Question: Normal No Spacing Heading1 Heading 2 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Cash Budget and Pro Forma Statements D & H Enterprises makes standard sized widgets for
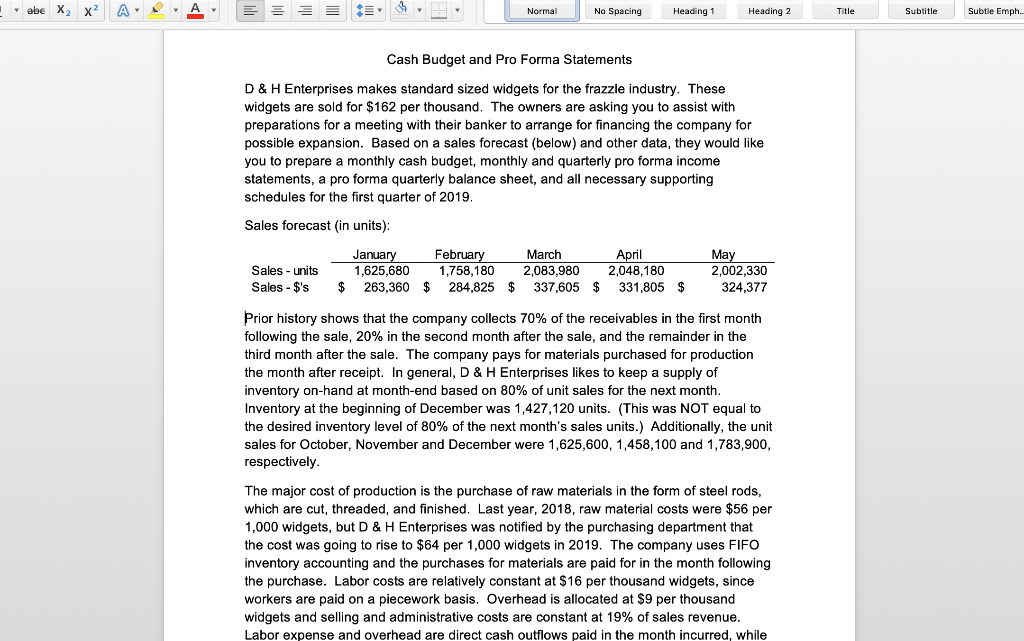
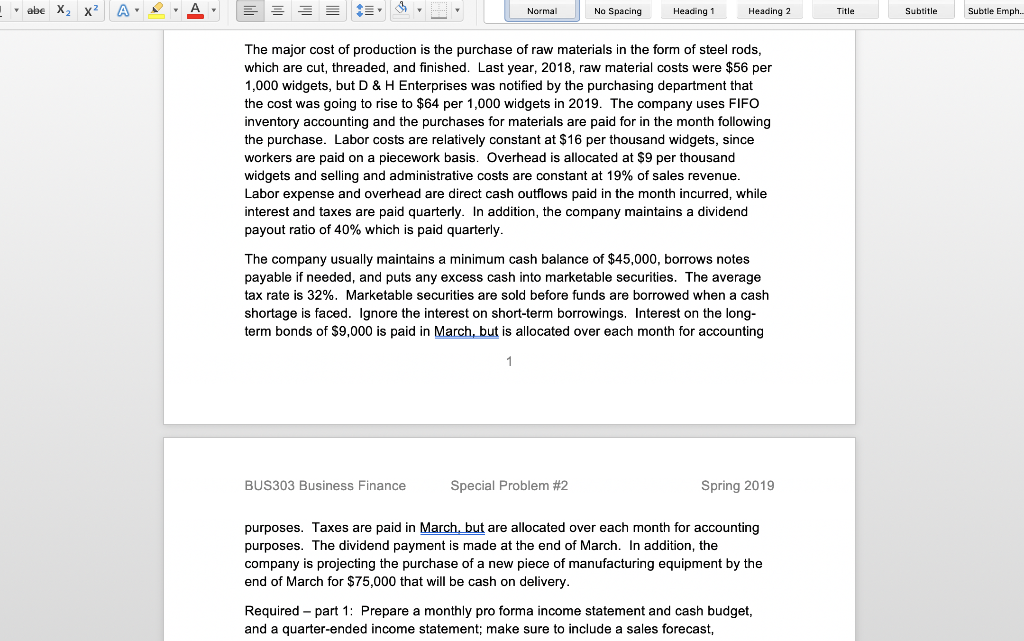
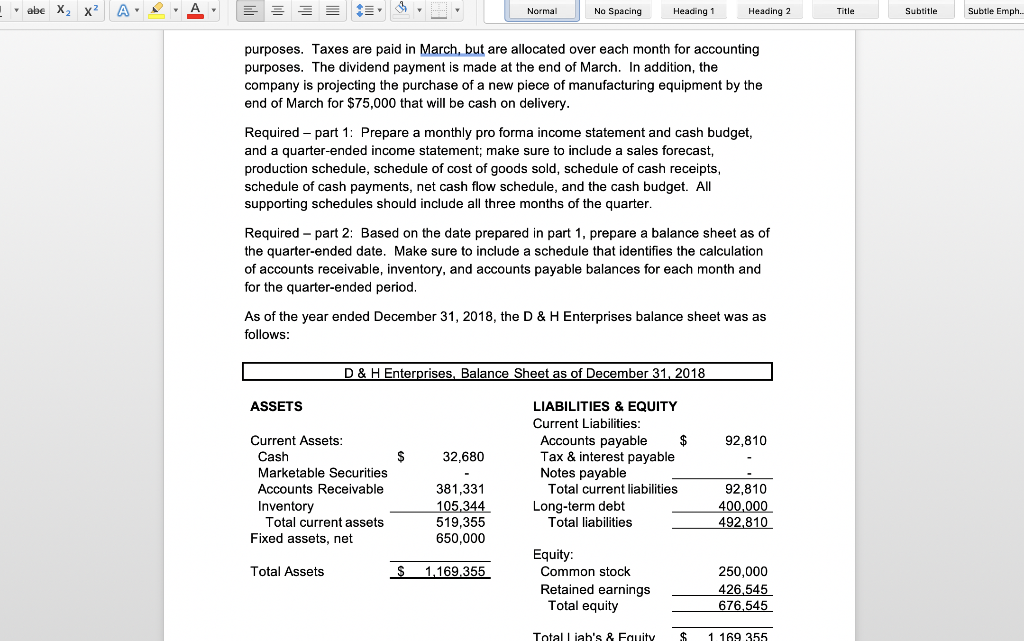
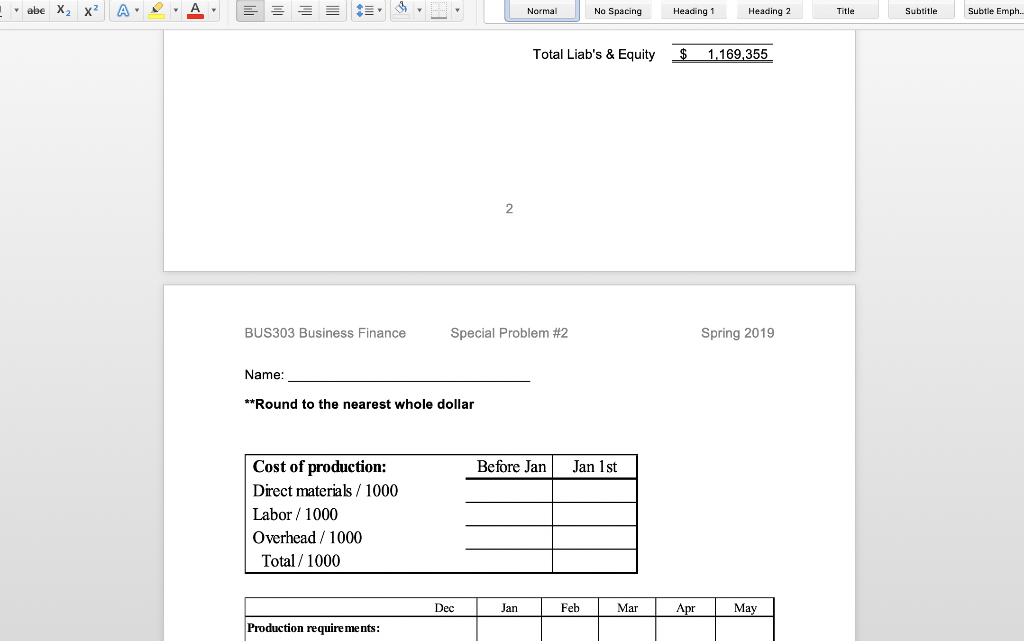
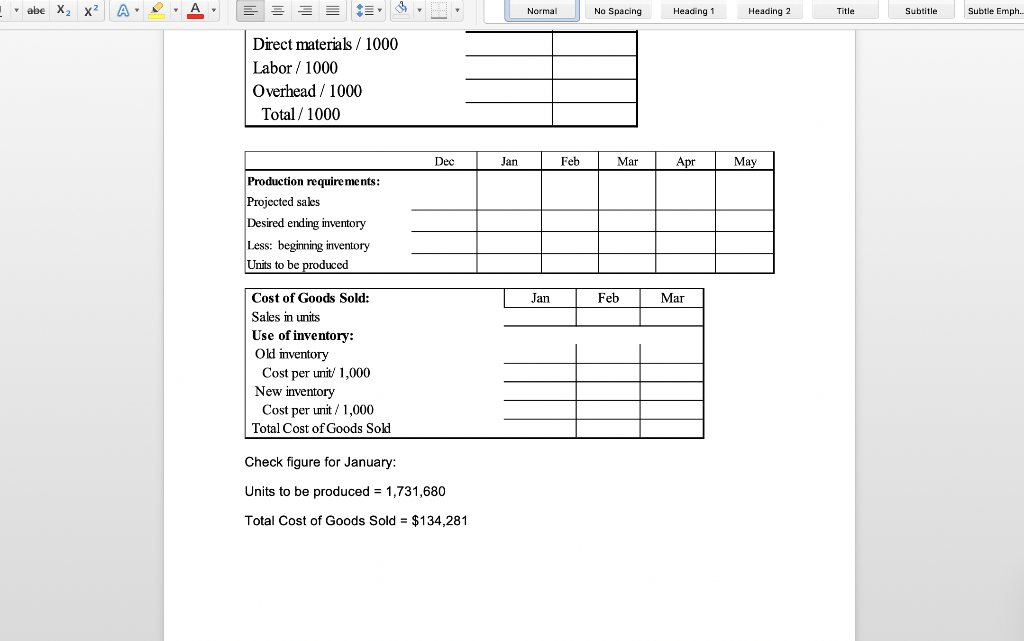
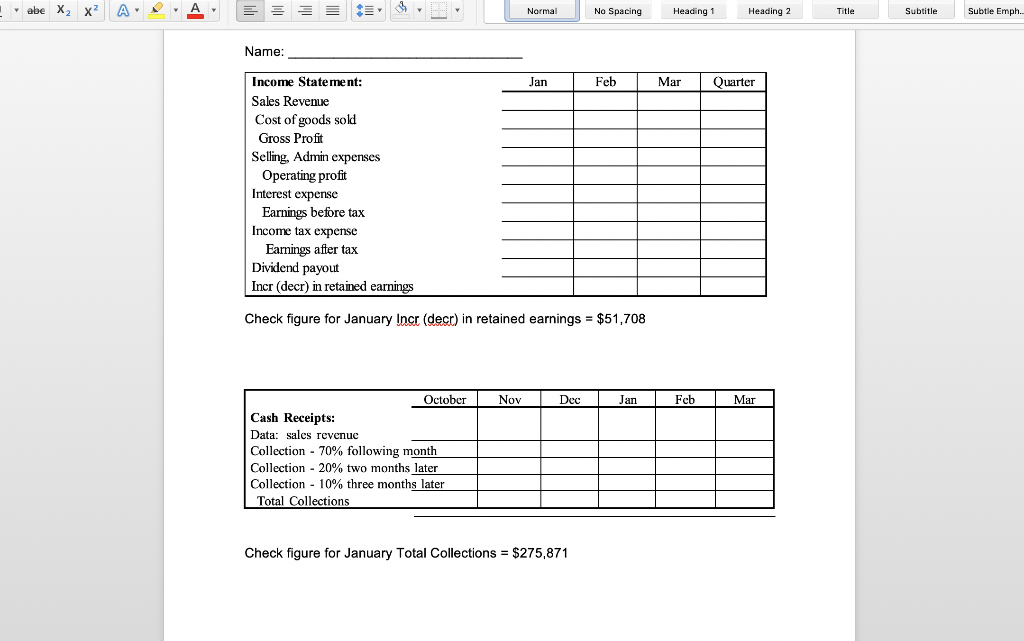
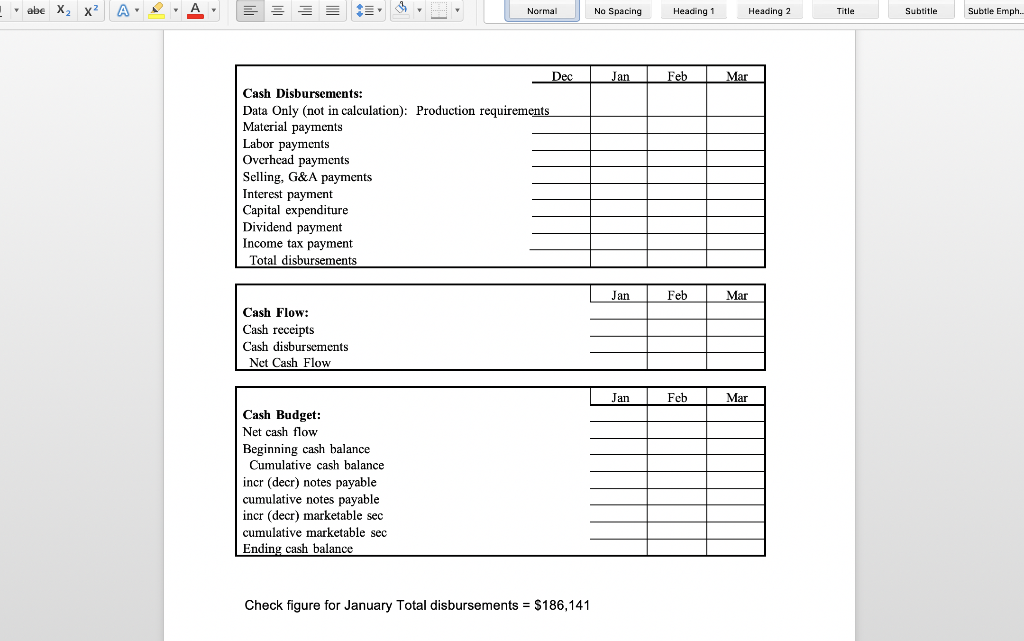
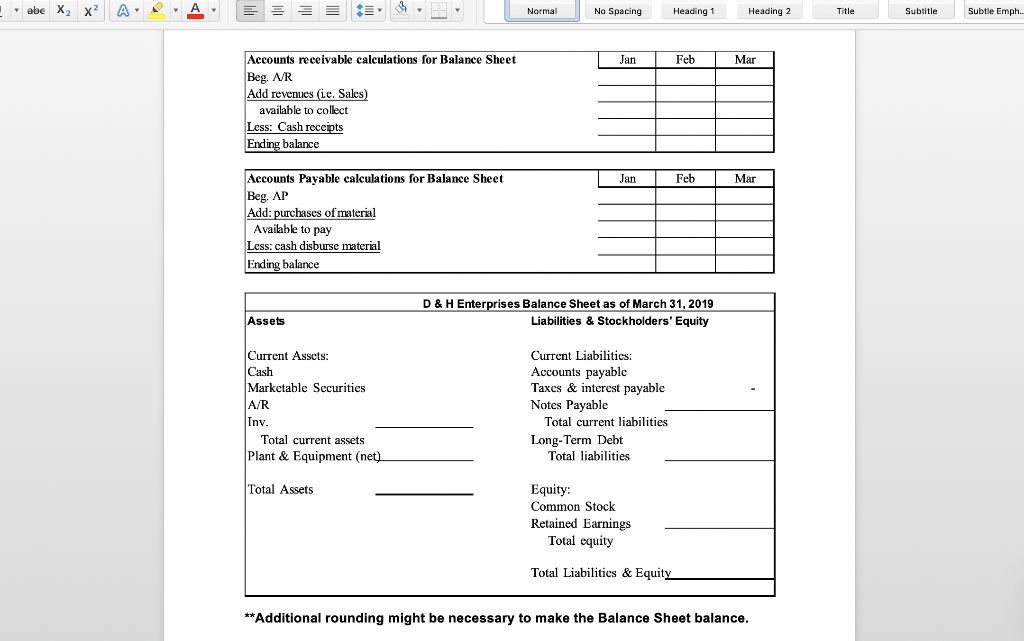
Normal No Spacing Heading1 Heading 2 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Cash Budget and Pro Forma Statements D & H Enterprises makes standard sized widgets for the frazzle industry. These widgets are sold for $162 per thousand. The owners are asking you to assist with preparations for a meeting with their banker to arrange for financing the company for possible expansion. Based on a sales forecast (below) and other data, they would like you to prepare a monthly cash budget, monthly and quarterly pro forma income statements, a pro forma quarterly balance sheet, and all necessary supporting schedules for the first quarter of 2019 Sales forecast (in units) Februa 1,758,180 2,083,980 2,048,180 March Ma 2,002,330 Janua Sales units 1,625,680 Sales $'s 263,360 $ 284,825 $ 337,605 $ 331,805 $ 324,377 Prior history shows that the company collects 70% of the receivables in the first month following the sale, 20% in the second month after the sale, and the remainder in the third month after the sale. The company pays for