Question: Need help. Kindly show your solutions. Thank you. Random Variables In some experiments such as tossing a coin three times, rolling a die twice, drawing
Need help. Kindly show your solutions. Thank you.

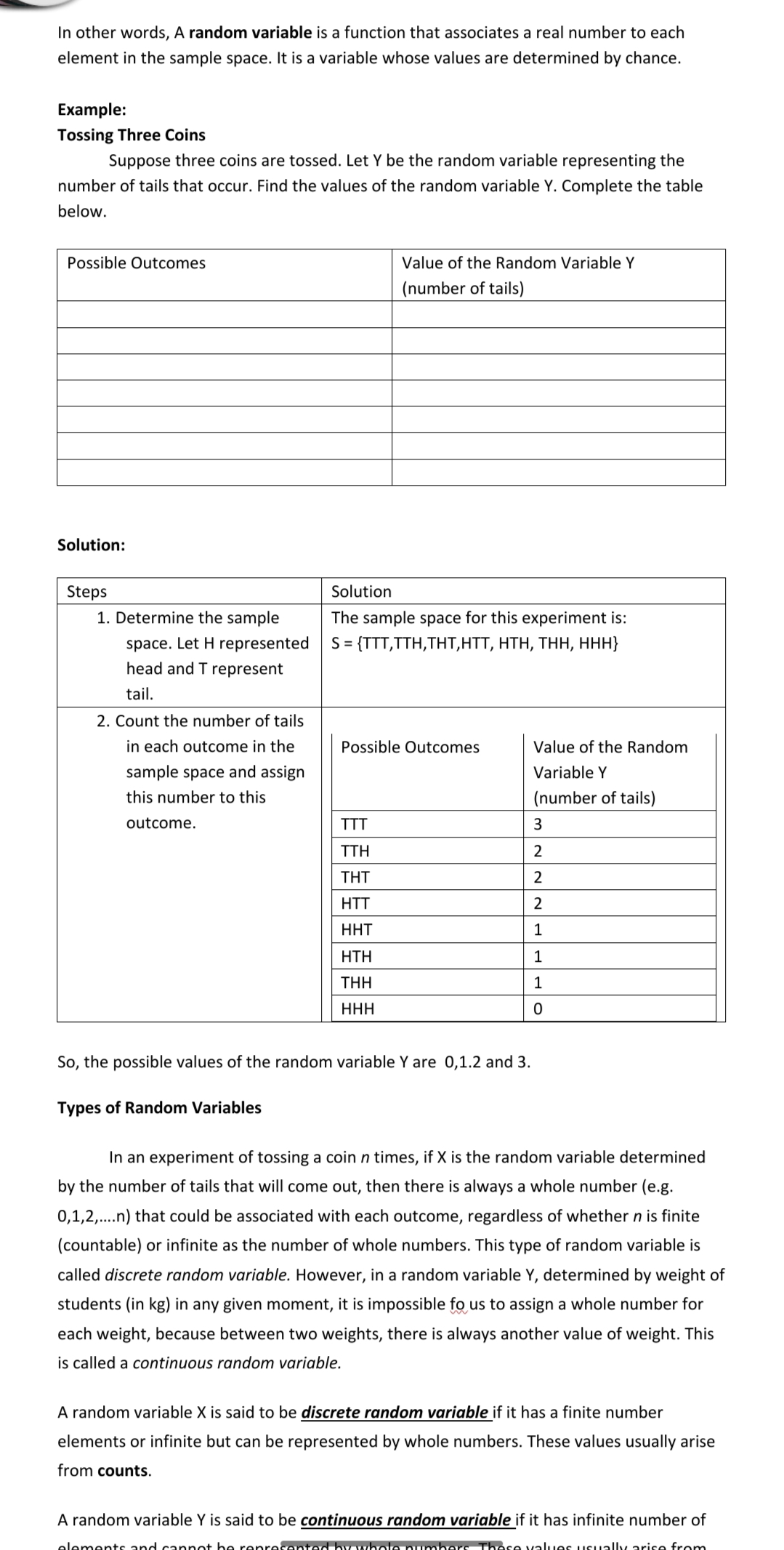


Random Variables In some experiments such as tossing a coin three times, rolling a die twice, drawing two balls from an urn and the like, we are not oftentimes concerned with every detail of the outcomes. We are usually interested in some numerals associated with the outcomes. For instance, if a coin tossed twice, the set of all possible outcomes (5) of the experiment is; S = {TT, TH, HT, HH} If we are interested in the number of tails that came out in the experiment, then we can assign numbers 0, 1, and 2 for each of the 4 possible outcomes. Thus, we can write Sample Space Number of tails From the table above, instead of writing number of tails, we can denote it as set X whose elements (x1, x2 , and x3) are 0,1 and 2. In symbol, X = {0 ,1, 2} Then X is called a random variable. A Random Variable is a set whose elements are the numbers assigned to the outcomes of an experiment. It is usually denoted by uppercase letters such as X, whose elements are denoted by lower case letters, x1, x2 , x3, and so on. In other words, A random variable is a function that associates a real number to each element in the sample space. It is a variable whose values are determined by chance. Example: Tossing Three Coins Suppose three coins are tossed. Let Y be the random variable representing the number of tails that occur. Find the values of the random variable Y. Complete the table below. Possible Outcomes Value of the Random Variable Y (number of tails) y In other words, A random variable is a function that associates a real number to each element in the sample space. It is a variable whose values are determined by chance. Example: Tossing Three Coins Suppose three coins are tossed. Let Y be the random variable representing the number of tails that occur. Find the values of the random variable Y. Complete the table below. Possible Outcomes Value of the Random Variable Y (number of tails) Solution: Steps Solution 1. Determine the sample The sample space for this experiment is: space. Let H represented S = (TTT.'|'|'H,THT,HTT, HTH, THH, HHH} head and T represent tail. 2. Count the number of tails in each outcome in the Possible Outcomes Value of the Random sample space and assign Variable Y this number to this (number of tails) outcome. TTT 3 TTH 2 THT 2 HTT 2 HHT 1 HTH 1 THH 1 HHH O So, the possible values of the random variable Y are 0,12 and 3. Types of Random Variables In an experiment of tossing a coin n times, if X is the random variable determined by the number of tails that will come out, then there is always a whole number (e.g. 0,1,2,....n) that could be associated with each outcome, regardless of whether n is finite (countable) or infinite as the number of whole numbers. This type of random variable is called discrete random variable. However, in a random variable Y, determined by weight of students (in kg) in any given moment, it is impossible fans to assign a whole number for each weight, because between two weights, there is always another value of weight. This is called a continuous random variable. A random variable X is said to be discrete random variable if it has a finite number elements or infinite but can be represented by whole numbers. These values usually arise from counts. A random variable Y is said to be continuous random variable if it has infinite number of alumna\" \"A \"an...