Question: Note: You can right-click the image then open in a new tab to better see the problem Consider a three-firm supply chain consisting of a

Note: You can right-click the image then open in a new tab to better see the problem
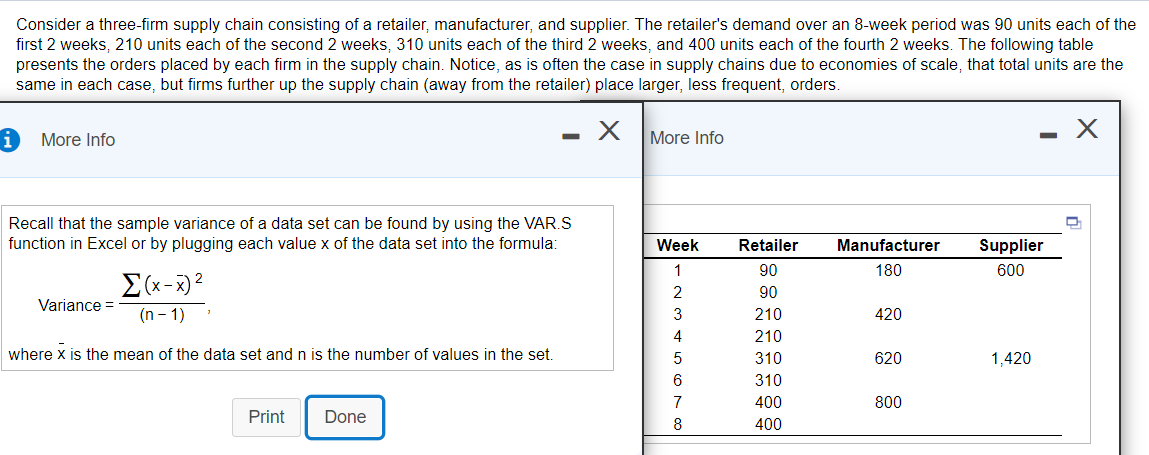
Consider a three-firm supply chain consisting of a retailer, manufacturer, and supplier. The retailer's demand over an 8-week period was 90 units each of the first 2 weeks, 210 units each of the second 2 weeks, 310 units each of the third 2 weeks, and 400 units each of the fourth 2 weeks. The following table presents the orders placed by each firm in the supply chain. Notice, as is often the case in supply chains due to economies of scale, that total units are the same in each case, but firms further up the supply chain (away from the retailer) place larger, less frequent, orders. More Info More Info Recall that the sample variance of a data set can be found by using the VAR.S function in Excel or by plugging each value x of the data set into the formula: Week Manufacturer 180 Supplier 600 (x-x) 2 Variance = (n-1) 420 Retailer 90 90 210 210 310 310 400 400 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 where x is the mean of the data set and n is the number of values in the set. 620 1,420 800 Print Done a) What is the bullwhip measure for the retailer? The bullwhip measure for the retailer is (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.) b) What is the bullwhip measure for the manufacturer? The bullwhip measure for the manufacturer is (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.) c) What is the bullwhip measure for the supplier? The bullwhip measure for the supplier is (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.) d) What conclusions can you draw regarding the impact that economies of scale may have on the bullwhip effect? Select all of the correct statements below. A. The effect of decreasing variance of orders with the less frequent orders could be reduced via channel coordination by determining lot sizes. B. The effect of increasing variance of orders with the less frequent orders could be reduced via channel coordination by determining lot sizes. C. Larger, less frequent orders imply a larger variance of orders. D. Larger, less frequent orders imply a smaller variance of orders
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


