Question: Numerical Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations: Initial Value Problems NOTE: Python is required , not MATLAB . 3. The motions of a swinging pendulum under
Numerical Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations: Initial Value Problems
NOTE:
Python is required, not MATLAB.
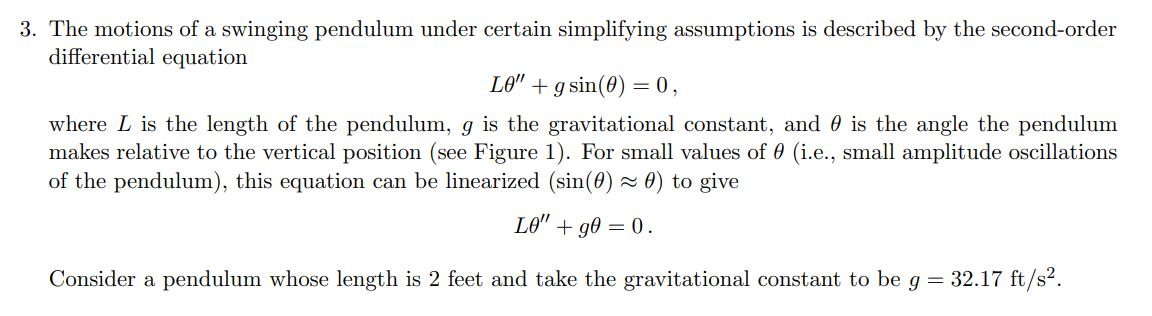
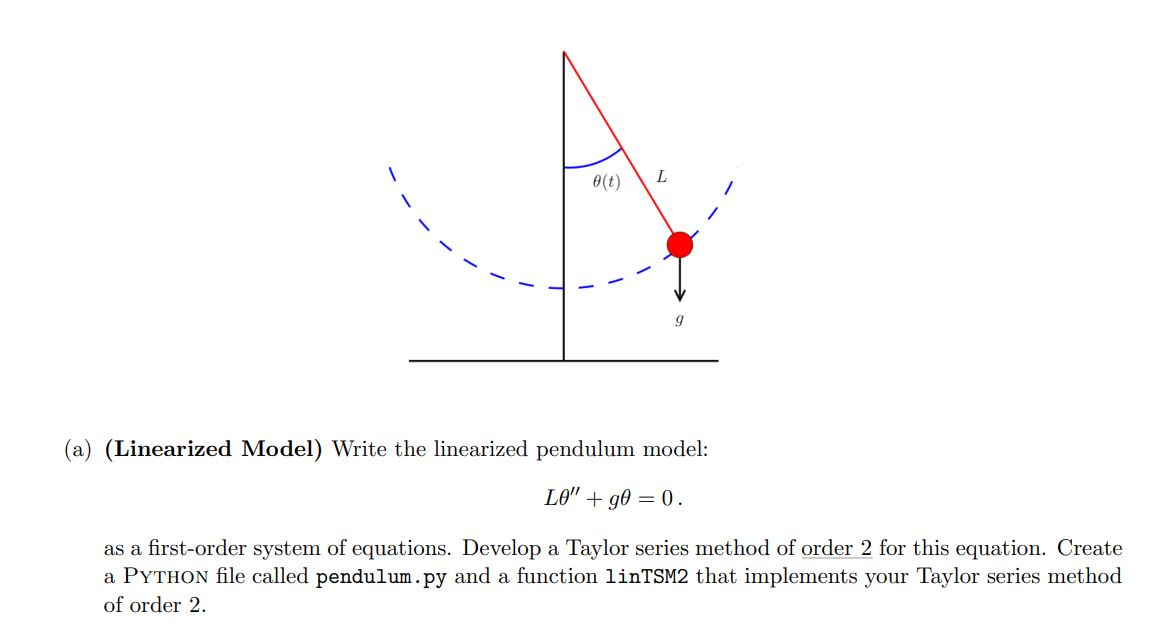
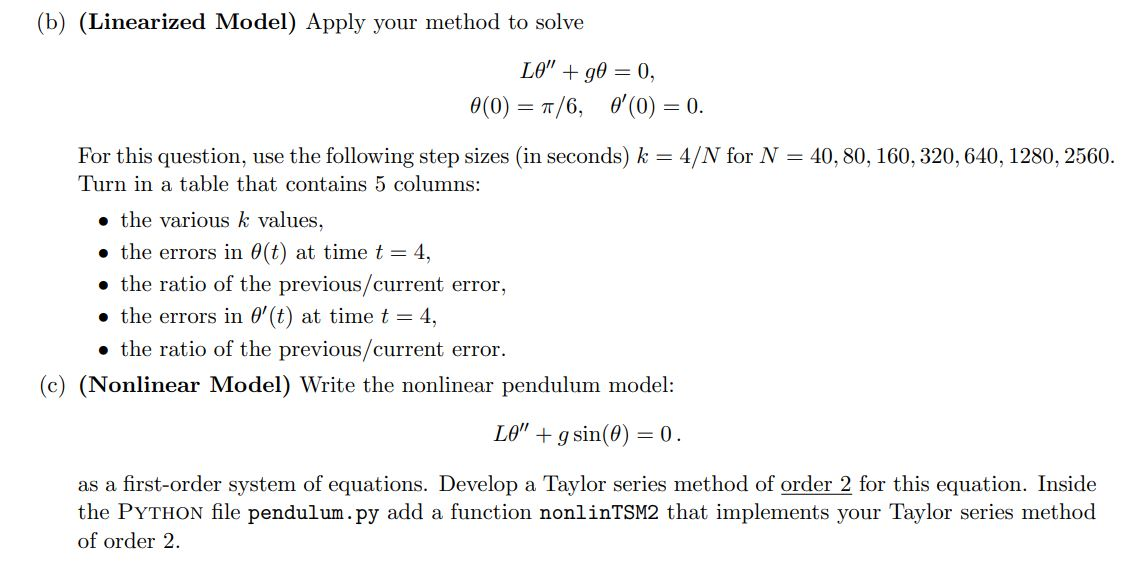
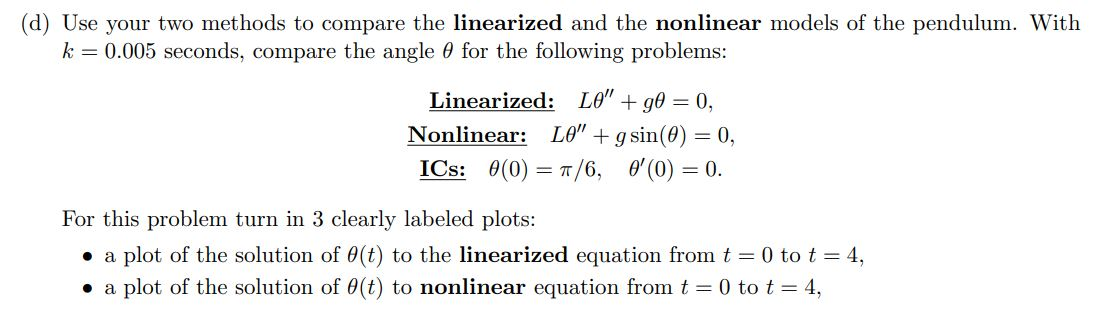

3. The motions of a swinging pendulum under certain simplifying assumptions is described by the second-order differential equation LO" +gsin(O) = 0, where L is the length of the pendulum, g is the gravitational constant, and is the angle the pendulum makes relative to the vertical position (see Figure 1). For small values of 0 (i.e., small amplitude oscillations of the pendulum), this equation can be linearized (sin(0) - 0) to give L" +90 = 0. Consider a pendulum whose length is 2 feet and take the gravitational constant to be g = 32.17 ft/s2. 0(t) L -- - (a) (Linearized Model) Write the linearized pendulum model: LO" + 0 = 0. as a first-order system of equations. Develop a Taylor series method of order 2 for this equation. Create a PYTHON file called pendulum.py and a function linTSM2 that implements your Taylor series method of order 2. (b) (Linearized Model) Apply your method to solve LO" +90 = 0, 0(0) = 1/6, 0'(0) = 0. For this question, use the following step sizes in seconds) k = 4/N for N = 40, 80, 160, 320, 640, 1280, 2560. Turn in a table that contains 5 columns: the various k values, the errors in 0(t) at time t = 4, the ratio of the previous/current error, the