materials purchased for production the month after receipt. In general, D & H Enterprises likes to keep a supply of inventory on-hand at month-end based on 80% of unit sales for the next month Inventory at the beginning of December was 1,427,120 units. (This was NOT equal to the desired inventory level of 80% of the next month's sales units.) Additionally, the unit sales for October, November and December were 1,625,600, 1,458,100 and 1,783,900 respectively The major cost of production is the purchase of raw materials in the form of steel rods which are cut, threaded, and finished. Last year, 2018, raw material costs were $56 per 1,000 widgets, but D & H Enterprises was notified by the purchasing department that the cost was going to rise to $64 per 1,000 widgets in 2019. The company uses FIFO inventory accounting and the purchases for materials are paid for in the month following the purchase. Labor costs are relatively constant at $16 per thousand widgets, since workers are paid on a piecework basis. Overhead is allocated at $9 per thousand widgets and selling and administrative costs are constant at 19% of sales revenue Labor expense and overhead are direct cash outflows paid in the month incurred, while Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph The major cost of production is the purchase of raw materials in the form of steel rods which are cut, threaded, and finished. Last year, 2018, raw material costs were $56 per 1,000 widgets, but D & H Enterprises was notified by the purchasing department that the cost was going to rise to $64 per 1,000 widgets in 2019. The company uses FIFO inventory accounting and the purchases for materials are paid for in the month following the purchase. Labor costs are relatively constant at $16 per thousand widgets, since workers are paid on a piecework basis. Overhead is allocated at $9 per thousand widgets and selling and administrative costs are constant at 19% of sales revenue Labor expense and overhead are direct cash outflows paid in the month incurred, while interest and taxes are paid quarterly. In addition, the company maintains a dividend payout ratio of 40% which is paid quarterly The company usually maintains a minimum cash balance of $45,000, borrows notes payable if needed, and puts any excess cash into marketable securities. The average tax rate is 32%. Marketable securities are sold before funds are borrowed when a cash shortage is faced. Ignore the interest on short-term borrowings. Interest on the long- term bonds of $9,000 is paid in March, but is allocated over each month for accounting BUS303 Business Finance Special Problem #2 Spring 2019 purposes. Taxes are paid in March, but are allocated over each month for accounting purposes. The dividend payment is made at the end of March. In addition, the company is projecting the purchase of a new piece of manufacturing equipment by the end of March for $75,000 that will be cash on delivery Required - part 1: Prepare a monthly pro forma income statement and cash budget and a quarter-ended income statement; make sure to include a sales