Question: need help with these questions please A2w)+2B(m)2AB(w) Initial partial pressures are PA2=1.0 bar and PB=2.6 bar. Data for the reaction was collected by monitoring the
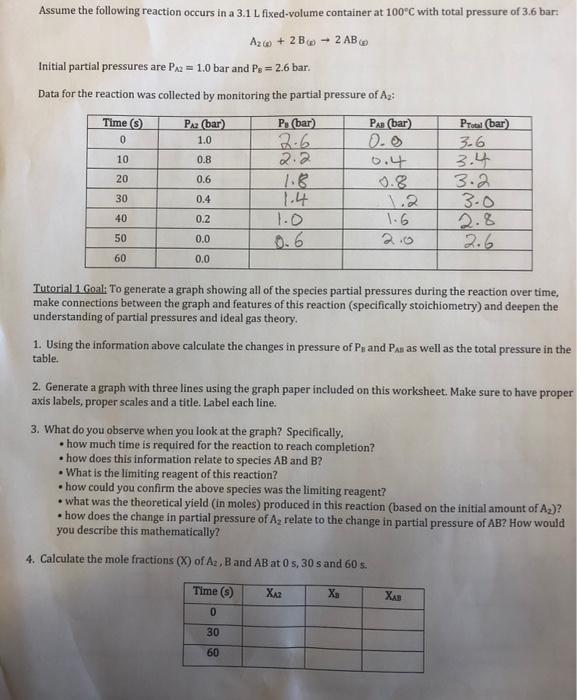
A2w)+2B(m)2AB(w) Initial partial pressures are PA2=1.0 bar and PB=2.6 bar. Data for the reaction was collected by monitoring the partial pressure of A2 : Tutorial1. Goal: To generate a graph showing all of the species partial pressures during the reaction over time, make connections between the graph and features of this reaction (specifically stoichiometry) and deepen the understanding of partial pressures and ideal gas theory. 1. Using the information above calculate the changes in pressure of P8 and Pasas well as the total pressure in the table. 2. Generate a graph with three lines using the graph paper included on this worksheet. Make sure to have proper axis labels, proper scales and a title. Label each line. 3. What do you observe when you look at the graph? Specifically. - how much time is required for the reaction to reach completion? - how does this information relate to species AB and B ? - What is the limiting reagent of this reaction? - how could you confirm the above species was the limiting reagent? - what was the theoretical yield (in moles) produced in this reaction (based on the initial amount of A2 )? - how does the change in partial pressure of A2 relate to the change in partial pressure of AB ? How would you describe this mathematically? 4. Calculate the mole fractions (X) of A2,B and AB at 0,5,30 s and 605 . A2w)+2B(m)2AB(w) Initial partial pressures are PA2=1.0 bar and PB=2.6 bar. Data for the reaction was collected by monitoring the partial pressure of A2 : Tutorial1. Goal: To generate a graph showing all of the species partial pressures during the reaction over time, make connections between the graph and features of this reaction (specifically stoichiometry) and deepen the understanding of partial pressures and ideal gas theory. 1. Using the information above calculate the changes in pressure of P8 and Pasas well as the total pressure in the table. 2. Generate a graph with three lines using the graph paper included on this worksheet. Make sure to have proper axis labels, proper scales and a title. Label each line. 3. What do you observe when you look at the graph? Specifically. - how much time is required for the reaction to reach completion? - how does this information relate to species AB and B ? - What is the limiting reagent of this reaction? - how could you confirm the above species was the limiting reagent? - what was the theoretical yield (in moles) produced in this reaction (based on the initial amount of A2 )? - how does the change in partial pressure of A2 relate to the change in partial pressure of AB ? How would you describe this mathematically? 4. Calculate the mole fractions (X) of A2,B and AB at 0,5,30 s and 605
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


