Question: need right answer , = 0, if y> 0, and V) = 0, if X, > 0 f57 6.1-4 Correspondence Between Primal and Dual Optimal
need right answer
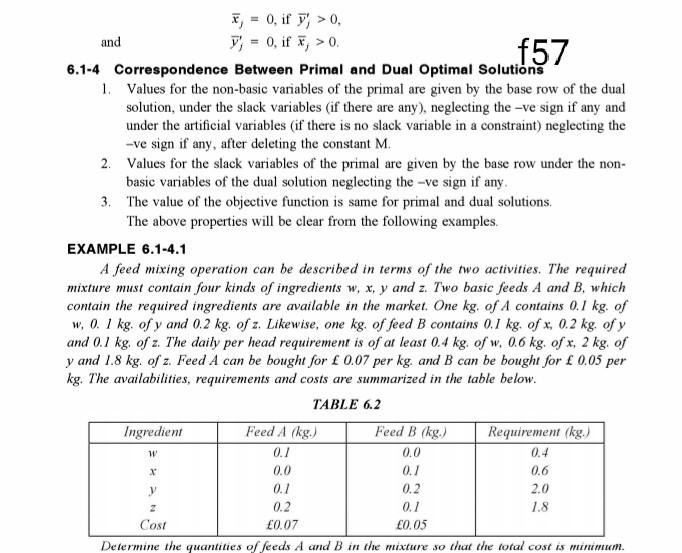
, = 0, if y> 0, and V) = 0, if X, > 0 f57 6.1-4 Correspondence Between Primal and Dual Optimal Solutions 1. Values for the non-basic variables of the primal are given by the base row of the dual solution, under the slack variables (if there are any), neglecting the -ve sign if any and under the artificial variables (if there is no slack variable in a constraint) neglecting the -ve sign if any, after deleting the constant M. 2. Values for the slack variables of the primal are given by the base row under the non- basic variables of the dual solution neglecting the -ve sign if any. 3. The value of the objective function is same for primal and dual solutions The above properties will be clear from the following examples. EXAMPLE 6.1-4.1 A feed mixing operation can be described in terms of the two activities. The required mixture must contain four kinds of ingredients w, x, y and z. Two basic feeds A and B, which contain the required ingredients are available in the market. One kg. of A contains 0.1 kg. of w. 0. 1 kg. of y and 0.2 kg. of z. Likewise, one kg, of feed B contains 0.1 kg. of x. 0.2 kg, of y and 0.1 kg, of z. The daily per head requirement is of at least 0.4 kg. of w. 0.6 kg. of x, 2 kg. of y and 1.8 kg. of z. Feed A can be bought for 0.07 per kg. and B can be bought for 0.05 per kg. The availabilities, requirements and costs are summarized in the table below. TABLE 6.2 Ingredient Feed A /kg) Feed B (kg.) Requirement (kg.) 0.0 0.1 0.6 y 2.0 0.2 0.1 1.8 Cost 0.07 0.05 Determine the quantities of feeds A and B in the mixture so that the total cost is minimum. 1 0.1 0.4 X 0.0 0.1 0.2Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