forecast, abe Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph purposes. Taxes are paid in March, but are allocated over each month for accounting purposes. The dividend payment is made at the end of March. In addition, the company is projecting the purchase of a new piece of manufacturing equipment by the end of March for $75,000 that will be cash on delivery Required - part 1: Prepare a monthly pro forma income statement and cash budget, and a quarter-ended income statement; make sure to include a sales forecast, production schedule, schedule of cost of goods sold, schedule of cash receipts schedule of cash payments, net cash flow schedule, and the cash budget. All supporting schedules should include all three months of the quarter Required- part 2: Based on the date prepared in part 1, prepare a balance sheet as of the quarter-ended date. Make sure to include a schedule that identifies the calculation of accounts receivable, inventory, and accounts payable balances for each month and for the quarter-ended period As of the year ended December 31, 2018, the D & H Enterprises balance sheet was as follows D & H Enterprises, Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2018 ASSETS LIABILITIES& EQUITY Current Liabilities Current Assets Accounts payable $92,810 Tax & interest payable Notes payable Cash Marketable Securities Accounts Receivable Inventory 32,680 381,331 519,355 Total current liabilities 92,810 Long-term debt Total liabilities492810 Total current assets Fixed assets, net 650,000 Equity Total Assets Common stock 250,000 Retained