Possible Outcomes Values of the Random Variable X HHH 0 HHT -- HTH HTT 1 ) THH N - THT TTH 2 TTT 2) 1. a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 2. a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 Number of Tails(X) PROBABILITY P(X) 0 3) 1 4) IN 5 ) 3 6 3. a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 1. 3 4. a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 5. a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 6. a. 0 b. 1 C. 2 d. 3 Determine whether the distribution represents a probability distribution. 7. X 0 2 3 P(X) 1/8 3/8 3/8 1/8 a. Probability Distribution b. Not a Probability Distribution 8. X 5 6 7 8 P(X) 1/4 2/4 3/4 4/4 a. Probability Distribution b. Not a Probability Distribution 9. X 10 20 30 P(X) 1/2 1/4 a. Probability Distribution b. Not a Probability Distribution 10. X 0 1 2 3 P(X) 1/8 1/2 1/8 a. Probability Distribution b. Not a Probability DistributionSP2.1 Module 4: MEAN AND VARIANCE OF DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLE 1. It is equal to the summation of the products of the value of the random variable and the corresponding probability. a. Mean b. Median c. Standard Deviation d. Variance 2. what is the value of the variance when all data in the set are equal? a. -1 b. 0 c. 1 d. 100% 3. A measure that tells us how spread the scores are from the mean and from each other, it is the average squared deviation. a. Variance b. Standard Deviation c. Median d. Mean 4. Find the MEAN of the given discrete random variable. Y 0 1 2 3 P(Y) 1/8 3/8 3/8 1/8 a. 0.5 b. 1 c. 1.5 d. 3 5. It is the symbols used to denote variance? a. u b. C. 02 d. 02 Module 5: MEAN AND VARIANCE OF DISCRETE RANDOM VARIABLE MEAN is a measure of central tendency than balances the distribution. It isalso known as average. Variance and Standard Deviation are measures of dispersion that tell us how spread the scores are from the mean and from each other. Compute the mean, variance, and standard deviation of the discrete probability distribution below 3 x P(X) X . P(X) Xz X2 . P(X) 2 1/8 1) 4 5 DAI 3/8 2) 16 6) 6 3/8 3) 36 7) 8 1/8 4) 64 8) 9 ) ) X . P (X) = EXz . P(X) = 28 1. a. 1/8 b. 2/8 C. 3/8 d. 4/8 2. a. 3/8 b. 6/8 c. 12/8 d. 24/8 3. a. 12/8 b. 24/8 C. 36/8 d. 48/8 4. a. 4/8 b. 8/8 C. 16/8 d. 32/8 5. a. 4/8 b. 8/8 C. 16/8 d. 32/8 6. a. 36/8 b. 48/8 c. 64/8 d. 108/8 7. a. 36/8 b. 48/8 C. 64/8 d. 108/8 8. a. 36/8 b. 48/8 C. 64/8 d. 108/8SP2.1 9. a. 3 b. 5 C. 7 d. 9 10. Standard Deviation o = VEX2 . P(X) - 42 0= a. 2.4 b. 3.8 C. 4. 8 d. 4.12
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


