Question: Not sure where to continue- please help! For the dissociation reaction of a weak acid in water, HA(aq)+H2O(l)H3O+(aq)+A(aq) Part A the equilibrium constant is the
Not sure where to continue- please help!
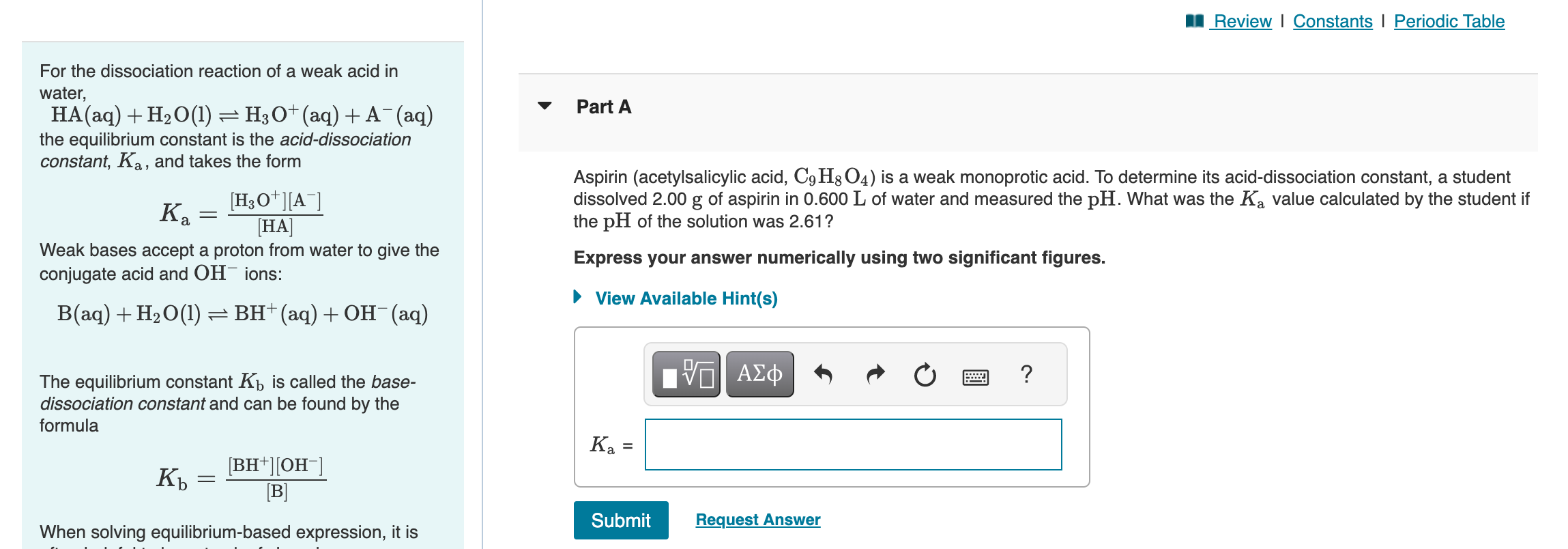
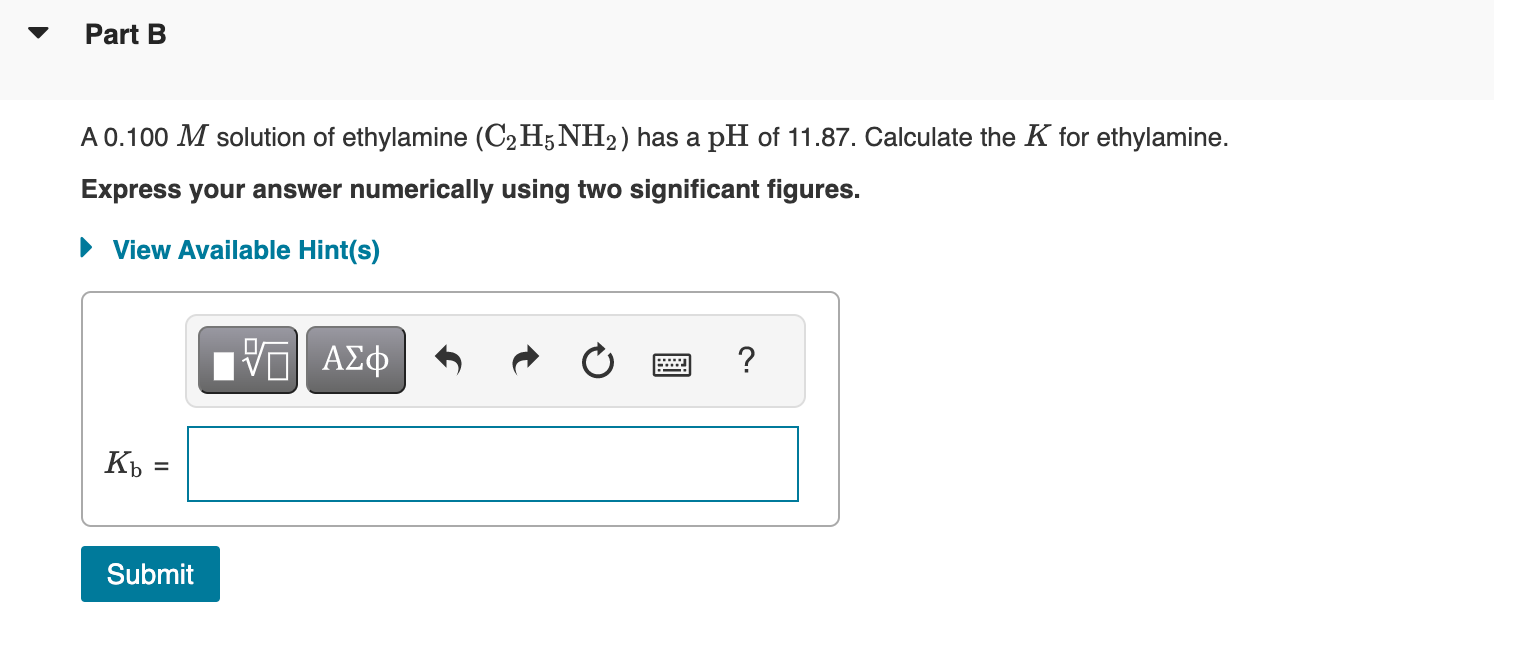
For the dissociation reaction of a weak acid in water, HA(aq)+H2O(l)H3O+(aq)+A(aq) Part A the equilibrium constant is the acid-dissociation constant, Ka, and takes the form Ka=[HA][H3O+][A] Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, C9H8O4 ) is a weak monoprotic acid. To determine its acid-dissociation constant, a student dissolved 2.00g of aspirin in 0.600L of water and measured the pH. What was the Ka value calculated by the student if the pH of the solution was 2.61 ? Weak bases accept a proton from water to give the Express your answer numerically using two significant figures. conjugate acid and OHions: B(aq)+H2O(l)BH+(aq)+OH(aq) The equilibrium constant Kb is called the basedissociation constant and can be found by the formula Kb=[B][BH+][OH] When solving equilibrium-based expression, it is A 0.100M solution of ethylamine (C2H5NH2) has a pH of 11.87. Calculate the K for ethylamine. Express your answer numerically using two significant figures
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