\" I-m mnmmm "an...\" \"mun" \"in rm... U A random variable X is said to be discrete random variable if it has a finite number elements or infinite but can be represented by whole numbers. These values usually arise from counts. A random variable Y is said to be continuous random variable if it has infinite number of elements and cannot be represented by whole numbers. These values usually arise from measurements. Examples: A teacher's record has the following (3) Scores of the students in a 50 item test, (b) Gender, (c) Height of the students Let: X = Scores of the students in a 50 item test Y = Gender 2 = Height of the students Classify each variable above as discrete or continuous. Answer: X is a discrete random variable because the scores of the students are represented by whole numbers. Y is also a discrete random variable because male and female could be coded 0 = female and 1 = male, and thus, could be counted. 2 is a continuous random variable because between two values of height, there are always infinite numbers of possible values for height, thus ma king representations to be impossible. Explore your understanding: What is the difference between continuous and discrete random variables? Firm - Up your knowledge: Classify the following random variable as discrete or continuous. 1. The number of defective computers produced by a manufacturer. 2. The weight of new-Weach year in a hospital. 3. The number of siblings in a family of a region. 4. The amount of paint utilized in a building project. 5. The number of dropout in a school district for a period of 10 years. Deepen your understanding: Give 3 examples of discrete and continuous random variable. Discrete random variable Continuous random variable Transfer: W, ....,., ..,.....,,.,. Y is also a discrete random variable because male and female could be coded O = female and 1 = male, and thus, could be counted. 2 is a continuous random variable because between two values of height, there are always infinite numbers of possible values for height, thus ma king representations to be impossible. Explore your understanding: What is the difference between continuous and discrete random variables? Firm - Up your knowledge: Classify the following random variable as discrete or continuous. 1. The number of defective computers produced by a manufacturer. 2. The weight of new-Weach year in a hospital. 3. The number of siblings in a family of a region. 4. The amount of paint utilized in a building project. 5. The number of dropout in a school district for a period of 10 years. Deepen your understanding: Give 3 examples of discrete and continuous random variable. Discrete random variable Continuous random variable Transfer: Four coins are tossed. Let Z be the random variable representing the number of heads that occur. Find the values of the random variable Z. Possible Outcomes Value of the Random Variable Z
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


