Question: Need help fixing the swapEvenOdd and append functions properly. Problem description Write a C++ program that will implement and test the five functions described below





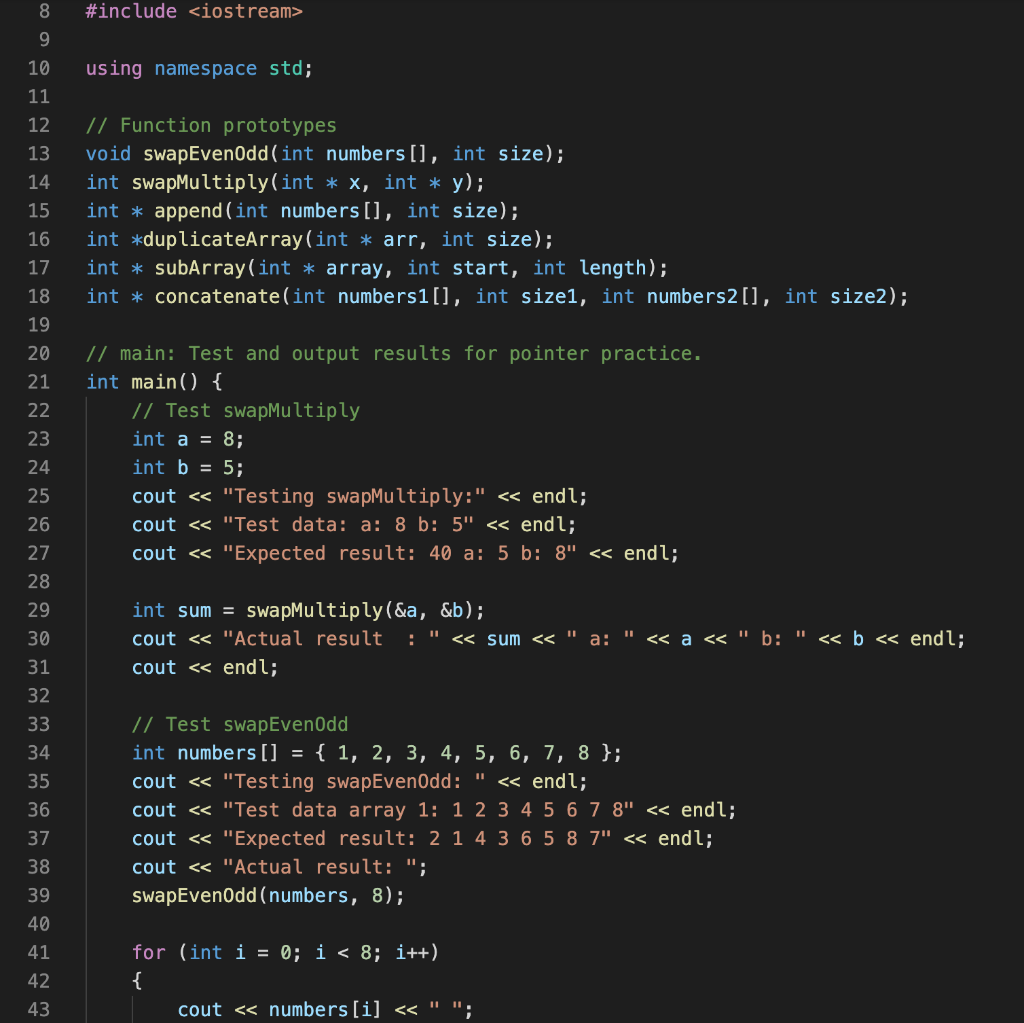
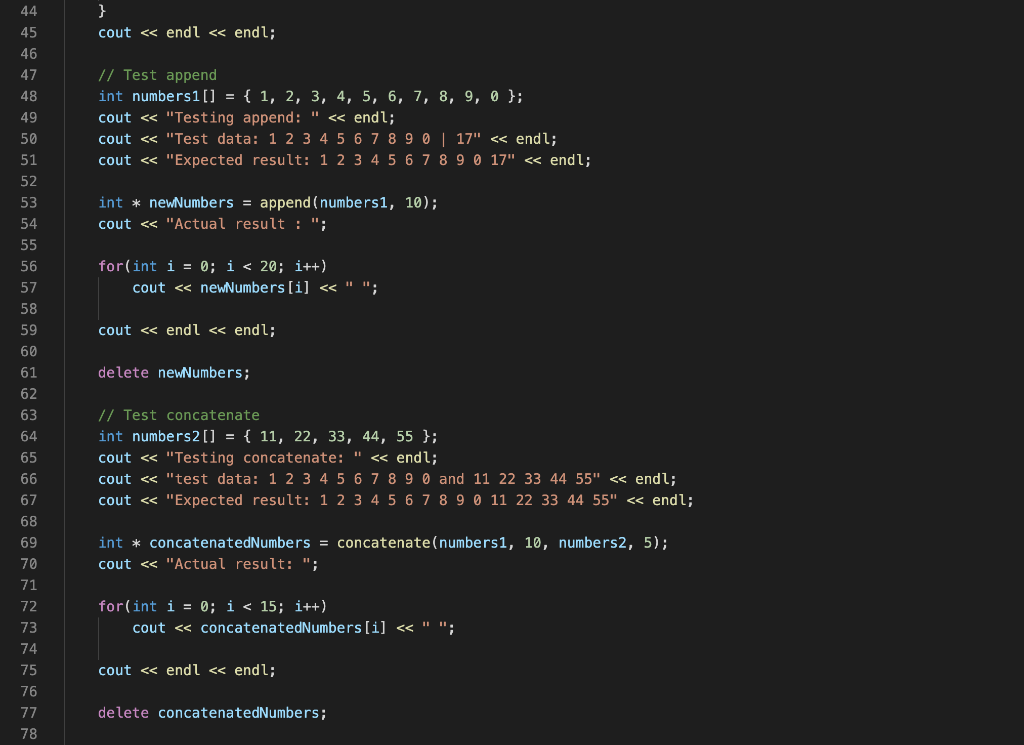
