Question: Need help on this question 80 100 120 140 Sample means How could you use the bootstrapped distribution to calculate ap-value to test whether the
Need help on this question

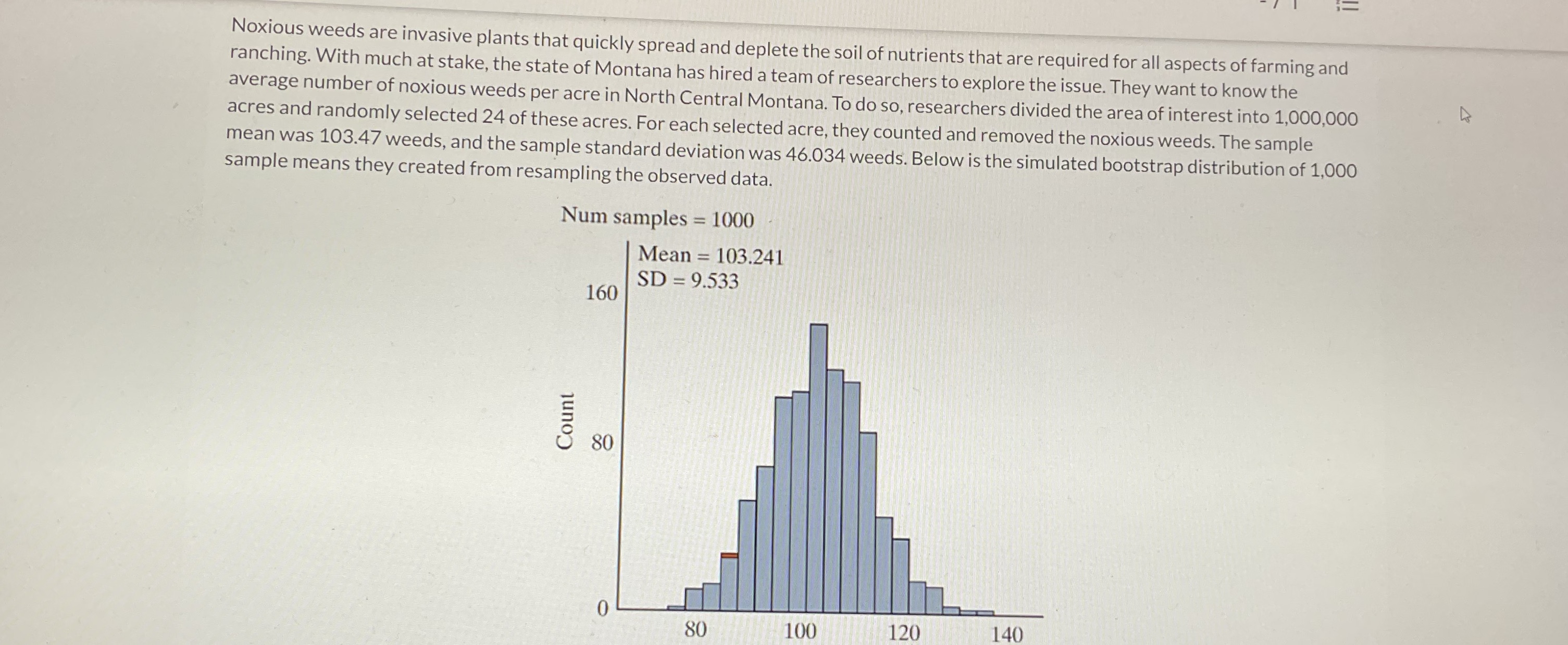
80 100 120 140 Sample means How could you use the bootstrapped distribution to calculate ap-value to test whether the mean number of noxious weeds in North Central Montana is larger than 90 weeds per acre? O Calculate the proportion of bootstrapped sample means that are equal to or larger than 90 on the bootstrap distribution above. O Calculate the proportion of bootstrapped sample means that are equal to or larger than 103.47 on the bootstrap distribution above. O Shift the bootstrap distribution to the left so that it's centered at 90, then calculate the proportion of shifted bootstrapped sample means that are equal to or larger than 90. O Shift the bootstrap distribution to the left so that it's centered at 90, then calculate the proportion of shifted bootstrapped sample means that are equal to or larger than 103.47.Noxious weeds are invasive plants that quickly spread and deplete the soil of nutrients that are required for all aspects of farming and ranching. With much at stake, the state of Montana has hired a team of researchers to explore the issue. They want to know the average number of noxious weeds per acre in North Central Montana. To do so, researchers divided the area of interest into 1,000,000 acres and randomly selected 24 of these acres. For each selected acre, they counted and removed the noxious weeds. The sample mean was 103.47 weeds, and the sample standard deviation was 46.034 weeds. Below is the simulated bootstrap distribution of 1,000 sample means they created from resampling the observed data. Num samples = 1000 Mean = 103.241 SD = 9.533 160 Count 80 0 80 100 120 140
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


