Question: Need this in python, a screenshot of the code and the code being copy and pasted would be greatly appreciated To develop the code we
Need this in python, a screenshot of the code and the code being copy and pasted would be greatly appreciated
To develop the code we will be working with the complete text of the story "Alice in Wonderland".
Open the stub file counter_stubs.py in IDLE. You'll find the beginning of the definition of the class Count. The Count class already defines three methods: "__init__", "increment_count", "lookup_count", "get_num_words", and "get_top_words" which we'll fill in next. You should not need to change the definition lines we provide to complete the methods.
Part 1 (10 points) - Object initialization
Save the file counter_stubs.py as counter1.py.
Find the method "__init__" and add code to print a message that the object is being initialized.
Look for an assignment statement creating the class Count attribute word_counts. Update it so that word_counts is initialized to an empty dictionary.
Next add a print statement that indicates that a new object has been constructed. Running the updated program should produce the following result:
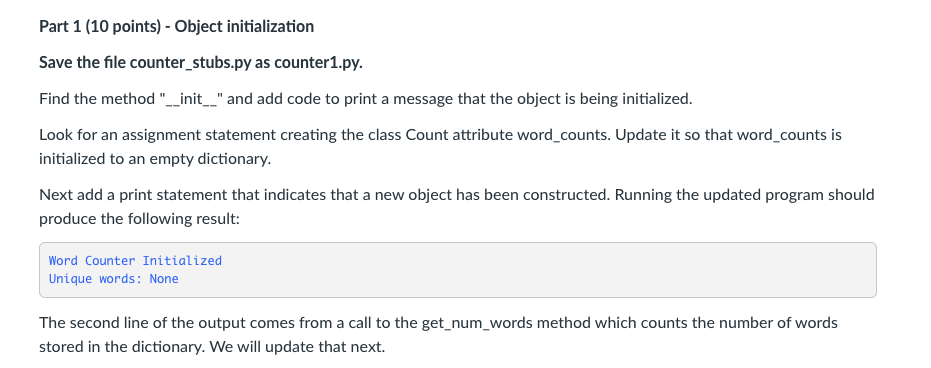
Word Counter Initialized Unique words: None
The second line of the output comes from a call to the get_num_words method which counts the number of words stored in the dictionary. We will update that next.
counter_stubs.py
# # Writing a word counting class and making a wordle # # import wordle import string
# # The Count class # # The class keyword below begins the definition of a new Python data type Count. # Count keeps word counts. All the methods that we can use with Count objects # and the variables (attributes) built inside Count objects are defined in the # this class definition. # class Count: # # Count constructor # # the __init__ method initializes the variables (attributes) # in Count objects, such as the dictionary datastructure that # hold the counts for each word. It is called when the count # object is first created using Count(). # # The variable self refers to the object being initialized # So self.word_counts is referring to the word_count dictionay # within the object. # # Always add self in front of word_counts to access it within a method. def __init__(self): # Initialize word_counts to an empty dictionary self.word_counts = None # The get_num_words method returns the number of words # (keys) in the word_counts dictionary. # This counts each word only once. def get_num_words(self): return
# The increment_count method increments the count of a word. # If word is not yet in the dictionary, self.word_counts, # it is added with a count of 1. If word is in the dictionary, # its count is incremented by 1. def increment_count(self,word): return
# The lookup_count method returns the count of word # from the self.word_counts dictionary. If the word # is not in the dictionary, it returns 0. def lookup_count(self,word): return
# The get_top_words method gets the words with the highest # counts out of the dictionary. # # The parameter num indicates how many words to return. # # The method returns a list of num (count,word) tuples # sorted from higest to lowest. def get_top_words(self,num): return # The main program def main(): ## Make a new Count object ## the counter object will keep track of ## the counts for all the words in the book counter = Count()
## Test code for Part 3 and 4. ## Uncomment for Part 3 and 4. ## counter.increment_count("Well,") ## counter.increment_count("oven") ## counter.increment_count("well") ## counter.increment_count("....'") ## print(counter.lookup_count("oven")) ## print(counter.lookup_count("well")) ## print(counter.lookup_count("pizza")) ## print(counter.lookup_count(""))
## For Part 5 Onward ## Open the user specified book file ## filename = input("Enter book file:") ## infile = open(filename) ## Put a loop here that extracts all words and ## inserts each word into the counter object by calling ## the counter.increment_count() method
## Test code for Part 5 and 6. ## Uncomment for Part 5 and 6. ## After completing Part 6 remove these lines ## print("alice:",counter.lookup_count("alice")) ## print("rabbit:",counter.lookup_count("rabbit")) ## print("and:",counter.lookup_count("and")) ## print("she:",counter.lookup_count("she")) ## Test code for Part 7. ## Uncomment for Part 7. ## print("Top 10 Words:") ## top_ten = counter.get_top_words(10) ## print(top_ten)
print("Unique words:", counter.get_num_words()) ## wordle.wordleFromObject(counter,30)
# Call the main program main()
Part 1 (10 points) - Object initialization Save the file counter_stubs.py as counter1.py. Find the method "__init__" and add code to print a message that the object is being initialized. Look for an assignment statement creating the class Count attribute word_counts. Update it so that word_counts is initialized to an empty dictionary. Next add a print statement that indicates that a new object has been constructed. Running the updated program should produce the following result: Word Counter Initialized Unique words: None The second line of the output comes from a call to the get_num_words method which counts the number of words stored in the dictionary. We will update that next
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