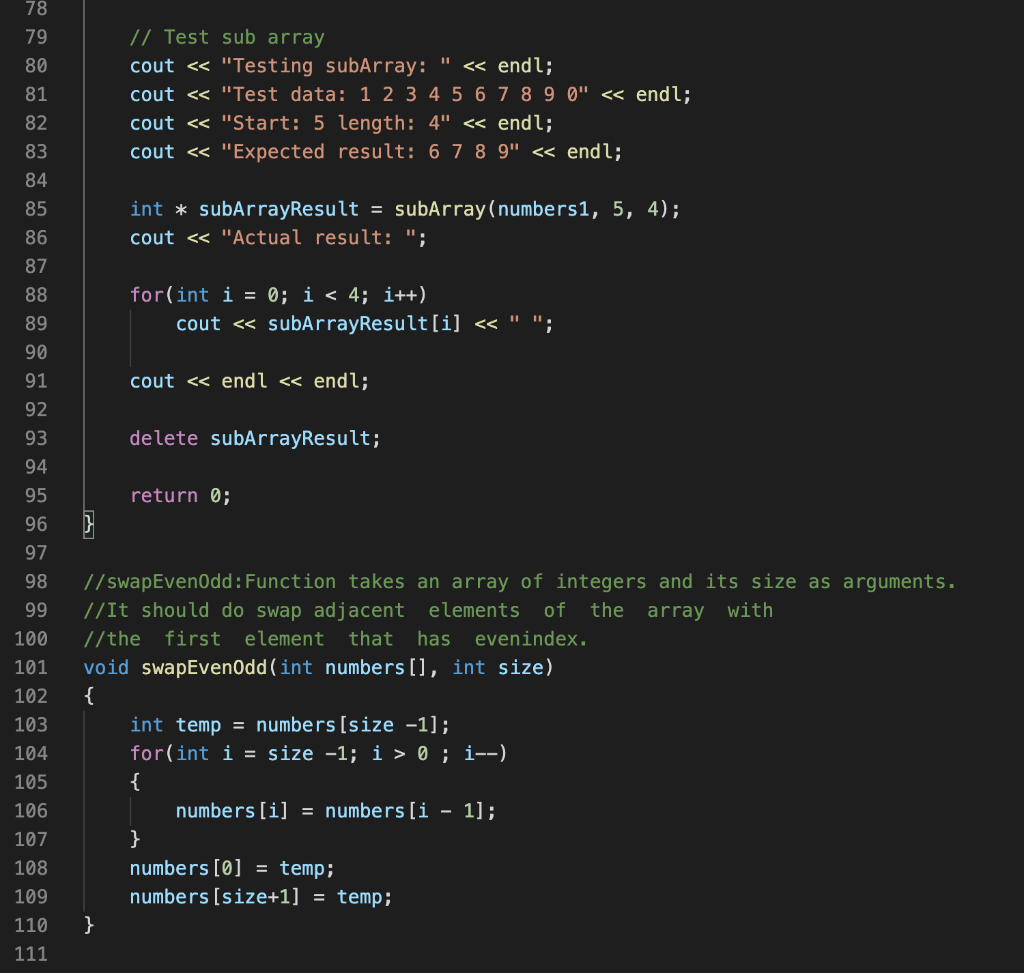
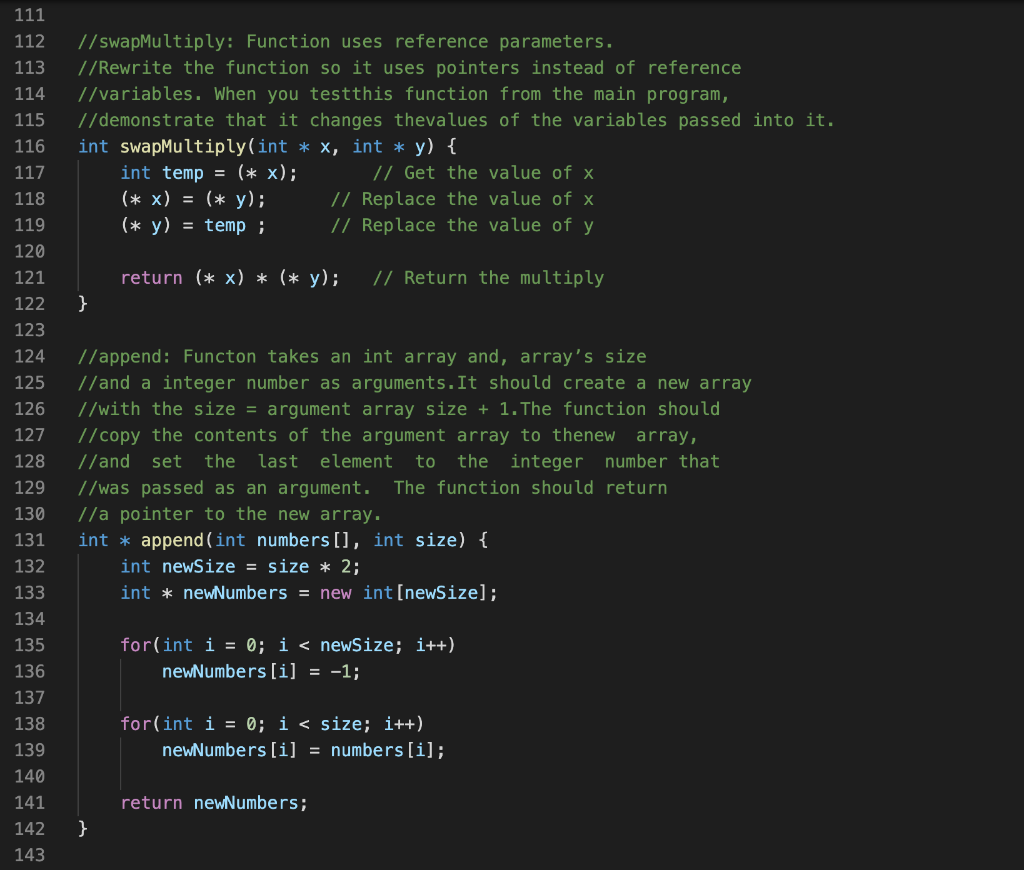
Need help fixing the "swapEvenOdd" and "append" functions properly.
