Question: Need Analysis for this case study Major Electronics is a multi-plant assembler of computers and computer products. It has 40 plants located in southern Ontario

Need Analysis for this case study
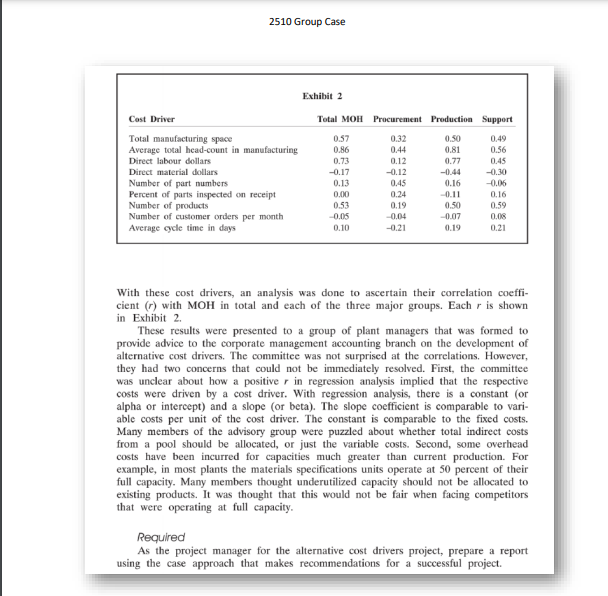
Major Electronics is a multi-plant assembler of computers and computer products. It has 40 plants located in southern Ontario and greater Montreal. In recent years, there have been concerns that its traditional method for allocating manufacturing overhead (MOH) is no longer relevant. Direct labour costs now average 6 percent of manufacturing costs for its 40 plants, with 55 percent for direct materials, and 39 percent for manufacturing overhead. The corporate management accounting branch is investigating alternative cost drivers. MOH is divided into three groups: procurement, production, and support. The standard chart of accounts for Major further classifies these costs into sub-classes (see Exhibit 1), which are ranked in order of importance. The corporate management accounting branch surveyed manufacturing managers at all 40 plants to obtain a list of the most important cost drivers for MOH. 2510 Group Case With these cost drivers, an analysis was done to ascertain their correlation coefficient (r) with MOH in total and each of the three major groups. Each r is shown in Exhibit 2 . These results were presented to a group of plant managers that was formed to provide advice to the corporate management accounting branch on the development of alternative cost drivers. The committee was not surprised at the correlations. However, they had two concerns that could not be immediately resolved. First, the committee was unclear about how a positive r in regression analysis implied that the respective costs were driven by a cost driver. With regression analysis, there is a constant (or alpha or intereept) and a slope (or beta). The slope coefficient is comparable to variable costs per unit of the cost driver. The constant is comparable to the fixed costs. Many members of the advisory group were puzzled about whether total indirect costs from a pool should be allocated, or just the variable costs. Second, some overhead costs have been incurred for capacities much greater than current production. For example, in most plants the materials specifications units operate at 50 percent of their full capacity. Many members thought underutilized capacity should not be allocated to existing products. It was thought that this would not be fair when facing competitors that were operating at full capacity. Required As the project manager for the alternative cost drivers project, prepare a report using the case approach that makes recommendations for a successful project. Major Electronics is a multi-plant assembler of computers and computer products. It has 40 plants located in southern Ontario and greater Montreal. In recent years, there have been concerns that its traditional method for allocating manufacturing overhead (MOH) is no longer relevant. Direct labour costs now average 6 percent of manufacturing costs for its 40 plants, with 55 percent for direct materials, and 39 percent for manufacturing overhead. The corporate management accounting branch is investigating alternative cost drivers. MOH is divided into three groups: procurement, production, and support. The standard chart of accounts for Major further classifies these costs into sub-classes (see Exhibit 1), which are ranked in order of importance. The corporate management accounting branch surveyed manufacturing managers at all 40 plants to obtain a list of the most important cost drivers for MOH. 2510 Group Case With these cost drivers, an analysis was done to ascertain their correlation coefficient (r) with MOH in total and each of the three major groups. Each r is shown in Exhibit 2 . These results were presented to a group of plant managers that was formed to provide advice to the corporate management accounting branch on the development of alternative cost drivers. The committee was not surprised at the correlations. However, they had two concerns that could not be immediately resolved. First, the committee was unclear about how a positive r in regression analysis implied that the respective costs were driven by a cost driver. With regression analysis, there is a constant (or alpha or intereept) and a slope (or beta). The slope coefficient is comparable to variable costs per unit of the cost driver. The constant is comparable to the fixed costs. Many members of the advisory group were puzzled about whether total indirect costs from a pool should be allocated, or just the variable costs. Second, some overhead costs have been incurred for capacities much greater than current production. For example, in most plants the materials specifications units operate at 50 percent of their full capacity. Many members thought underutilized capacity should not be allocated to existing products. It was thought that this would not be fair when facing competitors that were operating at full capacity. Required As the project manager for the alternative cost drivers project, prepare a report using the case approach that makes recommendations for a successful project
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


