Question: Normal Distribution Functions Norm.dist(x, mean, stdev, c) - calculates the normal distribution for a given value of x, where mean and stdev are the
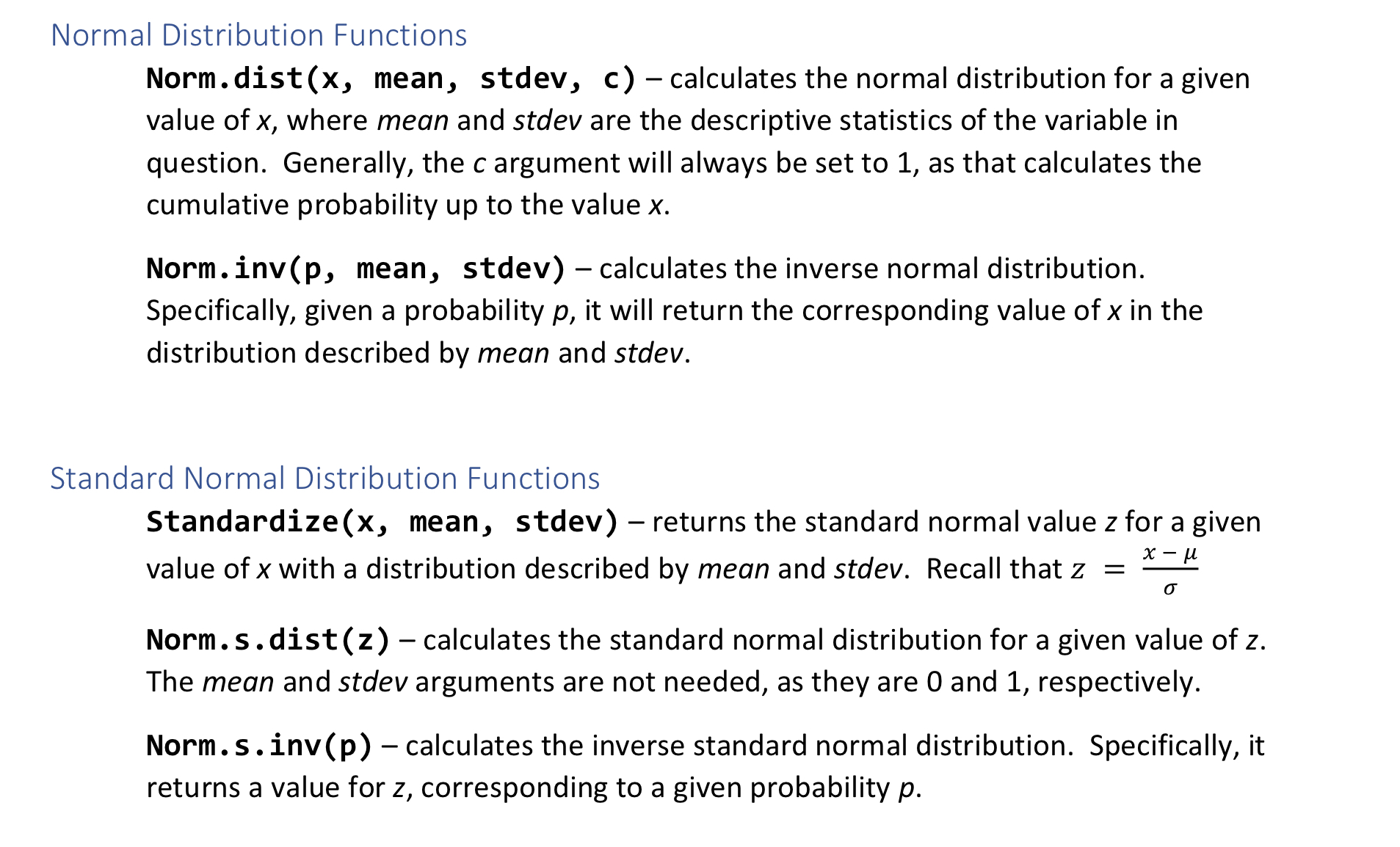

Normal Distribution Functions Norm.dist(x, mean, stdev, c) - calculates the normal distribution for a given value of x, where mean and stdev are the descriptive statistics of the variable in question. Generally, the c argument will always be set to 1, as that calculates the cumulative probability up to the value x. Norm.inv(p, mean, stdev) - calculates the inverse normal distribution. Specifically, given a probability p, it will return the corresponding value of x in the distribution described by mean and stdev. Standard Normal Distribution Functions = x- - Standardize(x, mean, stdev) - returns the standard normal value z for a given value of x with a distribution described by mean and stdev. Recall that z Norm.s.dist(z) - calculates the standard normal distribution for a given value of z. The mean and stdev arguments are not needed, as they are 0 and 1, respectively. Norm.s.inv(p) - calculates the inverse standard normal distribution. Specifically, it returns a value for z, corresponding to a given probability p. 19. WEIGHT WATCHERS DIET Assuming that the diet has no effect so the true mean amount of lost weight is 0 lb, find the probability of getting a sample of 40 subjects with a mean weight loss of 3.0 lb or higher. 0.0000540
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


