Question: NEEDS TO BE IN PYTHON import math class Point (object): # constructor # x and y are floats def __init__ (self, x = 0, y
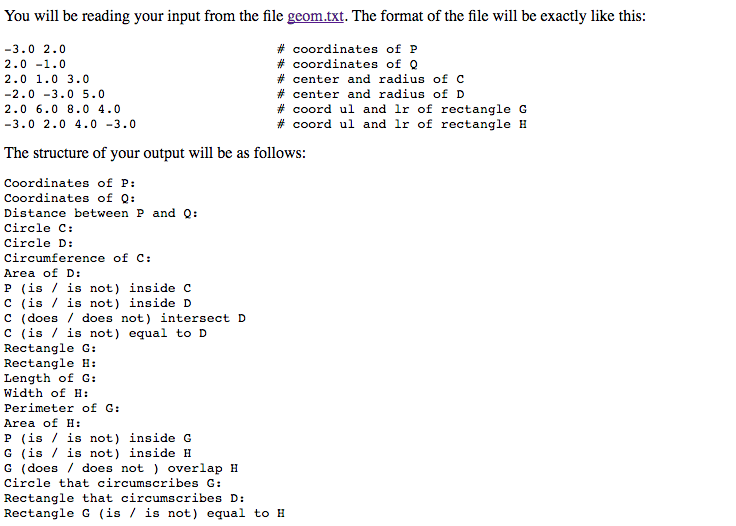
NEEDS TO BE IN PYTHONimport math class Point (object): # constructor # x and y are floats def __init__ (self, x = 0, y = 0): self.x = x self.y = y # get distance # other is a Point object def dist (self, other): return math.hypot (self.x - other.x, self.y - other.y) # get a string representation of a Point object # takes no arguments # returns a string def __str__ (self): return '(' + str(self.x) + ", " + str(self.y) + ")" # test for equality # other is a Point object # returns a Boolean def __eq__ (self, other): tol = 1.0e-16 return ((abs (self.x - other.x) lr_y)): self.ul = Point (ul_x, ul_y) self.lr = Point (lr_x, lr_y) else: self.ul = Point (0, 1) self.lr = Point (1, 0) # determine length of Rectangle (distance along the x axis) # takes no arguments, returns a float def length (self): # determine width of Rectangle (distance along the y axis) # takes no arguments, returns a float def width (self): # determine the perimeter # takes no arguments, returns a float def perimeter (self): # determine the area # takes no arguments, returns a float def area (self): # determine if a point is strictly inside the Rectangle # takes a point object p as an argument, returns a boolean def point_inside (self, p) # determine if another Rectangle is strictly inside this Rectangle # takes a rectangle object r as an argument, returns a boolean # should return False if self and r are equal def rectangle_inside (self, r): # determine if two Rectangles overlap (non-zero area of overlap) # takes a rectangle object r as an argument returns a boolean def does_intersect (self, other): # determine the smallest rectangle that circumscribes a circle # sides of the rectangle are tangents to circle c # takes a circle object c as input and returns a rectangle object def rect_circumscribe (self, c): # give string representation of a rectangle # takes no arguments, returns a string def __str__ (self): # determine if two rectangles have the same length and width # takes a rectangle other as argument and returns a boolean def __eq__ (self, other): def main(): # open the file geom.txt # create Point objects P and Q # print the coordinates of the points P and Q # find the distance between the points P and Q # create two Circle objects C and D # print C and D # compute the circumference of C # compute the area of D # determine if P is strictly inside C # determine if C is strictly inside D # determine if C and D intersect (non zero area of intersection) # determine if C and D are equal (have the same radius) # create two rectangle objects G and H # print the two rectangles G and H # determine the length of G (distance along x axis) # determine the width of H (distance along y axis) # determine the perimeter of G # determine the area of H # determine if point P is strictly inside rectangle G # determine if rectangle G is strictly inside rectangle H # determine if rectangles G and H overlap (non-zero area of overlap) # find the smallest circle that circumscribes rectangle G # goes through the four vertices of the rectangle # find the smallest rectangle that circumscribes circle D # all four sides of the rectangle are tangents to the circle # determine if the two rectangles have the same length and width # close the file geom.txt
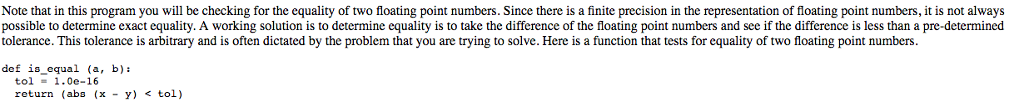
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


