Question: Need to create program in C++ language. Stuck at implementing the bool part: #include Shape.h #include Point.h #include Square.h #include #include using namespace std; Square::Square()
Need to create program in C++ language. Stuck at implementing the bool part:
#include "Shape.h" #include "Point.h" #include "Square.h" #include
Square::Square() : Shape() {
}
Square::Square(unsigned) : Shape() { this->anchor_.setX(0); this->anchor_.setY(0); this->dimension_ = 0; }
bool Square::inside(const Point&) const { if(fill-in) { return true; //point within boundary }else { return false; //point outisde boundary } }
In other words can you show and explain part 2 compeltely?
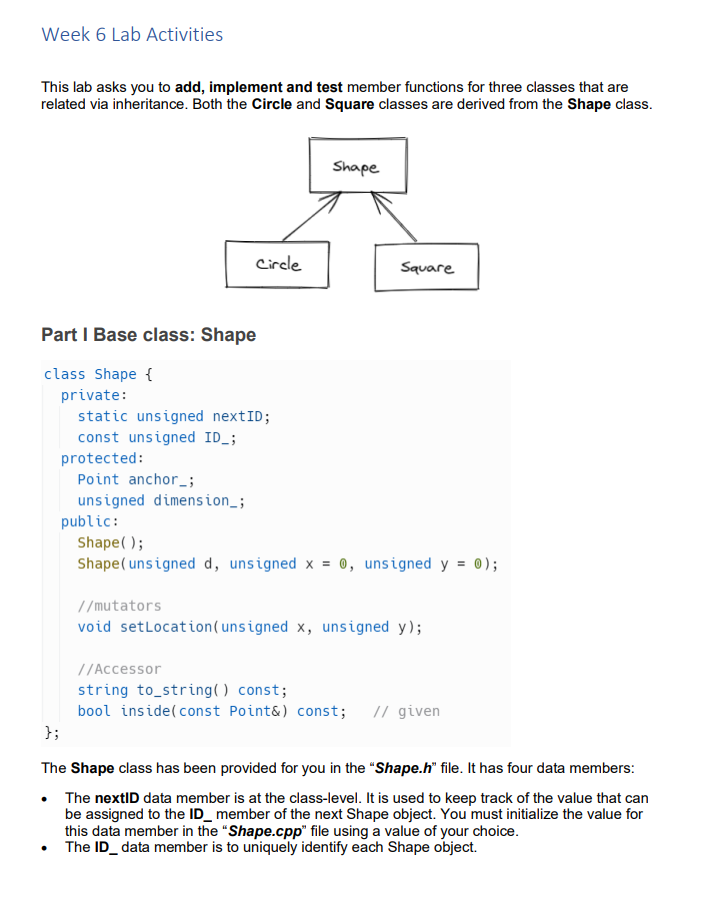



Week 6 Lab Activities This lab asks you to add, implement and test member functions for three classes that are related via inheritance. Both the Circle and Square classes are derived from the Shape class. Part I Base class: Shape class Shape \{ private: static unsigned nextID; const unsigned ID_; protected: Point anchor_; unsigned dimension_; public: Shape( ); Shape(unsigned d, unsigned x=0, unsigned y=0); //mutators void setLocation(unsigned x, unsigned y); //Accessor string to_string() const; bool inside(const Point\&) const; // given The Shape class has been provided for you in the "Shape.h" file. It has four data members: - The nextID data member is at the class-level. It is used to keep track of the value that can be assigned to the ID_ member of the next Shape object. You must initialize the value for this data member in the "Shape.cpp" file using a value of your choice. - The ID_data member is to uniquely identify each Shape object. - The anchor_data member is to identify the anchoring point of a shape. For example, the anchoring point for a square is its top left corner and the anchoring point for a circle is its center. The Point class has been defined and implemented for you in the "Point. h " and "Point.cpp" files. - The dimension_data member is to identify the size of a shape. For example, the dimension of a square is its side, and the dimension of a circle is its radius. The implementation of the inside function has been provided for you in the "Shape.cpp" file. You are asked to add the implementation of the other member functions of the Shape class in the "Shape.cpp" file and add statements in the main function to perform thorough testing. Shape( ); The default constructor shall set the anchor_of the shape to (0,0) and the dimension_of the shape to 10. In addition, the constructor shall set the ID_ for the shape using the current value of nextID and increase nextID by 1 . Shape(unsigned s, unsigned x=0, unsigned y=0 ); The fill constructor shall set the anchor_ of the shape to (x,y) and the dimension_of the shape to the value of the s parameter. In addition, the constructor shall set the ID_for the shape using the current value of nextID and increase nextID by 1 . void setLocation(unsigned x, unsigned y ); This function shall set the anchor_ of the shape to (x,y) without affecting the dimension_of the shape. string to_string( ) const; This function shall return a string including information about the shape's ID, dimension, and anchor coordinates. Below is a sample output for cout s s.to_string (); where s is a Shape object. The shape's ID is 10003. Its anchor is at the coordinates (9,6). Its size is 15. bool inside(const Point\& p) const; This function will be overridden by each derived class to return true if the Point parameter is considered within the boundary of the shape. This is an important tool for any 2D app to detect whether a mouse click or tap falls on an object. Currently, it is implemented to return false. Part II Derived class: Square class Square : public Shape \{ public: Square(); Square(unsigned); //Accessor bool inside(const Point \&) const; Add "Square.h" and "Square.cpp" files to the project to define and implement the above Square class as a derived class of the Shape class. Add statements in the main function to perform thorough testing. Square( ); The default constructor shall simply invoke the default constructor of the Shape class. It is important for you to demonstrate the creation of the Square object using its default constructor and then call the to string function to verify the data members are set properly. Square(unsigned) ; The fill constructor shall call upon the fill constructor of the Shape class to set the anchor (top left corner) of the square to (0,0) and the dimension of the shape to the value of the parameter. bool inside(const Point\&) const; This function shall return true if the Point parameter is considered within the boundary of the square. It shall return false if the Point parameter is outside of the square boundary. For example, given the following Square object s whose anchor is at (30,50) and whose dimension is 70 . - s.inside(Point (20,40)) shall return false since the point is to the top left of the square. - s.inside(Point(60, 140)) shall return false because the point is under the square. - s.inside(Point (50,80) ) and s.inside(Point (80,100) ) would return true. Part III Derived class: Circle Add "Circle.h" and "Circle.cpp" files to the project to define and implement a Circle class as a derived class of the Shape class. Add statements in the main function to perform thorough testing. The fill constructor shall invoke the fill constructor of the Shape class to set the anchor (center) of the circle to (10,10) and the dimension of the circle to the value of the parameter. This function shall return true if the Point parameter is considered within the boundary of the circle. It shall return false if the Point parameter is outside of the circle boundary. Hint: Find the distance between the Point p and the center of the circle. The point is inside the circle if the distance is smaller than the radius
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


