Question: Need help answering the following C2F2C++2eCu+Cl2+2eCu2v+2C++2e Question 9 (1 point) The equation for the andation halt-reaction would be: Cu(s)Cu2+(aq)+2cCu2+(aq)+2eCa(s)Ag(s)Ag+(aq)+1s Question 10 (1 point) Identily the




![correct equilibriam constant expression for the equilibrium 2H2(t) * O2(g)=2H2O(+).K=9i2T^2]1K=q2P2T[H2I2 K=Pi2I2[H2I2O2PlK=(M2MP2)H2OH Question](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f92e6abd105_37866f92e6a6fd55.jpg)
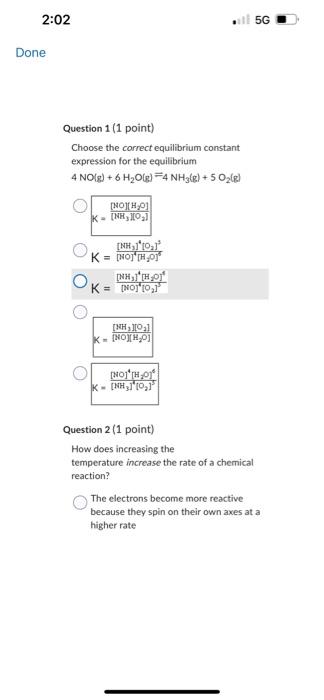
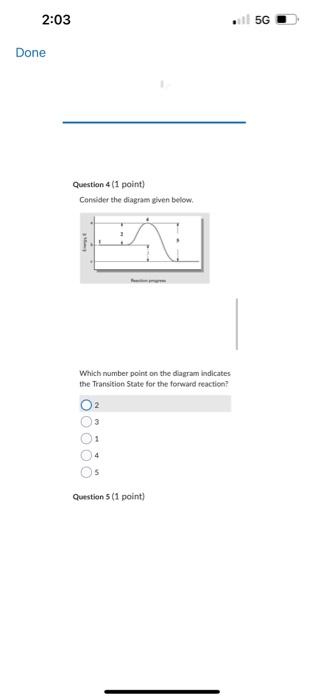
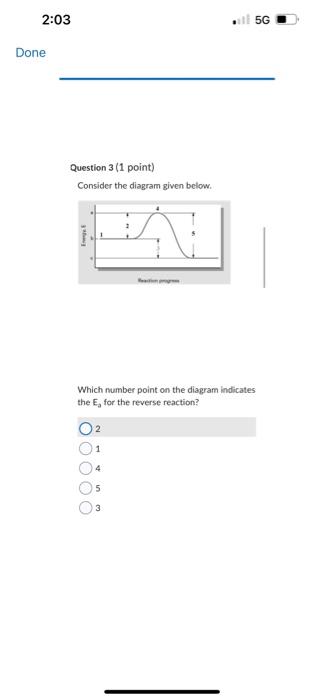
C2F2C++2eCu+Cl2+2eCu2v+2C++2e Question 9 (1 point) The equation for the andation halt-reaction would be: Cu(s)Cu2+(aq)+2cCu2+(aq)+2eCa(s)Ag(s)Ag+(aq)+1s Question 10 (1 point) Identily the reduction half-reaction in the redou equation: 4Ag+O2(c)+2H2O=4Ag4+4OH2H2O+2e=4OHAg=Ag+e2H2O+2e=H2+2OH4Ag+4e7=4AgO2(g)+2H2O+4ePOH Question 7 (1 point) Owidation-reduction reactiona are also known as.. electron-transfer reactions double-displacement reactiona proten-transfer feactians neutrafsation reactioen neutron bombardment reactions Question 8 (1 point) Identify the ovidation half-reaction in the redox equation: Cu(s)+Cl(g)=Cu2++2ClCu=Cu2++2eCl2+2e=2CiCu+2e=Cu2Cl2=2Cl+2eCu2+Cl2+2e2Cu2++2Cl+2e Question 6 \{1 point Choose the correct equilibriam constant expression for the equilibrium 2H2(t) * O2(g)=2H2O(+).K=9i2T^2]1K=q2P2T[H2I2 K=Pi2I2[H2I2O2PlK=(M2MP2)H2OH Question 7 (1 point) Ouidation-reduction reactions are also known as. electron-transfer reaction Question 5 (1 point) Choose the carrect equilibrlum constant expression tor the equilibrium CO(g)+O2(g) =COO2(g). K=[COCH2]2(COllCl2]2K[Foch2][colklFy1]K=Isolsh2!BoCl41K=POlel]22CoCh22 Question 6(1 pont) Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression tor the equilibrium 2H2 (s) * O2(g)=m2H2Ot).K=jjt22p2I1K=[H2]2P2][H2O2 Convider the diagram given below. Which number point on the diagram indicates the Transition State for the forvard reactice? 2 3 1. 4 5 Consider the diagram given below. Which number point on the diagram indicates the Ea for the reverse reaction? 2 1 4 5 3 Question 2 (1 point) How does increasing the temperature increase the rate of a chemical reaction? The electrons become more reactive because they spin on their own awes at a higher rate The fractioe of sample with the minimum kinetic enersk required to react be increased The bond energy of the reactants is. decreased The activation eneriy for the reaction is decreased The likellhood that molecules and ions will have the required geometry is increased Question 1 (1 point) Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression for the equilibrium 4NO(g)+6H2O(g)=4NH3(g)+5O2(g) K=[HO4[H2O5[NH3]4[O2]3K=[NO4]4[O2]5[NH3]4[H2O4 Question 2 (1 point) How does increasing the temperature increase the rate of a chemical reaction? The electrons become more reactive because they spin on their own axes at a higher rate
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