errors in 6'(t) at time t = 4, the ratio of the previous/current error. (c) (Nonlinear Model) Write the nonlinear pendulum model: LO" + g sin(0) = 0. as a first-order system of equations. Develop a Taylor series method of order 2 for this equation. Inside the PYTHON file pendulum.py add a function nonlin TSM2 that implements your Taylor series method of order 2. (d) Use your two methods to compare the linearized and the nonlinear models of the pendulum. With k= 0.005 seconds, compare the angle for the following problems: Linearized: LO" +90 = 0, Nonlinear: LO" + g sin(0) = 0, ICs: 0(0) = 7/6, 0'0) = 0. For this problem turn in 3 clearly labeled plots: a plot of the solution of (t) to the linearized equation from t=0 to t= 4, . a plot of the solution of 0(t) to nonlinear equation from t = 0 to t = 4, a plot that contains both solutions of (t) from t = 0 to t = 4. Make sure to include a legend for plot this plot. (e) What do these plots say about the validity of the linearized equation as an approximation to the nonlinear equation? 3. The motions of a swinging pendulum under certain simplifying assumptions is described by the second-order differential equation LO" +gsin(O) = 0, where L is the length of the pendulum, g is the gravitational constant, and is the angle the pendulum makes relative to the vertical position (see Figure 1). For small values of 0 (i.e., small amplitude oscillations of the pendulum), this equation can be linearized (sin(0) - 0) to give L" +90 = 0. Consider a pendulum whose length is 2 feet and take the gravitational constant to be g = 32.17 ft/s2. 