Question: Need help with this problem. the problem asks for an implementation file called ( stats.cpp ) for the file stats.h which is already given. I
Need help with this problem. the problem asks for an implementation file called (stats.cpp) for the file stats.h which is already given. I am posting the question along with the precode file stats.h. Just help me with the implementation file (stats.cpp) for the file stats.h. The implementation description is given in the problem. thanks in advance




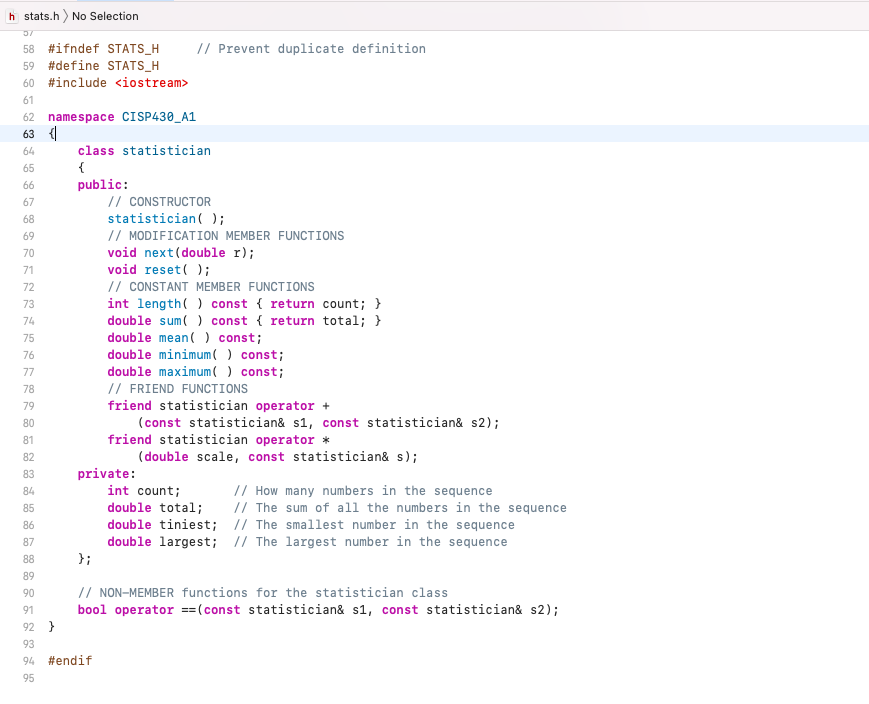
#ifndef STATS_H // Prevent duplicate definition
#define STATS_H
#include
namespace CISP430_A1
{
class statistician
{
public:
// CONSTRUCTOR
statistician( );
// MODIFICATION MEMBER FUNCTIONS
void next(double r);
void reset( );
// CONSTANT MEMBER FUNCTIONS
int length( ) const { return count; }
double sum( ) const { return total; }
double mean( ) const;
double minimum( ) const;
double maximum( ) const;
// FRIEND FUNCTIONS
friend statistician operator +
(const statistician& s1, const statistician& s2);
friend statistician operator *
(double scale, const statistician& s);
private:
int count; // How many numbers in the sequence
double total; // The sum of all the numbers in the sequence
double tiniest; // The smallest number in the sequence
double largest; // The largest number in the sequence
};
// NON-MEMBER functions for the statistician class
bool operator ==(const statistician& s1, const statistician& s2);
}
You will create, implement and test a small class called statistician, which is similar to some of the small classes in Chapter 2 of the text. The new class is called statistician, using a header file, stats.h (attached).(most of which is written for you) and an implementation file, stats.cpp (which you need to create and implement.). The statistician is a class that is designed to keep track of simple statistics about a sequence of real numbers. There are two member functions that you should understand at an informal level before you proceed any further. The prototypes for these two functions are shown here as part of the statistician class declaration: class statistician { public: void next (double r); double mean const; }; The member function "next" is used to give a sequence of numbers to the statistician one at a time. The member function "mean" is a constant member function that returns the ' arithmetic mean (i.e., the average) of all the numbers that have been given to the statistician. Example: Suppose that you want a statistician to compute the mean of the sequence 1.1, 2.8,-0.9. Then you could write these statements: // Declares a statistician object called s statistician si // Give the three numbers 1.1, 2.8 and -0.9 to the statistician S.next(1.1); S.next.(2.8); s.next(-0.9); // Call the mean function, and print the result followed by a carriage return cout 0. You cannot use these three member functions unless the statistician has been given at least one number!) A constant member function called sum, which returns the sum of all the numbers that have been given to the statistician. This function does NOT have a precondition. It may be called even if the statistician has NO numbers (in which case it should return 0). An overloaded operator == which tests to see whether two statisticians are "equal". The prototype is: bool operator ==(const statistician& s, const statistician& t); In order for two statisticians to be equal, they must have the same length (i.e., they have been given the same number of numbers). Also, if their length is greater than zero, they must also have the same mean, the same minimum, the same maximum, and the same sum. For example: Suppose that a statistician s has been given four numbers 1, 2, 3, 4. A second statistician t has been given four numbers 1, 1.5, 3.5, 4. Then the test (s==t) must return true since both s and t have equal values for all the member functions, as shown here: s.length() and t.length() are both 4 s.mean() and t.mean(are both 2.5 s.sum() and t.sum() are both 10.0 s.minimum and t.minimum are both 1 s.maximum and t.maximum are both 4 An overloaded + operator which has two statisticians as arguments, and returns a third statistician, as shown in this prototype: statistician operator +(const statisticiana s, const statistician& t); An overloaded * operator which allows you to "multiply" a double number times a statistician. Here is the prototype: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. . the statistician t has been given the numbers 4, 5. Then the assignment statement u=s+t will result in u behaving as if it had been given the five numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. n stats.h) No Selection 66 68 69 73 74 76 58 #ifndef STATS_H // Prevent duplicate definition 59 #define STATS_H 60 #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


