Question: need help with both numbers 1 & 2 plz if u can 1. Master theorem (10 points) Use the master theorem to find tight asymptotic
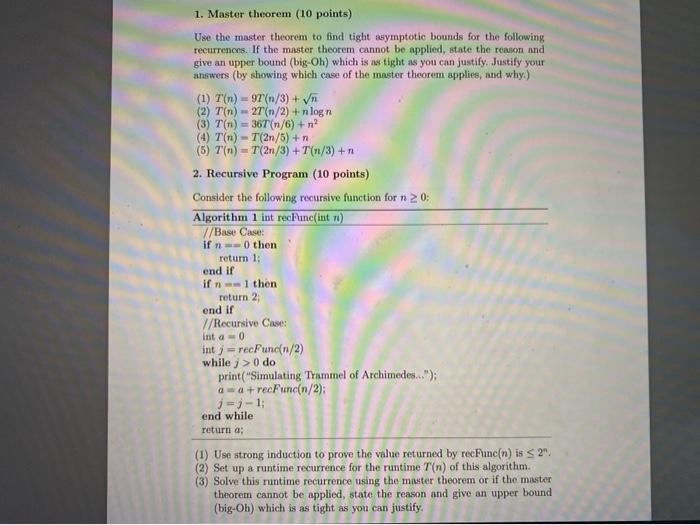
1. Master theorem (10 points) Use the master theorem to find tight asymptotic bounds for the following recurrences. If the master theorem cannot be applied, state the reason and give an upper bound (big-Oh) which is a tight as you can justify. Justify your answers (by showing which case of the master theorem applies, and why) (1) T(n) = 97(1/3) + Vn (2) T(n) = 2Tm/2) + n log I (3) T(m) = 36T(n/6) + n? (4) T(n) - 7(2n/5)+n (5) 7(n) = T(2n/3) +T(n/3) +n 2. Recursive Program (10 points) Consider the following recursive function for n 20: Algorithm 1 int recunc(int nu) Base Case: if n then return 1: end if if I then return 2, end ir 7/Recursive Case: int a 0 int j - recFuncn/2) while j> 0 do print("Simulating Trammel of Archimedes."); a = a +recFunc(n/2); i = 3-1 end while return a; (1) Use strong induction to prove the value returned by recFunc(n) is s2 (2) Set up a runtime recurrence for the runtime T'(n) of this algorithm (3) Solve this runtime recurrence using the master theorem or if the master theorem cannot be applied, state the reason and give an upper bound (big-Oh) which is as tight as you can justify. 1. Master theorem (10 points) Use the master theorem to find tight asymptotic bounds for the following recurrences. If the master theorem cannot be applied, state the reason and give an upper bound (big-Oh) which is a tight as you can justify. Justify your answers (by showing which case of the master theorem applies, and why) (1) T(n) = 97(1/3) + Vn (2) T(n) = 2Tm/2) + n log I (3) T(m) = 36T(n/6) + n? (4) T(n) - 7(2n/5)+n (5) 7(n) = T(2n/3) +T(n/3) +n 2. Recursive Program (10 points) Consider the following recursive function for n 20: Algorithm 1 int recunc(int nu) Base Case: if n then return 1: end if if I then return 2, end ir 7/Recursive Case: int a 0 int j - recFuncn/2) while j> 0 do print("Simulating Trammel of Archimedes."); a = a +recFunc(n/2); i = 3-1 end while return a; (1) Use strong induction to prove the value returned by recFunc(n) is s2 (2) Set up a runtime recurrence for the runtime T'(n) of this algorithm (3) Solve this runtime recurrence using the master theorem or if the master theorem cannot be applied, state the reason and give an upper bound (big-Oh) which is as tight as you can justify
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