0(t) L -- - (a) (Linearized Model) Write the linearized pendulum model: LO" + 0 = 0. as a first-order system of equations. Develop a Taylor series method of order 2 for this equation. Create a PYTHON file called pendulum.py and a function linTSM2 that implements your Taylor series method of order 2. (b) (Linearized Model) Apply your method to solve LO" +90 = 0, 0(0) = 1/6, 0'(0) = 0. For this question, use the following step sizes in seconds) k = 4/N for N = 40, 80, 160, 320, 640, 1280, 2560. Turn in a table that contains 5 columns: the various k values, the errors in 0(t) at time t = 4, the ratio of the previous/current error, the errors in 6'(t) at time t = 4, the ratio of the previous/current error. (c) (Nonlinear Model) Write the nonlinear pendulum model: LO" + g sin(0) = 0. as a first-order system of equations. Develop a Taylor series method of order 2 for this equation. Inside the PYTHON file pendulum.py add a function nonlin TSM2 that implements your Taylor series method of order 2. (d) Use your two methods to compare the linearized and the nonlinear models of the pendulum. With k= 0.005 seconds, compare the angle for the following problems: Linearized: LO" +90 = 0, Nonlinear: LO" + g sin(0) = 0, ICs: 0(0) = 7/6, 0'0) = 0. For this problem turn in 3 clearly labeled plots: a plot of the solution of (t) to the linearized equation from t=0 to t= 4, . a plot of the solution of 0(t) to nonlinear equation from t = 0 to t = 4, a plot that contains both solutions of (t) from t = 0 to t = 4. Make sure to include a legend for plot this plot. (e) What do these plots say about the validity of the linearized equation as an approximation to the nonlinear equation
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