earnings426,545 545 Total equity Total l iah's & Fquity 1.169 355 abe X2 X Heading 2 Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Total Liab's &Equty 1.169 355 BUS303 Business Finance Special Problem #2 Spring 2019 Name **Round to the nearest whole dolla Cost of production: Direct materials / 1000 Labor / 1000 Overhead /1000 Before JanJan 1st Total/ 1000 Dec an Feb Mar Production requirements abe Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Direct materials irect materials 1000 Labor 1000 Overhead 1000 Total/ 1000 Dec Jan Feb Mar Apr May Production requirements: Projected sakes Desired ending inventory Less: beginning inventory Units to be ed Feb Cost of Goods Sold: Sales in units Use of inventory Old inventory Jan Mar Cost per unit 1,000 New inventory Cost per unit 1,000 Total Cost of Goods Sold Check figure for January Units to be produced- 1,731,680 Total Cost of Goods Sold $134,281 Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Name Feb Income Statement: Sales Revenue Cost of goods sold ar Quarter an Gross Profit Selng, Admin expenses Operating profit Interest expense Earnings before tax Income tax expense Earnings after tax Dividend payout Incr (decr) in retained earnings Check figure for January Incr (decr) in retained earnings $51,708 OV Dec an Fcb Mar Cash Receipts: Data: sales revenuc Collection-70% following month Collection-20% two months later Collection-10% three months later Total Collections Check figure for January Total Collections = $275,871 Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Heading 