Question: Need help with my code...C Language, I ran code got errors Errors The mixing step of our permutation takes four uint32_t variables, a/b/c/d, and updates
Need help with my code...C Language, I ran code got errors

 Errors
Errors
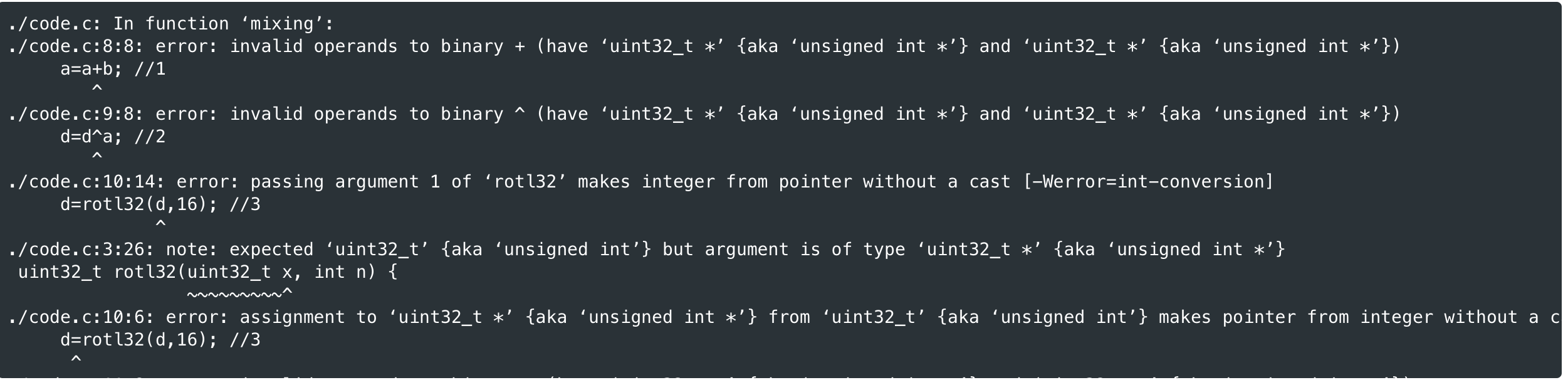
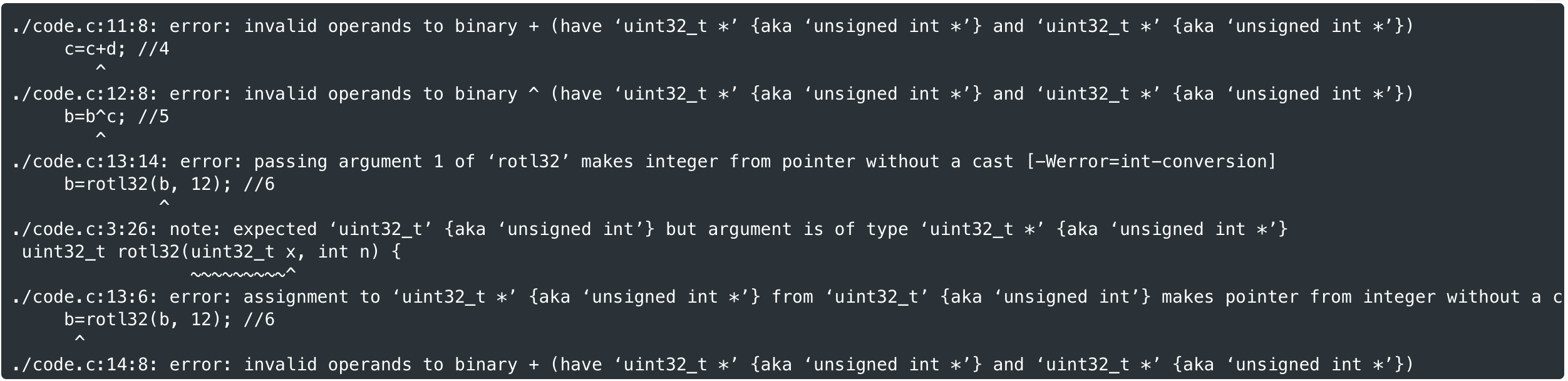
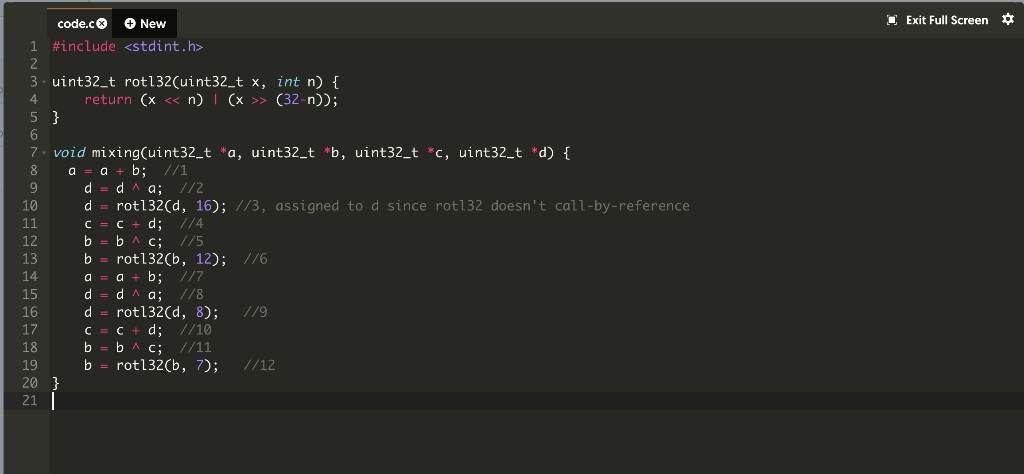
The mixing step of our permutation takes four uint32_t variables, a/b/c/d, and updates them according to the following schematic. 6 d SIG (388) The circles indicate XOR, the squares indicated addition, and the rectangles indicate rotate-left by the number of bits indicated (there are four of each operation in the picture). Implement the schematic using the starter code below. The fact that the parameters are of type (uint32_t *) means that pointers to uint32_t variables are being passed and not the variables themselves. This is how "call-by-reference" is acheived in C and how changes to variables outside of a function are achieved inside of a function. 1 Exit Full Screen code.c + New 1 #include 2 3. uint32_t rot132(uint32_t x, int n) { 4 return (x > (32-n)); 5} 6 7. void mixing(uint32_t *a, uint32_t *b, uint32_t *c, uint32_t *d) { 8 a = a + b; //1 9 d = da; 1/2 10 d = rot132(d, 16); //3, assigned to d since rot132 doesn't call-by-reference 11 C + d; 1/4 12 b bic; //5 13 b rotl32Cb, 12); //6 14 a + b; 1/7 15 d = da; //8 16 d rot132(d, 8); //9 17 C = c + d; //10 18 b bic; //11 19 b = rotl32Cb, 7); 1/12 20 } 21 ./code.c: In function mixing': ./code.c:8:8: error: invalid operands to binary + (have uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} and uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'}) a=a+b; //1 ./code.c:9:8: error: invalid operands to binary ^ (have uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} and uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'}) d=d^a; //2 ./code.c:10:14: error: passing argument 1 of 'rot132' makes integer from pointer without a cast [-Werror=int-conversion] d=rot132(d,16); //3 ../code.c:3:26: note: expected uint32_t' {aka unsigned int'} but argument is of type uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} uint32_t rot132 (uint32_t x, int n) { ./code.c:10:6: error: assignment to uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} from uint32_t'{aka unsigned int'} makes pointer from integer without a c d=rot132(d,16); //3 ./code.c:11:8: error: invalid operands to binary + (have 'uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} and uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'}) C=C+d; //4 ./code.c:12:8: error: invalid operands to binary b=b^c; //5 (have uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} and uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'}) ./code.c:13:14: error: passing argument 1 of rot132' makes integer from pointer without a cast [-Werror=int-conversion] b=rot132(b, 12); //6 ./code.c:3:26: note: expected 'uint32_t' {aka unsigned int'} but argument is of type uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} uint32_t rot132 (uint32_t x, int n) { ./code.c:13:6: error: assignment to uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} from uint32_t' {aka unsigned int'} makes pointer from integer without a c b=rot132(b, 12); //6 ./code.c:14:8: error: invalid operands to binary + (have uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} and uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'}) The mixing step of our permutation takes four uint32_t variables, a/b/c/d, and updates them according to the following schematic. 