Question: Objectives: 1. Declare and initialize null-terminated string 2. Apply indirect address 3. Write loop 4. Apply Irvine.inc library functions to display a string Problem Description:

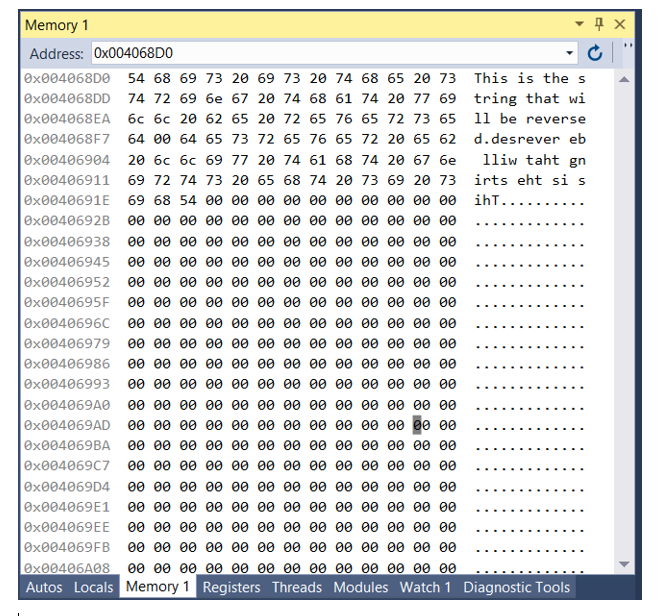
Objectives: 1. Declare and initialize null-terminated string 2. Apply indirect address 3. Write loop 4. Apply Irvine.inc library functions to display a string Problem Description: Write a program with a loop and indirect address that copies a string from source to target. Revising the character order in the process. Use the following variables: source BYTE This is the string that will be reversed", o target BYTE SIZEOF source DUP('#') You may refer to the Programming Exercise #7 on Page 138 of the textbook. Hint: You may study the book example "Copying a String" on page 127 first. However, this project has three different things from the book's example. 1. You need two index register. One for the index of source, another for index of target. You can use Register ESI for index of source and Register EDI for index of target 2. You will not copy the last character in source, which is null character (the terminator of source string). So the initial value of ESI shall be set as OFFSET target - 2 since the target string is stored right after the source string in memory 3. After the loop, you need add null character to the end of the target string How to View Output: After Chapter Five, you will be able to write statement to print out the output on screen. So far, you need to see output in memory. After your project can be assembled and run successfully, you may do following things: 1. Click on the grey bar located on the left of side of the "invoke ExitProcess, 0" statement to set up the Break Point I. 51 | invoke ExitProcess, 2. Go to Debug and click on Start Debugging 3. Go to Debug -> Windows -> Memory -> Memory 1 (or: ALT + 5). You will see a window on the right side of your code. Type 0x004068D0 in Address field and you will see the following window (next page). If you don't see the source string, then your computer may store.data section in difference memory location. You may need to search to find it. If you see the source string but the string after it is not a reverse of source string, then your program has logic errors. 4. After check the result, press F10 to continue and finish the program execution. Memory 1 1 x Address: 0x004068DO x4068 54 68 69 13 20 69 13 20 74 68 65 20 73 This is the s x4068D 74 72 69 6e 67 20 74 68 61 74 20 77 59 tring that wi 0x04068A 6c 6c 20 62 65 20 72 65 76 65 72 73 65 ll be reverse [0x0040687 64 64 65 13 12 65 16 65 12 20 65 62 d. desrever eb x0406904 20 6c 6c 69 17 20 14 61 68 14 20 67 6e lliw taht gn 0x00406911 69 72 14 13 20 65 68 74 20 73 69 20 73 irts eht si s ox040691 69 68 54 0 ih... 0x042692 ox406938 x0406945 ox406952 x40695F ox040696 ox0406979 x406986 0 0 0 x0406993 0x004069 ox04069A 0 0 ox04069 x04069c7 [0x0040694 [0x040691 0x004069 0 0 [x04069F lox426A8 _ Autos Locals Memory 1 Registers Threads Modules Watch 1 Diagnostic Tools Objectives: 1. Declare and initialize null-terminated string 2. Apply indirect address 3. Write loop 4. Apply Irvine.inc library functions to display a string Problem Description: Write a program with a loop and indirect address that copies a string from source to target. Revising the character order in the process. Use the following variables: source BYTE This is the string that will be reversed", o target BYTE SIZEOF source DUP('#') You may refer to the Programming Exercise #7 on Page 138 of the textbook. Hint: You may study the book example "Copying a String" on page 127 first. However, this project has three different things from the book's example. 1. You need two index register. One for the index of source, another for index of target. You can use Register ESI for index of source and Register EDI for index of target 2. You will not copy the last character in source, which is null character (the terminator of source string). So the initial value of ESI shall be set as OFFSET target - 2 since the target string is stored right after the source string in memory 3. After the loop, you need add null character to the end of the target string How to View Output: After Chapter Five, you will be able to write statement to print out the output on screen. So far, you need to see output in memory. After your project can be assembled and run successfully, you may do following things: 1. Click on the grey bar located on the left of side of the "invoke ExitProcess, 0" statement to set up the Break Point I. 51 | invoke ExitProcess, 2. Go to Debug and click on Start Debugging 3. Go to Debug -> Windows -> Memory -> Memory 1 (or: ALT + 5). You will see a window on the right side of your code. Type 0x004068D0 in Address field and you will see the following window (next page). If you don't see the source string, then your computer may store.data section in difference memory location. You may need to search to find it. If you see the source string but the string after it is not a reverse of source string, then your program has logic errors. 4. After check the result, press F10 to continue and finish the program execution. Memory 1 1 x Address: 0x004068DO x4068 54 68 69 13 20 69 13 20 74 68 65 20 73 This is the s x4068D 74 72 69 6e 67 20 74 68 61 74 20 77 59 tring that wi 0x04068A 6c 6c 20 62 65 20 72 65 76 65 72 73 65 ll be reverse [0x0040687 64 64 65 13 12 65 16 65 12 20 65 62 d. desrever eb x0406904 20 6c 6c 69 17 20 14 61 68 14 20 67 6e lliw taht gn 0x00406911 69 72 14 13 20 65 68 74 20 73 69 20 73 irts eht si s ox040691 69 68 54 0 ih... 0x042692 ox406938 x0406945 ox406952 x40695F ox040696 ox0406979 x406986 0 0 0 x0406993 0x004069 ox04069A 0 0 ox04069 x04069c7 [0x0040694 [0x040691 0x004069 0 0 [x04069F lox426A8 _ Autos Locals Memory 1 Registers Threads Modules Watch 1 Diagnostic Tools
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