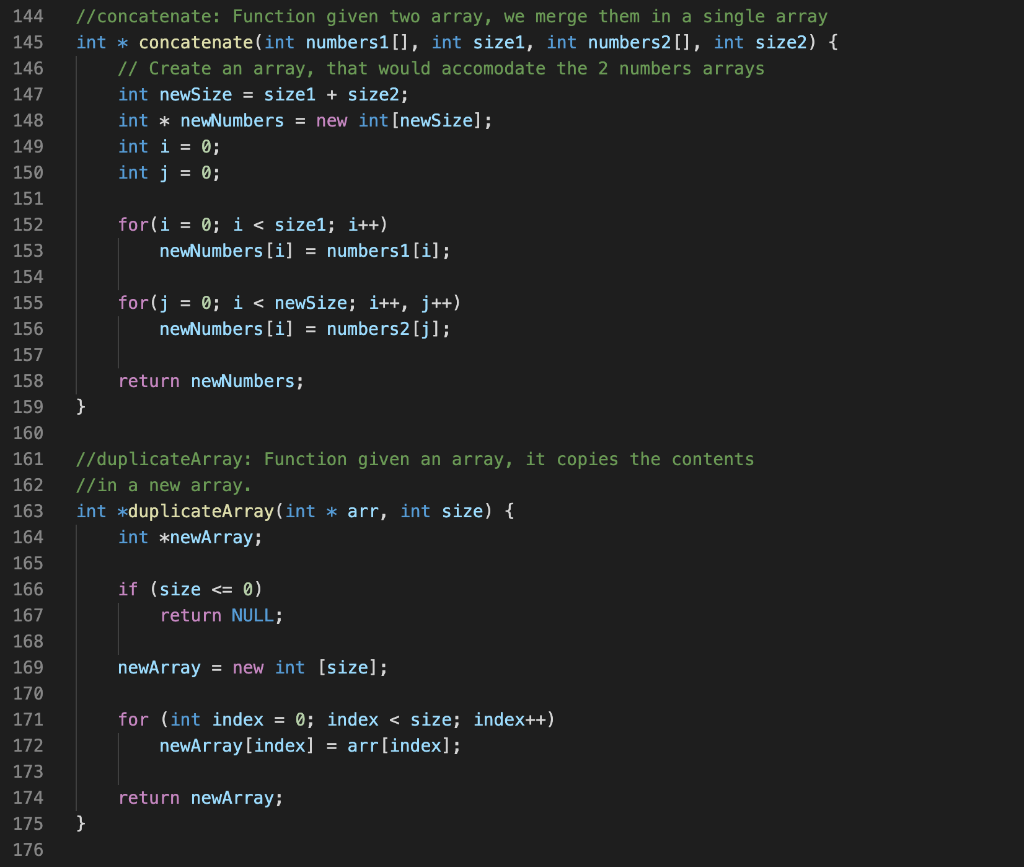
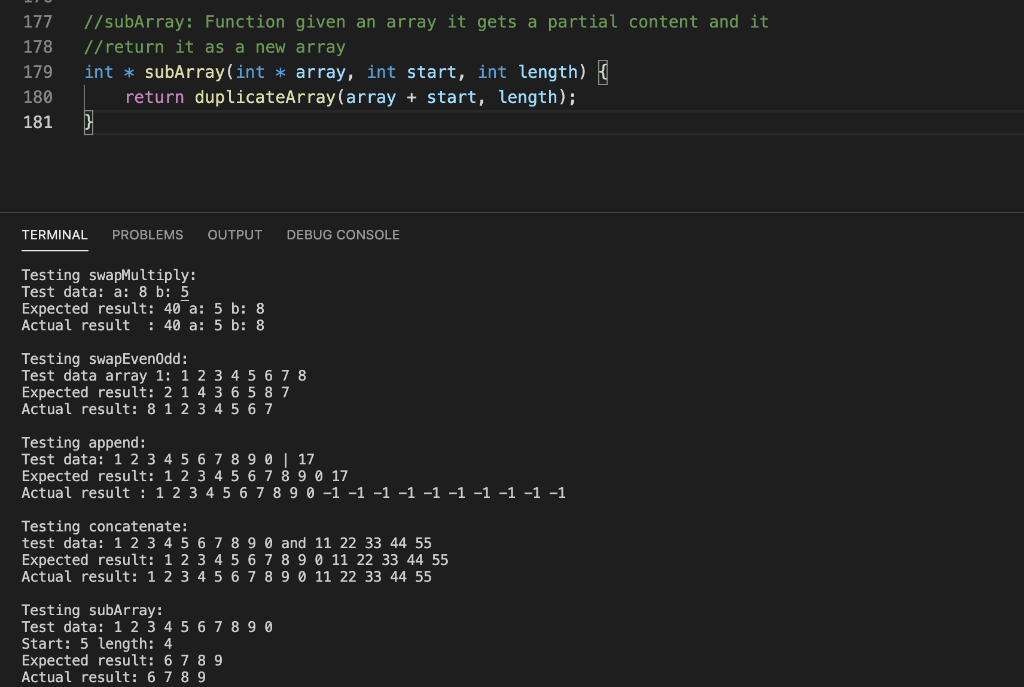
Problem description Write a C++ program that will implement and test the five functions described below that use pointers and dynamic memory allocation. The Functions: You will write the five functions described below. Then you will call them from the main function, to demonstrate their correctness. 1) swap Multiply The following function uses reference parameters. Rewrite the func- tion so it uses pointers instead of reference variables. When you test this function from the main program, demonstrate that it changes the values of the variables passed into it. int swapMultiply (int &x, int &y) { int temp = x; X = y; y = temp; return x * y; } 2) swapEvenOdd Takes an array of integers and its size as arguments. It should do swap adjacent elements of the array with the first element that has even index. You MUST use swap Multiply function to do it. Disregard the return value of the swapMultiply function. Do not use square brackets anywhere in the function, not even the parameter list (use pointer notation instead). Example: swapEvenOdd([1 2 3 4 5]) + [21435] 3) append Takes an int array and, array's size and a integer number as arguments. It should create a new array with the size argument array size + 1. The function should copy the contents of the argument array to the new array, and set the last element to the integer number that was passed as an argument. The function should return a pointer to the new array 4) concatenate Takes two int arrays and the arrays' sizes as arguments (that's 4 argu- ments). It should create a new array big enough to store both arrays. Then it should copy the contents of the first array to the new array, and then copy the contents of the second array to the new array in the remaining elements, and return a pointer to the new array. 5) sub Array Takes an int array, a start index and a length as arguments. It creates a new array that is a copy of the elements from the original array starting at the start index, and has length equal to the length argument. For example, subArray(aa,5,4) would return a new array containing only the elements aa[5], aa[6], aa[7], and aa[8]. You must define subArray as follows: Add the code for the du- plicateArray function from the lecture slides for Unit 3 (slide 24) to your program. Add the code for the subArray function given below to your program. Fill in the blanks with expressions so that the function subArray behaves as