Question: Need help solving problems 5-1, 5-2, 5-3 (question goes from the bottom of Picture #1 to top of Picture #2) , and 5-7 (has information
Need help solving problems 5-1, 5-2, 5-3 (question goes from the bottom of "Picture #1" to top of "Picture #2"), and 5-7 (has information in the question that pertains to solving/filling in the blank sections for the problem):
*This is all of the information that I have available for the questions below*
Picture #1:
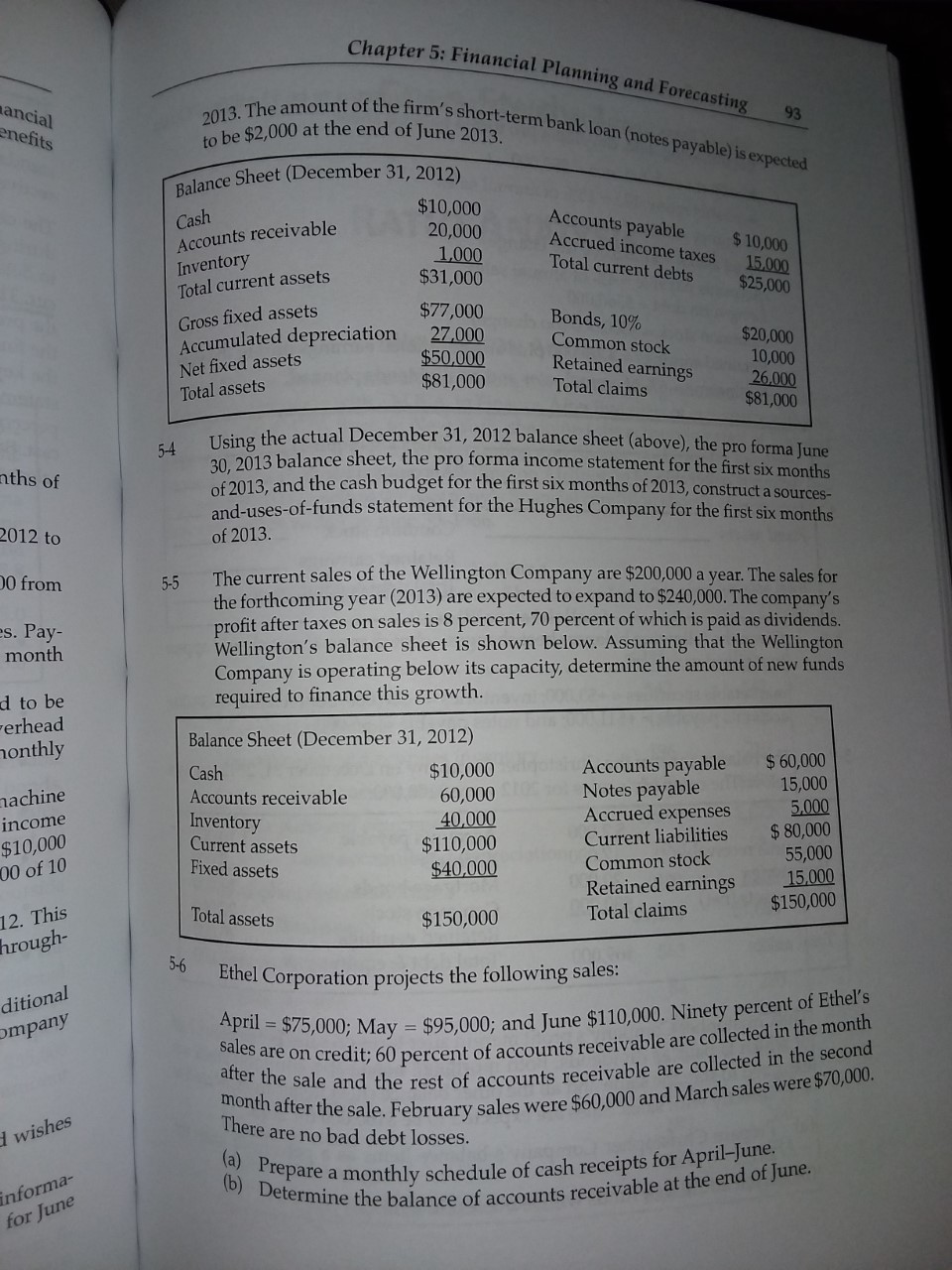
Chapter 5: Financial Planning and Forecasting ancial enefits 2013. The amount of the firm's short-term bank loan (notes payable) is expected to be $2,000 at the end of June 2013. 93 Balance Sheet (December 31, 2012) Cash $10,000 Accounts receivable 20,000 Accounts payable Inventory 1,000 Accrued income taxes $ 10,000 Total current assets $31,000 Total current debts 15,000 $25,000 Gross fixed assets $77,000 Accumulated depreciation 27,000 Bonds, 10% Common stock $20,000 Net fixed assets $50,000 Retained earnings 10,000 Total assets $81,000 Total claims 26,000 $81,000 5-4 Using the actual December 31, 2012 balance sheet (above), the pro forma June ths of 30, 2013 balance sheet, the pro forma income statement for the first six months of 2013, and the cash budget for the first six months of 2013, construct a sources- 2012 to of 2013. and-uses-of-funds statement for the Hughes Company for the first six months 10 from 5-5 The current sales of the Wellington Company are $200,000 a year. The sales for the forthcoming year (2013) are expected to expand to $240,000. The company's s. Pay- profit after taxes on sales is 8 percent, 70 percent of which is paid as dividends. month Wellington's balance sheet is shown below. Assuming that the Wellington Company is operating below its capacity, determine the amount of new funds d to be required to finance this growth. erhead onthly Balance Sheet (December 31, 2012) Cash $10,000 Accounts payable $ 60,000 achine Accounts receivable 60,000 Notes payable 15,000 income Inventory Accrued expenses 5,000 $10,000 40,000 Current assets 00 of 10 $110,000 Current liabilities $ 80,000 Fixed assets $40,000 Common stock 55,000 Retained earnings 15,000 12. This Total assets $150,000 Total claims $150,000 hrough- 5-6 ditional Ethel Corporation projects the following sales: mpany April = $75,000; May = $95,000; and June $110,000. Ninety percent of Ethel's sales are on credit; 60 percent of accounts receivable are collected in the month after the sale and the rest of accounts receivable are collected in the second I wishes month after the sale. February sales were $60,000 and March sales were $70,000. There are no bad debt losses. informa- (a) Prepare a monthly schedule of cash receipts for April-June. for June (b) Determine the balance of accounts receivable at the end of June.PART 2: FINANCIAL PLANNING AND CONTROL 94 5-7 Sales of Dana Corporation for next year are expected to be $3 million. Give the following data, develop a pro forma balance sheet. Minimum cash balance = $90,000 Accounts receivable = 15% of annual sales Inventory = 10% of annual sales Fixed assets = $1,275,000 (no change) Accounts payable = 4% of annual sales Long-term debt = $360,000 Common stock = $300,000 (no change) Retained earnings = $720,000 plus any additional earnings during the year Net income = 6% of annual sales and no dividends planned. Meliss Financing required univer Cash of the Accounts receivable Accounts payable Airlin