Question: Obj. 2, 3 PR 6-1B FIFO perpetual inventory The beginning inventory at Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending
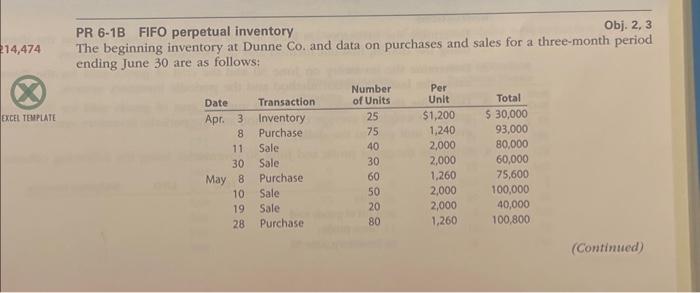

Obj. 2, 3 PR 6-1B FIFO perpetual inventory The beginning inventory at Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending June 30 are as follows: Instructions 1. Record the inventory, parchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory recond similir to the one allustrated in Fxhibit 3 , uning the firstin. firstout mecthod. 2. Determine the total ssles and the total cost of goods sold for the period. Journaliue the ertite in the sales and cost of soods sold accounts. Assume. that all soles were on account. 3. Deternaine the gross profit from sales for the period: 4. Determine the ending inventory cost on fune 30 5. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the endling imentony using the Lust-in, fine. out method to be higher or loner? PA 6-2B LFO perpetual inventory Ob:2,3 The beginning inventory for Dunne C0, and dats on purchases and vales for a three-menth periox are shown in Problem 6:18. Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchaves, and cost of goods sold data in a perperast inveatory reoved similar to the one lliwstrated in Exhibit 4, using the lase in, first-out mechod. 2. Determine the total salo, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profis from sales for the period. 3. Determine the ending inveotory cost on fune 30 PR 6-3B Weighted averago cost method with perpetual inventery Ob| 2,3 are shown in Problem 6-18 Instructions 1. Recond the insentory; purchases, and coit of goods sold data in a perpetual inventocy secoed similar to the one illuwrated in Fxhibit 5 , using the weightand averase cont method. 2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit frum sules for the period. 3. Determine the ending inventory cost on June 30 PR 6-4B Periodic inventory by three methods The beginning immentory for Dunne C0. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Probless 6.18. Instructions 1. Defermine the inventory on June 30 and the cost of goods sold foe the three-month periol. using the firstin, first-cout method and the periodic imvertory synters. 2. Determine the inventory on June 30 and the cont of goods sold for the threemonth pend. using the lass in, firstout method and the periodic inventory systerm. 3. Determine the inveriony on June 30 and the cost of boods wold for the three-month period. asing the weighted average cost method and the periodic inventory sy4tem. Risund the weighed aserage unit const to the dollar: 4. Cotnpare dae gross profit and June 30 inventorios using the following column heating:- Obj. 2, 3 PR 6-1B FIFO perpetual inventory The beginning inventory at Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending June 30 are as follows: Instructions 1. Record the inventory, parchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory recond similir to the one allustrated in Fxhibit 3 , uning the firstin. firstout mecthod. 2. Determine the total ssles and the total cost of goods sold for the period. Journaliue the ertite in the sales and cost of soods sold accounts. Assume. that all soles were on account. 3. Deternaine the gross profit from sales for the period: 4. Determine the ending inventory cost on fune 30 5. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the endling imentony using the Lust-in, fine. out method to be higher or loner? PA 6-2B LFO perpetual inventory Ob:2,3 The beginning inventory for Dunne C0, and dats on purchases and vales for a three-menth periox are shown in Problem 6:18. Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchaves, and cost of goods sold data in a perperast inveatory reoved similar to the one lliwstrated in Exhibit 4, using the lase in, first-out mechod. 2. Determine the total salo, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profis from sales for the period. 3. Determine the ending inveotory cost on fune 30 PR 6-3B Weighted averago cost method with perpetual inventery Ob| 2,3 are shown in Problem 6-18 Instructions 1. Recond the insentory; purchases, and coit of goods sold data in a perpetual inventocy secoed similar to the one illuwrated in Fxhibit 5 , using the weightand averase cont method. 2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit frum sules for the period. 3. Determine the ending inventory cost on June 30 PR 6-4B Periodic inventory by three methods The beginning immentory for Dunne C0. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Probless 6.18. Instructions 1. Defermine the inventory on June 30 and the cost of goods sold foe the three-month periol. using the firstin, first-cout method and the periodic imvertory synters. 2. Determine the inventory on June 30 and the cont of goods sold for the threemonth pend. using the lass in, firstout method and the periodic inventory systerm. 3. Determine the inveriony on June 30 and the cost of boods wold for the three-month period. asing the weighted average cost method and the periodic inventory sy4tem. Risund the weighed aserage unit const to the dollar: 4. Cotnpare dae gross profit and June 30 inventorios using the following column heating
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


