Question: OC + E het 7.45 Since many pollutants enter lakes and other water- 0=-U, bodies for that matter) at their peripheries, an important [fc ,
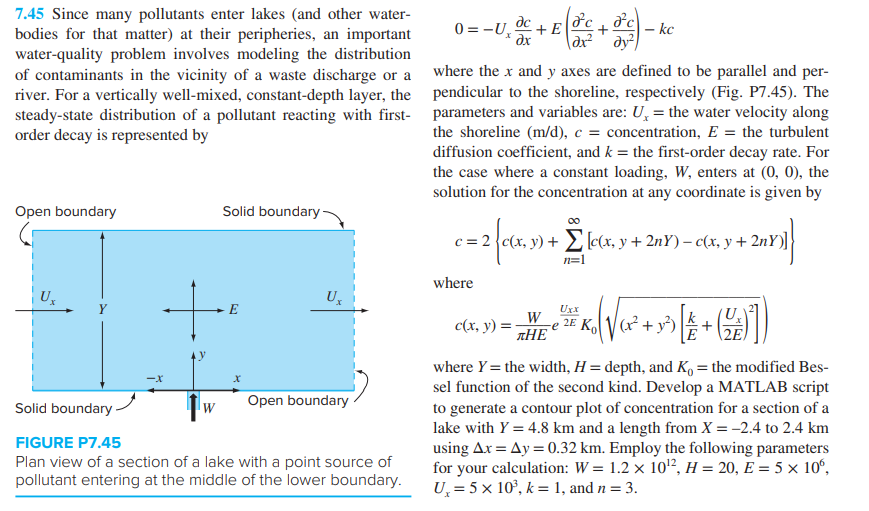
OC + E het 7.45 Since many pollutants enter lakes and other water- 0=-U, bodies for that matter) at their peripheries, an important [fc , c |- kk lax dy water-quality problem involves modeling the distribution of contaminants in the vicinity of a waste discharge or a where the x and y axes are defined to be parallel and per- river. For a vertically well-mixed, constant-depth layer, the pendicular to the shoreline, respectively (Fig. P7.45). The steady-state distribution of a pollutant reacting with first- parameters and variables are: U= the water velocity along order decay is represented by the shoreline (m/d), c = concentration, E = the turbulent diffusion coefficient, and k = the first-order decay rate. For the case where a constant loading, W, enters at (0, 0), the solution for the concentration at any coordinate is given by Open boundary Solid boundary c - 2nY)] n=1 where =2 {ex.v) + Elek, v + 2nY)= ctx. s + Ya [4+ (%) U. U E UxX -X x Solid boundary W Open boundary W 2EK, V(x + y2) c(x, y) = k THE where Y= the width, H = depth, and K = the modified Bes- sel function of the second kind. Develop a MATLAB script to generate a contour plot of concentration for a section of a lake with Y = 4.8 km and a length from X = -2.4 to 2.4 km using Ax= Ay = 0.32 km. Employ the following parameters for your calculation: W= 1.2 x 102, H = 20, E = 5 x 10, Uz = 5 x 10, k= 1, and n= 3. FIGURE P7.45 Plan view of a section of a lake with a point source of pollutant entering at the middle of the lower boundary
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