described above. int *subArray (int *array, int start, int length) { int *result = duplicateArray (--- return result; } DO NOT alter duplicateArray, DO NOT alter subArray as defined above. Program execution Test these five functions using the main function as a driver. The driver should pass (constant) test data as arguments to the functions. Select appropriate test data for each function and then call that func- tion using the test data. For each function, you should output four lines: a label indicating which function is being tested, the test data, the expected results, and the actual results. For the test data and Expected result, you should hard code the output values (use string literals containing the numeric values), for the Actual results, use the actual values returned/altered by the function. Testing swapMultiply cout 9 using namespace std; // Function prototypes void swapEvenOdd(int numbers[], int size); int swapMultiply(int * x, int * y); int * append(int numbers[], int size); int *duplicateArray(int * arr, int size); int * subArray(int * array, int start, int length); int * concatenate(int numbers1[], int sizei, int numbers2[], int size2); 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 // main: Test and output results for pointer practice. int main() { // Test swapMultiply int a = 8; int b = 5; cout 0; i--) { numbers [i] = numbers [i - 1]; } numbers [0] = temp; numbers [size+1] = temp; } 111 // swapMultiply: Function uses reference parameters. //Rewrite the function so it uses pointers instead of reference //variables. When you testthis function from the main program, //demonstrate that it changes thevalues of the variables passed into it. int swapMultiply(int * X, int * y) { int temp = (* x); // Get the value of x (* x) = (* y); // Replace the value of x (* y) = temp; // Replace the value of y 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 return (* x) * (* y); // Return the multiply } //append: Functon takes an int array and, array's size //and a integer number as arguments. It should create a new array //with the size = argument array size + 1. The function should //copy the contents of the argument array to thenew array, //and set the last element to the integer number that //was passed as an argument. The function should return I/a pointer to the new array. int * append(int numbers [], int size) { int newSize = size * 2; int * new Numbers = new int[newSize]; 131 for(int i = 0; i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