2 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Cash Disbursements: Data Only (not in calculation): Production requirem Material payments Labor payments Overhcad payments Selling, G&A payments Interest payment Capital expenditure Dividend payment Income tax payment Total disbursements Jan Feb Mar Cash Flow: Cash receipts Cash disbursements Nct Cash Flow an Feb Mar Cash Budget: Net cash flow Beginning cash balance Cumulative cash balance incr (decr) notes payable cumulative notes payable incr (decr) marketable sec cumulative marketable sec Ending cash balance Check figure for January Total disbursements = $186,141 abe X2 X Heading 2 Normal No Spacing Heading 1 Title Subtitle Subtle Emph Accounts receivable calculations for Balance Sheet Jan Feb Mar Beg. AR Add revenues (ie. Sales available to collect Less: Cash rece Ending balance Accounts Payable calculations for Balance Sheet Beg. AP Add:purchases of material Jan Feb Mar Available to pay Less: cash disburse material Ending balance D & H Enterprises Balance Sheet as of March 31, 2019 Assets Liabilities & Stockholders' Equity Current Assets: Cash Marketable Securities A/R Inv Current Liabilities: Accounts payable Taxes & interest payable Notes Payable Total current liabilities Total current assets Long-Term Debt Plant & Equipment (net_ Total liabilities Equity: Common Stock Retained Earnings Total Assets Total equity Total Liabilitics & Equit *Additional rounding might be necessary to make the Balance Sheet balance
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


