Question: need an explanation for these codes 8. [10] Define a recursive function createIntList for constructing a flat list of integers from a nested list of
![need an explanation for these codes 8. [10] Define a recursive](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3145250525_48166f31451e926c.jpg)
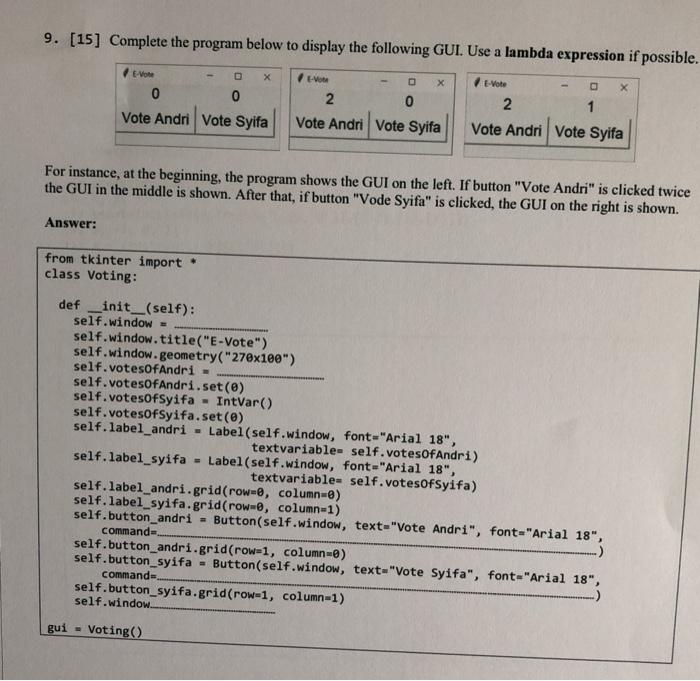
8. [10] Define a recursive function createIntList for constructing a flat list of integers from a nested list of integers and strings. You are not allowed to use for loop or while loop. You should use isinstance(element, type) to check the type of an element. Examples: >>> createIntList(1) 0 >>> createIntList([8,[2,3,[4]]]) [8, 2, 3, 4] >>> createIntList([9, 'Python', [[5, '6']], [[-2], [3],[7]]]) [9, 5, -2, 3, 7] createIntList([[['9']]]) [ >>> X = Answer: def createIntList(1st): 9. [15] Complete the program below to display the following GUI. Use a lambda expression if possible. O X X 0 0 Vote Andri Vote Syifa E- 2 0 Vote Andri Vote Syifa 2 1 Vote Andri Vote Syifa For instance, at the beginning, the program shows the GUI on the left. If button "Vote Andri" is clicked twice the GUI in the middle is shown. After that, if button "Vode Syifa" is clicked, the GUI on the right is shown. Answer: from tkinter import class Voting: def _init__(self): self.window - self window.title("E-Vote") self.window.geometry("270x180") self.votesOfAndri - self.votesOfAndri.set(0) self.votesOfSyifa - IntVar() self.votesOfSyifa.set(e) self.label_andri - Label(self.window, font="Arial 18", textvariable= self.votesOfAndri) self. label_syifa - Label(self.window, font="Arial 18", textvariable= self.votesofSyifa) self.label_andri.grid(row=0, column-8) self. label_syifa.grid(row=@, column=1) self.button_andri - Button(self.window, text-"Vote Andri", font="Arial 18", commands self.button_andri.grid(row=1, column-) self.button_syifa - Button(self.window, text="Vote Syifa", font="Arial 18", commands self.button_syifa.grid(row-1, column-1) self.window gui - Voting() 8. [10] Define a recursive function createIntList for constructing a flat list of integers from a nested list of integers and strings. You are not allowed to use for loop or while loop. You should use isinstance(element, type) to check the type of an element. Examples: >>> createIntList(1) 0 >>> createIntList([8,[2,3,[4]]]) [8, 2, 3, 4] >>> createIntList([9, 'Python', [[5, '6']], [[-2], [3],[7]]]) [9, 5, -2, 3, 7] createIntList([[['9']]]) [ >>> X = Answer: def createIntList(1st): 9. [15] Complete the program below to display the following GUI. Use a lambda expression if possible. O X X 0 0 Vote Andri Vote Syifa E- 2 0 Vote Andri Vote Syifa 2 1 Vote Andri Vote Syifa For instance, at the beginning, the program shows the GUI on the left. If button "Vote Andri" is clicked twice the GUI in the middle is shown. After that, if button "Vode Syifa" is clicked, the GUI on the right is shown. Answer: from tkinter import class Voting: def _init__(self): self.window - self window.title("E-Vote") self.window.geometry("270x180") self.votesOfAndri - self.votesOfAndri.set(0) self.votesOfSyifa - IntVar() self.votesOfSyifa.set(e) self.label_andri - Label(self.window, font="Arial 18", textvariable= self.votesOfAndri) self. label_syifa - Label(self.window, font="Arial 18", textvariable= self.votesofSyifa) self.label_andri.grid(row=0, column-8) self. label_syifa.grid(row=@, column=1) self.button_andri - Button(self.window, text-"Vote Andri", font="Arial 18", commands self.button_andri.grid(row=1, column-) self.button_syifa - Button(self.window, text="Vote Syifa", font="Arial 18", commands self.button_syifa.grid(row-1, column-1) self.window gui - Voting()
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