Inventory Long-term debt assum Common stock respor Fixed assets Retained earnings fiscal Total assets Total debt & equity 5-8 Given the following balance sheet changes, what change, if any, should appear in retained earnings? marketable securities = +$3,000; inventories = +$10,000; depreciation =+$3,000; accounts payable = +$11,000; and notes payable = -$6,000 5-9 The balance sheet of the Christopher Company on December 31, 2012 is given below. The company's sales for 2012 were $100,000. Cash Accounts receivable $ 2,000 Inventories 17,000 Accounts payable $ 10,000 Fixed assets (net) 20,000 Accruals 5,000 $30,000 Mortgage bonds Common stock 14,000 Total assets 20,000 $69,000 Retained earnings 20.000 Total debt & equity $69,000 The Christopher Company's profit margin after taxes on sales is 4 percent, hall of which is paid as dividends. Both mortgage bonds and common stock at expected to stay the same and all the other balance sheet items are expected to vary directly with sales. Sales are expected to be $160,000 for 2013. 2012 . (a) Prepare Christopher Company's balance items as a percent of sales to (b) What additional funds will be needed in 2013?92 PART 2: FINANCIAL PLANNING AND CON Define the phrase "pro forma" and explain the purpose of pro forma finan statements. Explain pro forma earnings, problems with pro forma, and ben lal of pro forma analysis. . http:/ / www.investopedia.com/terms/p/proforma.asp B LIST OF KEY TERMS budgets management information system cash budget sales budget pro forma balance sheet production budget percent-of-sales method pro forma income statement sale expense budget pro forma funds flow statement PROBLEMS 5-4 5-1 Prepare the cash budget of the Hughes Company for the first six months of 2013 on the basis of the following estimates: (1) Credit sales are expected to be $20,000 a month from December 2012 to June 2013. (2) Monthly credit purchases of raw materials are expected to be $10,000 from December 2012 to June 2013. 5-5 (3) Accounts receivable are collected in the month following the sales. Pay- ments for raw materials are also made in the month following the month in which these costs were incurred. (4) Wages and salaries used in the production process are expected to be $3,000 each month, paid in the month they are incurred; factory overhead is $1,000 per month; selling expenses are $1,500 each month; and monthly (5) administrative expenses are $500. The company's capital budget calls for the purchase of a new machine costing $10,000 whose payment is expected to be made in May; income tax payments of $5,000 are due in March; dividend payments of $10,000 are planned in March; and semiannual interest of $1,000 on $20,000 of 10 percent bonds is due in June. (6) The company has a cash balance of $10,000 on December 31, 2012. This 5-2 amount is the minimum cash balance which should be maintained through- out the budget period. Using the cash budget worked out in Problem 5-1 and the following additional information, prepare a pro forma income statement for the Hughes Company for the six months ending June 30, 2013. 5-6 (7) The company's tax rate is 50 percent. 8) Depreciation charges are $500 a month. 5-3 (9) The company had an inventory of $1,000 at the close of 2012 and wishes to increase its inventory level to $8,000 by the end of June 2013. Use the information given in Problems 5-1 and 5-2 and the following informa- tion to construct a pro forma balance sheet for the Hughes Company for June