Question: Need homework assistance Quantitative Methods for Business 13th ed Chapter 10 Please see ALL questions below Chapter 10 Distribution and Network Models - Self-Test Question
Need homework assistance
Quantitative Methods for Business 13th ed
Chapter 10
Please see ALL questions below

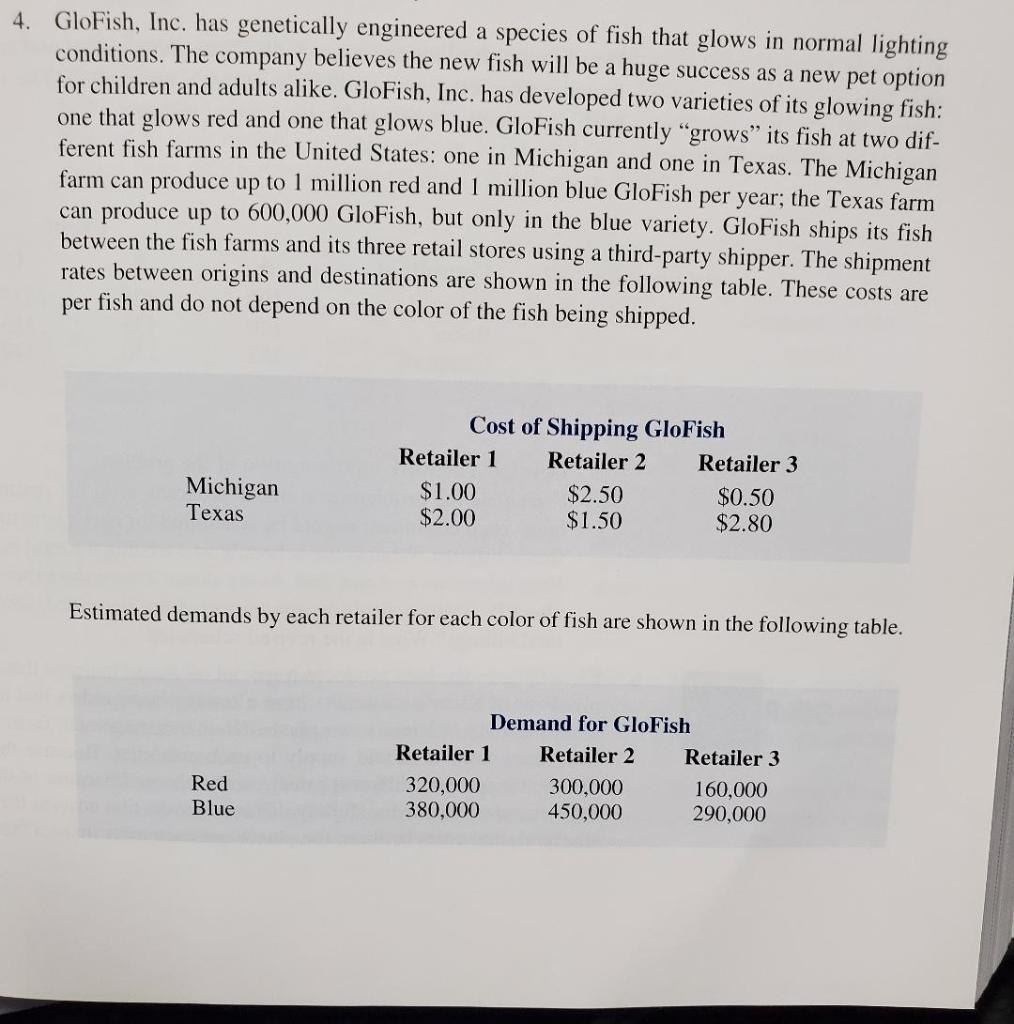


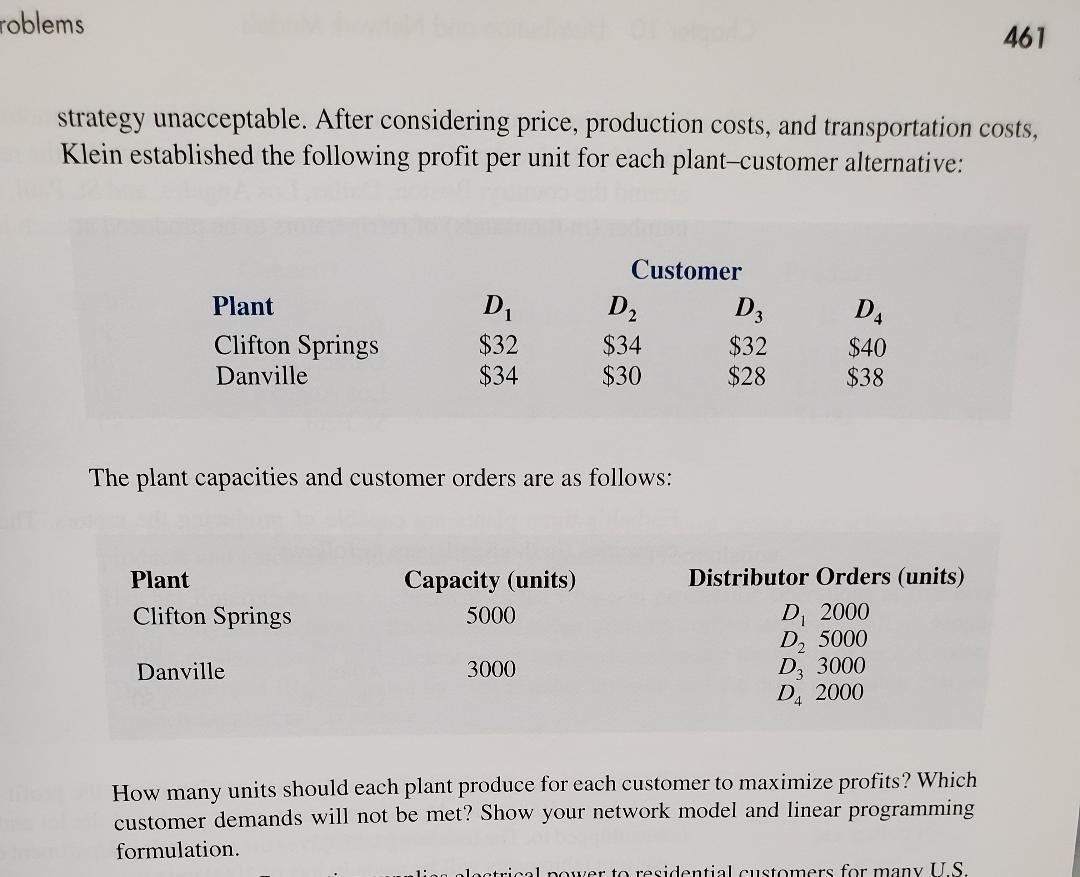
Chapter 10 Distribution and Network Models - Self-Test Question 4 and 6 GloFish, Inc. has genetically engineered a species of fish that glows in normal lighting conditions. The company believes the new fish will be a huge success as a new pet option for children and adults alike. GloFish, Inc. has developed two varieties of its glowing fish: one that glows red and one that glows blue. GloFish currently "grows" its fish at two different fish farms in the United States: one in Michigan and one in Texas. The Michigan farm can produce up to 1 million red and 1 million blue GloFish per year; the Texas farm can produce up to 600,000 GloFish, but only in the blue variety. GloFish ships its fish between the fish farms and its three retail stores using a third-party shipper. The shipment rates between origins and destinations are shown in the following table. These costs are per fish and do not depend on the color of the fish being shipped. Estimated demands by each retailer for each color of fish are shown in the following table. Chapter 10 Distribution and Network Models a. What is the optimal policy for the fish farms? How many red and blue fish should be produced in Michigan and shipped to each retailer? How many blue fish should be produced in Texas and shipped to each retailer? b. What is the minimum shipping cost that can be incurred and still meet demand require. ments at retailers 1,2 , and 3 ? c. How much should GloFish be willing to invest to enable the Texas farm to produce both red and blue GloFish while maintaining the maximum of 600,000 total fish produced at the Texas farm? 6. Klein Chemicals, Inc., produces a special oil-based material that is currently in short supply. Four of Klein's customers have already placed orders that together exceed the combined capacity of Klein's two plants. Klein's management faces the problem of deciding how many units it should supply to each customer. Because the four customers are in different industries, different prices can be charged because of the various industry pricing structures. However, slightly different production costs at the two plants and varying transportation costs between the plants and customers make a "sell to the highest bidder" strategy unacceptable. After considering price, production costs, and transportation costs, Klein established the following profit per unit for each plant-customer alternative: The plant capacities and customer orders are as follows: How many units should each plant produce for each customer to maximize profits? Which customer demands will not be met? Show your network model and linear programming formulation








