Question: Module 5 Bonus Problem Set 2. Statistical measures of stand-alone risk Remember, the expected value of a probability distribution is a statistical measure of the
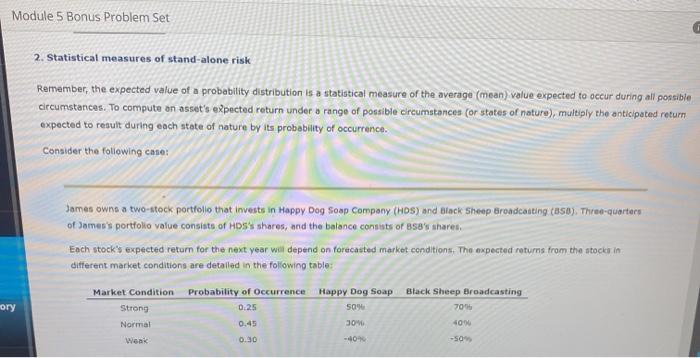
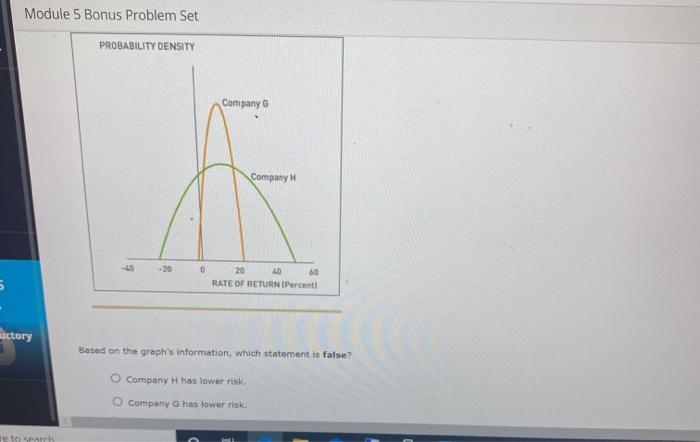
Module 5 Bonus Problem Set 2. Statistical measures of stand-alone risk Remember, the expected value of a probability distribution is a statistical measure of the average (mean) value expected to occur during all possible circumstances. To compute an asset's expected return under a range of possible circumstances (or states of nature), multiply the anticipated return expected to result during each state of nature by its probability of occurrence. Consider the following case: James owns a two-stock portfolio that invests in Happy Dog Soap Company (HDS) and Black Sheep Broadcasting (850). Three-quarters of Domen's portfolio value consists of HDS's shares, and the balance consists of 888shares Each stock's expected return for the next year we depend on forecasted market conditions. The expected returns from the stocken in different market conditions are detalled in the following tables Market Condition Probability of Occurrence Happy Dog Soap Strong mory Black Sheep Broadcasting 70% 0.25 509 0.45 30W 409 Normal Wank 0.30 -0% -50 Calculate expected returns for the individual stocks in James's portfolio as well as the expected rate of return of the entire portfolio over the three possible market conditions next year. The expected rate of return on Happy Dog Soap's stock over the next year is The expected rate of return on Black Sheep Broadcasting's stock over the next year is The expected rate of return on James's portfolio over the next year it The expected returns for James's portfolio ware calculated based on three possible conditions in the market. Such conditions will vary from time to time, and for each condition there will be a specific outcome. These probabilities and outcomes can be represented in the form of a continuous probability distribution graph. For example, the continuous probability distributions of rates of return on stocks for two different companies are shown on the following graphs Module 5 Bonus Problem Set PROBABILITY DENSITY Company Company H -20 0 5 20 LO 60 RATE OF RETURN (Percent uctory Based on the graph's Information, which statement is false? Company H has lower risk Company has lower risk letos
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


