Question: Need finished within 2 hours please Reed Tons owns an editorial firm, which prints books and sells them to bookstores. Reed budgeted to sell 100,000
Need finished within 2 hours please
Reed Tons owns an editorial firm, which prints books and sells them to bookstores. Reed budgeted to sell 100,000 books this year. She also provides you with the following budgeting data:
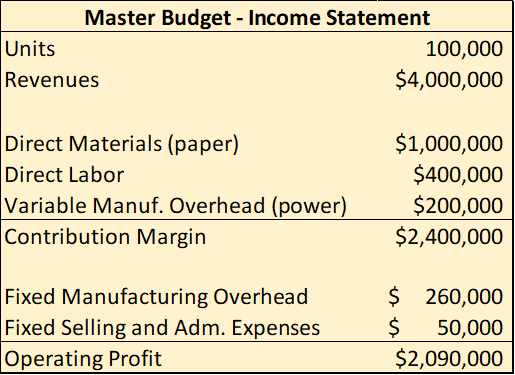
In addition, Reed provides you with the following standard information:

(Above, Kwh stands for kilowatt-hour.)
The actual performance of the firm, however, did not measure up to her expectations. She was worried because of the competition from electronic books the actual number of books she sold was exactly 10% less than the budgeted volume. She was disappointed about this outcome but thought that the situation was under control. The main problem was the volume of sales, and that could be fixed with a larger expenditure in advertising. Reed provided you with the following statement about the actual results:
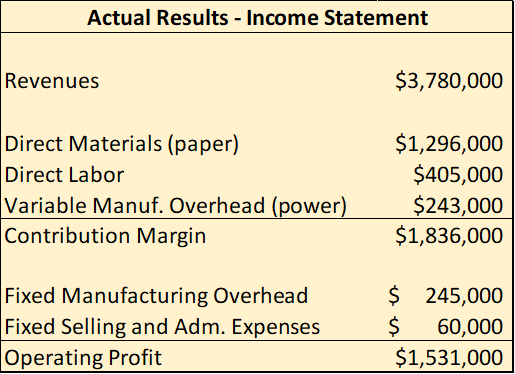
Finally, Reed was also able to obtain the following information:
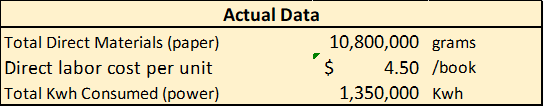
Reed further recalled that the actual cost of per direct labor hour was as she had budgeted.
Problem 1 Part A (15 points)
Reed wants you to help her figure out how she could be so wrong when forecasting the performance of the firm. In particular, she wants you to calculate the following:
- How much profit should Reed have made with the actual volume of sales (in number of books) if everything else was as budgeted (i.e., the flexible budget profit).
- Calculate the Sales Volume Variance and the Flexible Budget Variance.
- Calculate the Sales Volume Variance for Revenues and the Sales Price Variance.
Make sure to tell Reed whether the variances are favorable or unfavorable.
Problem 1 Part B (15 points)
Reed wants you to help her find out more about the underlying causes of the flexible-budget variance. In particular, she wants you to calculate the following variances:
- Price and efficiency variances for the direct materials.
- Price and efficiency variances for the direct labor.
- Price and efficiency variances for variable manufacturing overhead.
Make sure to tell Reed whether the variances are favorable or unfavorable.
Problem 1 Part C (10 points)
Reed wants you to help her to interpret the variances you just calculated. Take 2 pairs of variances from parts A or B and tell Reed a story for each pair. Each of the two stories must relate two variances and make sense.
Master Budget - Income Statement Units 100,000 Revenues $4,000,000 Direct Materials (paper) Direct Labor Variable Manuf. Overhead (power) Contribution Margin $1,000,000 $400,000 $200,000 $2,400,000 Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Fixed Selling and Adm. Expenses Operating Profit $ 260,000 $ 50,000 $2,090,000 Standard Information Total Direct Materials (paper) 10,000,000 grams Direct Labor Hours per unit 0.20 hrs Var. Manuf. OH (power) $ 0.20 /kwh Actual Results - Income Statement Revenues $3,780,000 Direct Materials (paper) Direct Labor Variable Manuf. Overhead (power) Contribution Margin $1,296,000 $405,000 $243,000 $1,836,000 Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Fixed Selling and Adm. Expenses Operating Profit $ 245,000 $ 60,000 $1,531,000 Actual Data Total Direct Materials (paper) 10,800,000 grams Direct labor cost per unit $ 4.50 /book Total Kwh Consumed (power) 1,350,000 kwh
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


