Question: NUUD Highest: 16 5. Present value To find the present value of a cash flow expected to be paid or received in the future, you
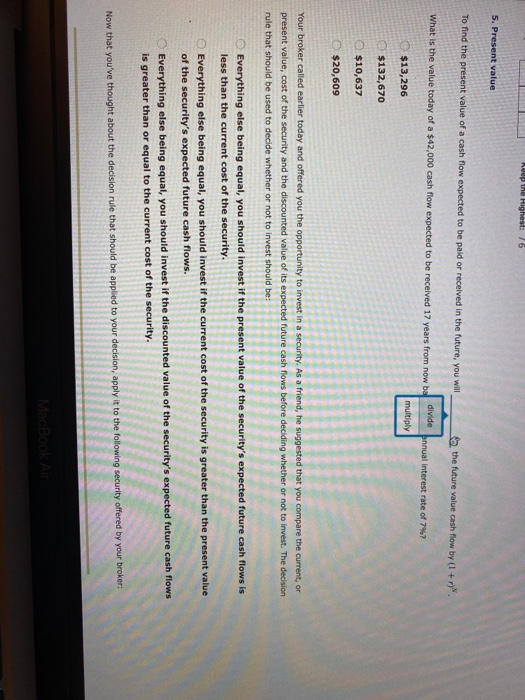
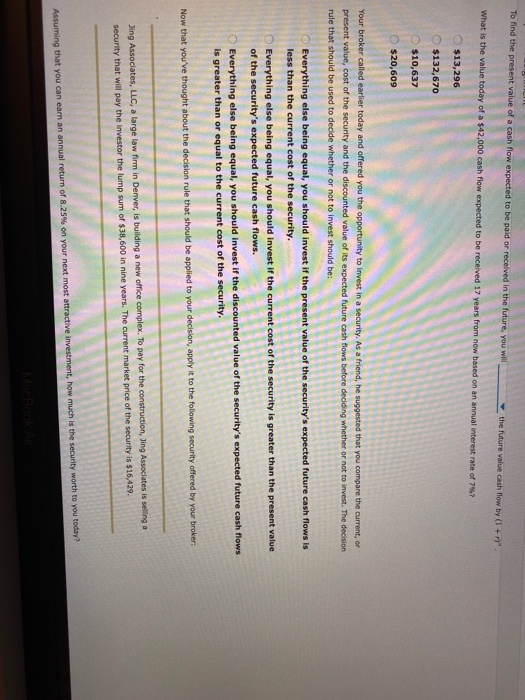
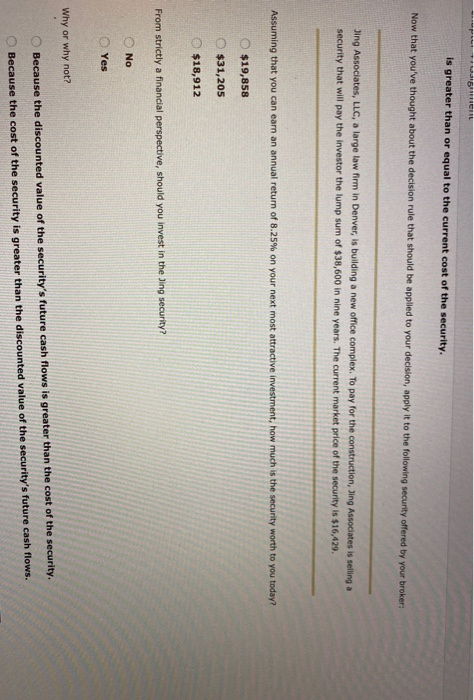
NUUD Highest: 16 5. Present value To find the present value of a cash flow expected to be paid or received in the future, you will Sa the future value cash flow by (1 + r) divide What is the value today of a $42,000 cash flow expected to be received 17 years from now be nnual Interest rate of 7%? multiply $13,296 $132,670 $10,637 $20,609 Your broker called earlier today and offered you the opportunity to invest in a security. As a friend, he suggested that you compare the current, or present value, cost of the security and the discounted value of its expected future cash flows before deciding whether or not to invest. The decision rule that should be used to decide whether or not to invest should be: Everything else being equal, you should invest if the present value of the security's expected future cash flows is less than the current cost of the security. Everything else being equal, you should invest if the current cost of the security is greater than the present value of the security's expected future cash flows. Everything else being equal, you should invest if the discounted value of the security's expected future cash flows is greater than or equal to the current cost of the security. Now that you've thought about the decision rule that should be applied to your decision, apply it to the following security offered by your broker: To find the present value of a cash flow expected to be paid or received in the future, you will the future value cash flow by (I + ry". What is the value today of a $42.000 cash flow expected to be received 17 years from now based on an annual interest rate of 7%? $13,296 $132,670 $10,637 $20,609 Your broker called earlier today and offered you the opportunity to invest in a security. As a friend, he suggested that you compare the current or present value, cost of the security and the discounted value of its expected future cash flows before deciding whether or not to invest. The decision rule that should be used to decide whether or not to invest should be: Everything else being equal, you should invest if the present value of the security's expected future cash flows is less than the current cost of the security. Everything else being equal, you should invest if the current cost of the security is greater than the present value of the security's expected future cash flows. Everything else being equal, you should invest if the discounted value of the security's expected future cash flows is greater than or equal to the current cost of the security. Now that you've thought about the decision rule that should be applied to your decision, apply it to the following security offered by your broker: Jing Associates, LLC, a large law firm in Denver, is building a new office complex. To pay for the construction, Jing Associates is selling a security that will pay the investor the lump sum of $38,600 in nine years. The current market price of the security is $16,429. Assuming that you can earn an annual return of 8.25% on your next most attractive investment, how much is the security worth to you today? CRL is greater than or equal to the current cost of the security. Now that you've thought about the decision rule that should be applied to your decision, apply it to the following security offered by your broker: Jing Associates, LLC, a large law firm in Denver, is building a new office complex. To pay for the construction, Jing Associates is selling a security that will pay the investor the lump sum of $38,600 in nine years. The current market price of the security is $16,429. Assuming that you can earn an annual return of 8.25% on your next most attractive investment, how much is the security worth to you today? $19,858 $31,205 $18,912 From strictly a financial perspective, should you invest in the Jing security? No Yes Why or why not? Because the discounted value of the security's future cash flows is greater than the cost of the security. Because the cost of the security is greater than the discounted value of the security's future cash flows
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