6 d SIG (388) The circles indicate XOR, the squares indicated addition, and the rectangles indicate rotate-left by the number of bits indicated (there are four of each operation in the picture). Implement the schematic using the starter code below. The fact that the parameters are of type (uint32_t *) means that pointers to uint32_t variables are being passed and not the variables themselves. This is how "call-by-reference" is acheived in C and how changes to variables outside of a function are achieved inside of a function. 1 Exit Full Screen code.c + New 1 #include 2 3. uint32_t rot132(uint32_t x, int n) { 4 return (x > (32-n)); 5} 6 7. void mixing(uint32_t *a, uint32_t *b, uint32_t *c, uint32_t *d) { 8 a = a + b; //1 9 d = da; 1/2 10 d = rot132(d, 16); //3, assigned to d since rot132 doesn't call-by-reference 11 C + d; 1/4 12 b bic; //5 13 b rotl32Cb, 12); //6 14 a + b; 1/7 15 d = da; //8 16 d rot132(d, 8); //9 17 C = c + d; //10 18 b bic; //11 19 b = rotl32Cb, 7); 1/12 20 } 21 ./code.c: In function mixing': ./code.c:8:8: error: invalid operands to binary + (have uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} and uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'}) a=a+b; //1 ./code.c:9:8: error: invalid operands to binary ^ (have uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} and uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'}) d=d^a; //2 ./code.c:10:14: error: passing argument 1 of 'rot132' makes integer from pointer without a cast [-Werror=int-conversion] d=rot132(d,16); //3 ../code.c:3:26: note: expected uint32_t' {aka unsigned int'} but argument is of type uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} uint32_t rot132 (uint32_t x, int n) { ./code.c:10:6: error: assignment to uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} from uint32_t'{aka unsigned int'} makes pointer from integer without a c d=rot132(d,16); //3 ./code.c:11:8: error: invalid operands to binary + (have 'uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} and uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'}) C=C+d; //4 ./code.c:12:8: error: invalid operands to binary b=b^c; //5 (have uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} and uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'}) ./code.c:13:14: error: passing argument 1 of rot132' makes integer from pointer without a cast [-Werror=int-conversion] b=rot132(b, 12); //6 ./code.c:3:26: note: expected 'uint32_t' {aka unsigned int'} but argument is of type uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} uint32_t rot132 (uint32_t x, int n) { ./code.c:13:6: error: assignment to uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} from uint32_t' {aka unsigned int'} makes pointer from integer without a c b=rot132(b, 12); //6 ./code.c:14:8: error: invalid operands to binary + (have uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'} and uint32_t *' {aka unsigned int *'})

 Errors
Errors




