Question: Need these programs done together for review in Java using linked lists involving biological sequences.project 3 images has a description of what you will be




 Need these programs done together for review in Java using linked lists involving biological sequences.project 3 images has a description of what you will be doing and what implementation will be used.project 4 is a enhancement of project 3.project 4 screenshots will show you new functions that will need to be added and what you will need the program to output as the end result.The screenshots will show you what needs to be done.
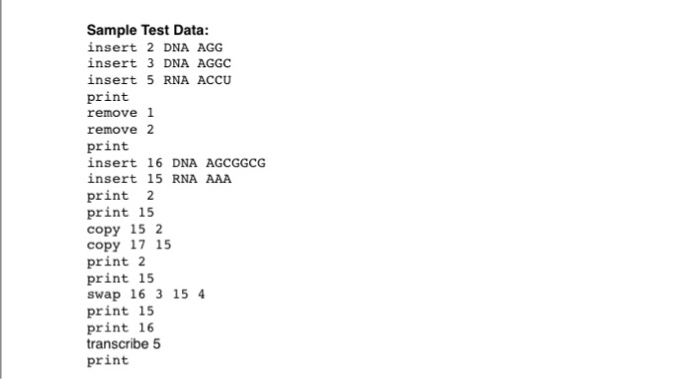
Need these programs done together for review in Java using linked lists involving biological sequences.project 3 images has a description of what you will be doing and what implementation will be used.project 4 is a enhancement of project 3.project 4 screenshots will show you new functions that will need to be added and what you will need the program to output as the end result.The screenshots will show you what needs to be done. Programming Project #3 A key element in many bioinformatics problems is the biological sequence. A biological sequence is just a list of characters chosen from some alphabet. Two of the common biological sequences are DNA (composed of the four characters A, C, G, and T) and RNA (composed of the four characters A, C, G, and U). In this project, you will implement some basic functionality for manipulating DNA and RNA sequences. Implementation You will implement sequences using linked lists, storing one letter of the sequence per linked list node. In addition to the linked lists of sequences, you will maintain a "sequence array which stores the various sequences. Commands that manipulate sequences will refer directly to entries in the sequence array. The sequence array will store the sequence type (RNA or DNA) and a pointer or other form of access to the linked list that stores the sequence itself. The type field should also be able to indicate that a given position in the sequence array is unused Many of the commands that you will process require you to create and delete linked-list nodes. All indexing (both for the sequence array and for positions in a sequence) will begin with position zero. It is mandatory that your linked-list remain application independent. The program will be invoked from the command-line as: bio3 carray-size>
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


