Question: Need numerical questions help with detailed explanation 7. (30 points) Consider a linear system Ax = b, where A E Roxn and x, b E
Need numerical questions help with detailed explanation

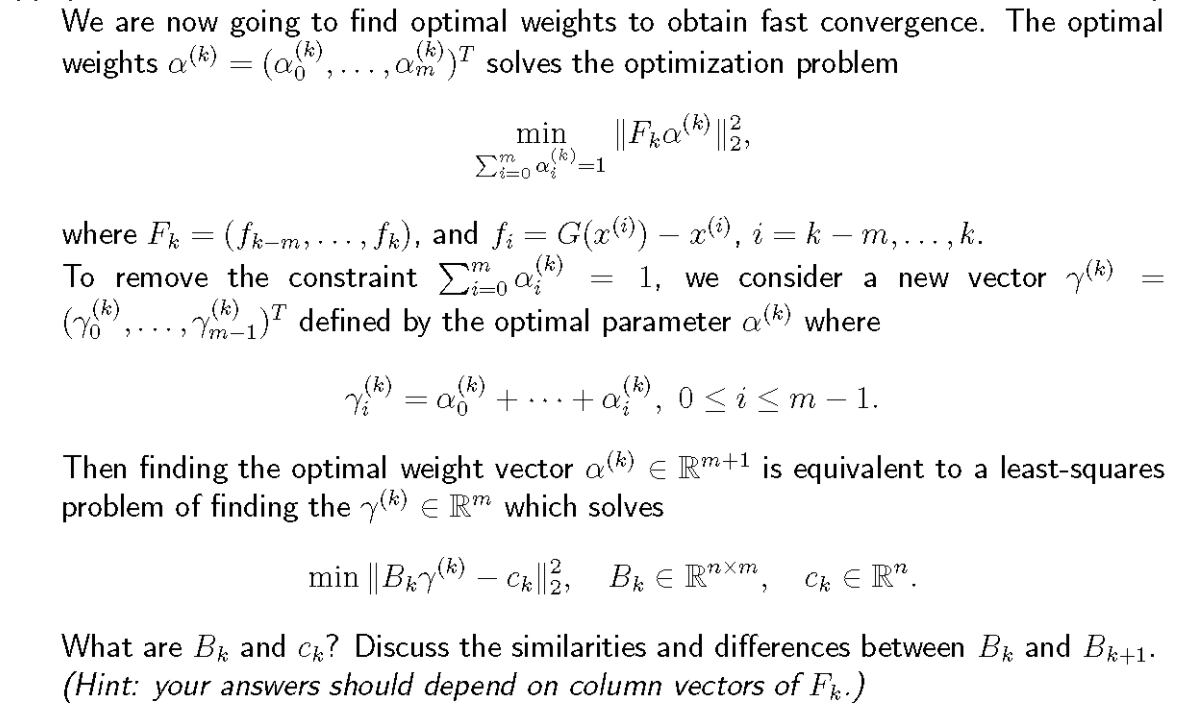
7. (30 points) Consider a linear system Ax = b, where A E Roxn and x, b E R". We denote the diagonal part of A as a new matrix D, 0 D = ann and assume that D is non-singular. Consider the following iterative scheme. Given an arbitrary initial vector x() E In, x (*+1) = G(x()) := (1 - D'A) x( * ) + D-1b, k = 0, 1, 2, .... I E nxn is the identity matrix. (a) Show that G : R" + R is a fixed-point operator, and the fixed-point solution solves the linear system Ax = b. (b) Compute the number of floating-point operations (flops) for each iteration of the fixed-point method. When is this iterative scheme preferred to the LU factorization for solving a linear system Ax = b based on the computational complexity? (c) If lasil > E laijl, which holds for i = 1, 2, ..., n, show that R:= (|D-1A-Ill. , ogrgmL Then finding the optimal weight vector all\") E Rm\" is equivalent to a least-squares problem of finding the 70\") E Rm which solves min H8167\") ck\"; Bk E Rnxm, ck E R\". What are Bk and Ch? Discuss the similarities and differences between Bk and Bk+1- (Hint: your answers should depend on column vectors of Fk.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


