Question: need python code OR manual calculation process for calculating, and answer the following questions After the first iteration of EM, what is the value of
need python code OR manual calculation process for calculating, and answer the following questions
After the first iteration of EM, what is the value of g for pair 1?
After the first iteration of EM, what is the value of g for pair 2?
After the first iteration of EM, what is the value of g for pair 3?
After the first iteration of EM, what is the m-probability of First Name?
After the first iteration of EM, what is the m-probability of Last Name?
After the first iteration of EM, what is the m-probability of Gender?
After the first iteration of EM, what is the u-probability of First Name?
After the first iteration of EM, what is the u-probability of Last Name?
After the first iteration of EM, what is the u-probability of Gender?
After the first iteration of EM, what is the value of p (the proportion of matched records)?
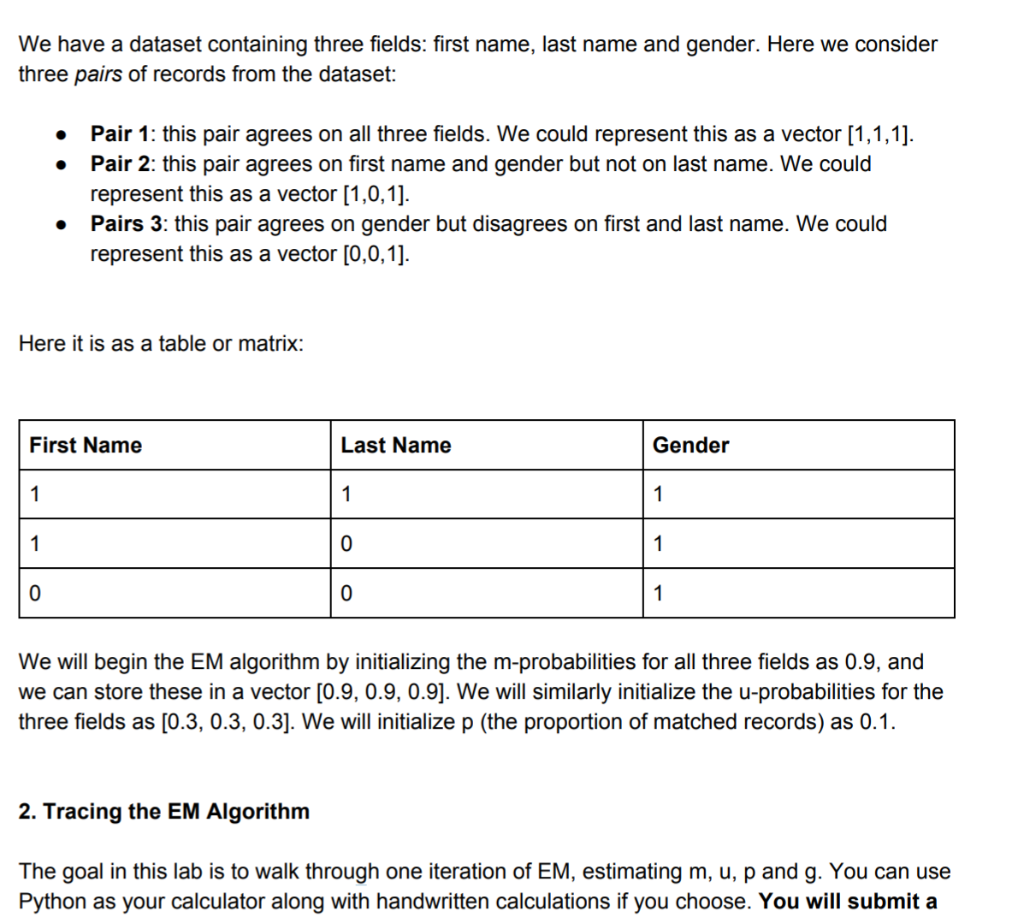
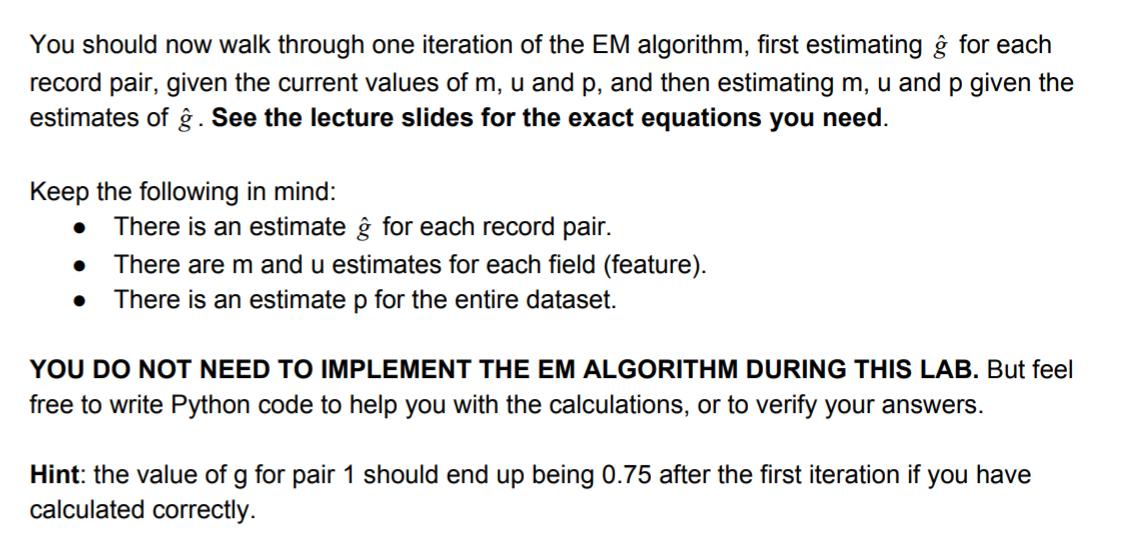
We have a dataset containing three fields: first name, last name and gender. Here we consider three pairs of records from the dataset: . . Pair 1: this pair agrees on all three fields. We could represent this as a vector (1,1,1). Pair 2: this pair agrees on first name and gender but not on last name. We could represent this as a vector (1,0,1). Pairs 3: this pair agrees on gender but disagrees on first and last name. We could represent this as a vector [0,0,1). Here it is as a table or matrix: First Name Last Name Gender 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 We will begin the EM algorithm by initializing the m-probabilities for all three fields as 0.9, and we can store these in a vector [0.9, 0.9, 0.9]. We will similarly initialize the u-probabilities for the three fields as [0.3, 0.3, 0.3]. We will initialize p (the proportion of matched records) as 0.1. 2. Tracing the EM Algorithm The goal in this lab is to walk through one iteration of EM, estimating m, u, p and g. You can use Python as your calculator along with handwritten calculations if you choose. You will submit a You should now walk through one iteration of the EM algorithm, first estimating for each record pair, given the current values of m, u and p, and then estimating m, u and p given the estimates of . See the lecture slides for the exact equations you need. . Keep the following in mind: There is an estimate for each record pair. There are mand u estimates for each field (feature). There is an estimate p for the entire dataset. . YOU DO NOT NEED TO IMPLEMENT THE EM ALGORITHM DURING THIS LAB. But feel free to write Python code to help you with the calculations, or to verify your answers. Hint: the value of g for pair 1 should end up being 0.75 after the first iteration if you have calculated correctly. We have a dataset containing three fields: first name, last name and gender. Here we consider three pairs of records from the dataset: . . Pair 1: this pair agrees on all three fields. We could represent this as a vector (1,1,1). Pair 2: this pair agrees on first name and gender but not on last name. We could represent this as a vector (1,0,1). Pairs 3: this pair agrees on gender but disagrees on first and last name. We could represent this as a vector [0,0,1). Here it is as a table or matrix: First Name Last Name Gender 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 We will begin the EM algorithm by initializing the m-probabilities for all three fields as 0.9, and we can store these in a vector [0.9, 0.9, 0.9]. We will similarly initialize the u-probabilities for the three fields as [0.3, 0.3, 0.3]. We will initialize p (the proportion of matched records) as 0.1. 2. Tracing the EM Algorithm The goal in this lab is to walk through one iteration of EM, estimating m, u, p and g. You can use Python as your calculator along with handwritten calculations if you choose. You will submit a You should now walk through one iteration of the EM algorithm, first estimating for each record pair, given the current values of m, u and p, and then estimating m, u and p given the estimates of . See the lecture slides for the exact equations you need. . Keep the following in mind: There is an estimate for each record pair. There are mand u estimates for each field (feature). There is an estimate p for the entire dataset. . YOU DO NOT NEED TO IMPLEMENT THE EM ALGORITHM DURING THIS LAB. But feel free to write Python code to help you with the calculations, or to verify your answers. Hint: the value of g for pair 1 should end up being 0.75 after the first iteration if you have calculated correctly
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


