Question: need help with b-d 17. You are conducting a large concurrent cohort study evaluating the association between drinking alcohol and the likelihood of contracting an
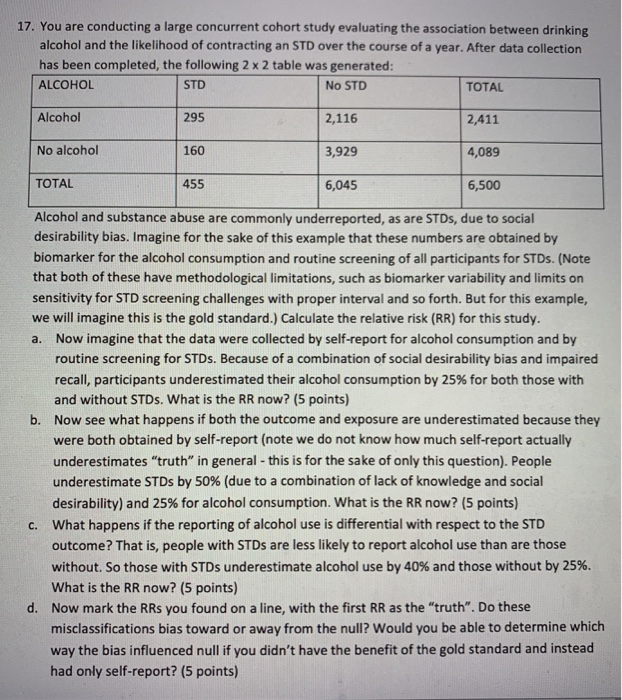
17. You are conducting a large concurrent cohort study evaluating the association between drinking alcohol and the likelihood of contracting an STD over the course of a year. After data collection has been completed, the following 2 x 2 table was generated: ALCOHOL No STD TOTAL STD Alcohol 295 2,116 2,411 No alcohol 160 3,929 4,089 TOTAL 455 6,045 6,500 Alcohol and substance abuse are commonly underreported, as are STDs, due to social desirability bias. Imagine for the sake of this example that these numbers are obtained by biomarker for the alcohol consumption and routine screening of all participants for STDs. (Note that both of these have methodological limitations, such as biomarker variability and limits on sensitivity for STD screening challenges with proper interval and so forth. But for this example, we will imagine this is the gold standard.) Calculate the relative risk (RR) for this study. a. Now imagine that the data were collected by self-report for alcohol consumption and by routine screening for STDs. Because of a combination of social desirability bias and impaired recall, participants underestimated their alcohol consumption by 25% for both those with and without STDs. What is the RR now? (5 points) b. Now see what happens if both the outcome and exposure are underestimated because they were both obtained by self-report (note we do not know how much self-report actually underestimates "truth" in general - this is for the sake of only this question). People underestimate STDs by 50% (due to a combination of lack of knowledge and social desirability) and 25% for alcohol consumption. What is the RR now? (5 points) C. What happens if the reporting of alcohol use is differential with respect to the STD outcome? That is, people with STDs are less likely to report alcohol use than are those without. So those with STDs underestimate alcohol use by 40% and those without by 25%. What is the RR now? (5 points) d. Now mark the RRs you found on a line, with the first RR as the "truth". Do these misclassifications bias toward or away from the null? Would you be able to determine which way the bias influenced null if you didn't have the benefit of the gold standard and instead had only self-report? (5 points) 17. You are conducting a large concurrent cohort study evaluating the association between drinking alcohol and the likelihood of contracting an STD over the course of a year. After data collection has been completed, the following 2 x 2 table was generated: ALCOHOL No STD TOTAL STD Alcohol 295 2,116 2,411 No alcohol 160 3,929 4,089 TOTAL 455 6,045 6,500 Alcohol and substance abuse are commonly underreported, as are STDs, due to social desirability bias. Imagine for the sake of this example that these numbers are obtained by biomarker for the alcohol consumption and routine screening of all participants for STDs. (Note that both of these have methodological limitations, such as biomarker variability and limits on sensitivity for STD screening challenges with proper interval and so forth. But for this example, we will imagine this is the gold standard.) Calculate the relative risk (RR) for this study. a. Now imagine that the data were collected by self-report for alcohol consumption and by routine screening for STDs. Because of a combination of social desirability bias and impaired recall, participants underestimated their alcohol consumption by 25% for both those with and without STDs. What is the RR now? (5 points) b. Now see what happens if both the outcome and exposure are underestimated because they were both obtained by self-report (note we do not know how much self-report actually underestimates "truth" in general - this is for the sake of only this question). People underestimate STDs by 50% (due to a combination of lack of knowledge and social desirability) and 25% for alcohol consumption. What is the RR now? (5 points) C. What happens if the reporting of alcohol use is differential with respect to the STD outcome? That is, people with STDs are less likely to report alcohol use than are those without. So those with STDs underestimate alcohol use by 40% and those without by 25%. What is the RR now? (5 points) d. Now mark the RRs you found on a line, with the first RR as the "truth". Do these misclassifications bias toward or away from the null? Would you be able to determine which way the bias influenced null if you didn't have the benefit of the gold standard and instead had only self-report? (5 points)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


