Question: Old MathJax webview . . 2 3 ne : Reimbursement department: Reimbursement date: 4 lame Bran Brand Specification model Unit Quantity Unit Price Amount Supply
Old MathJax webview
.
.
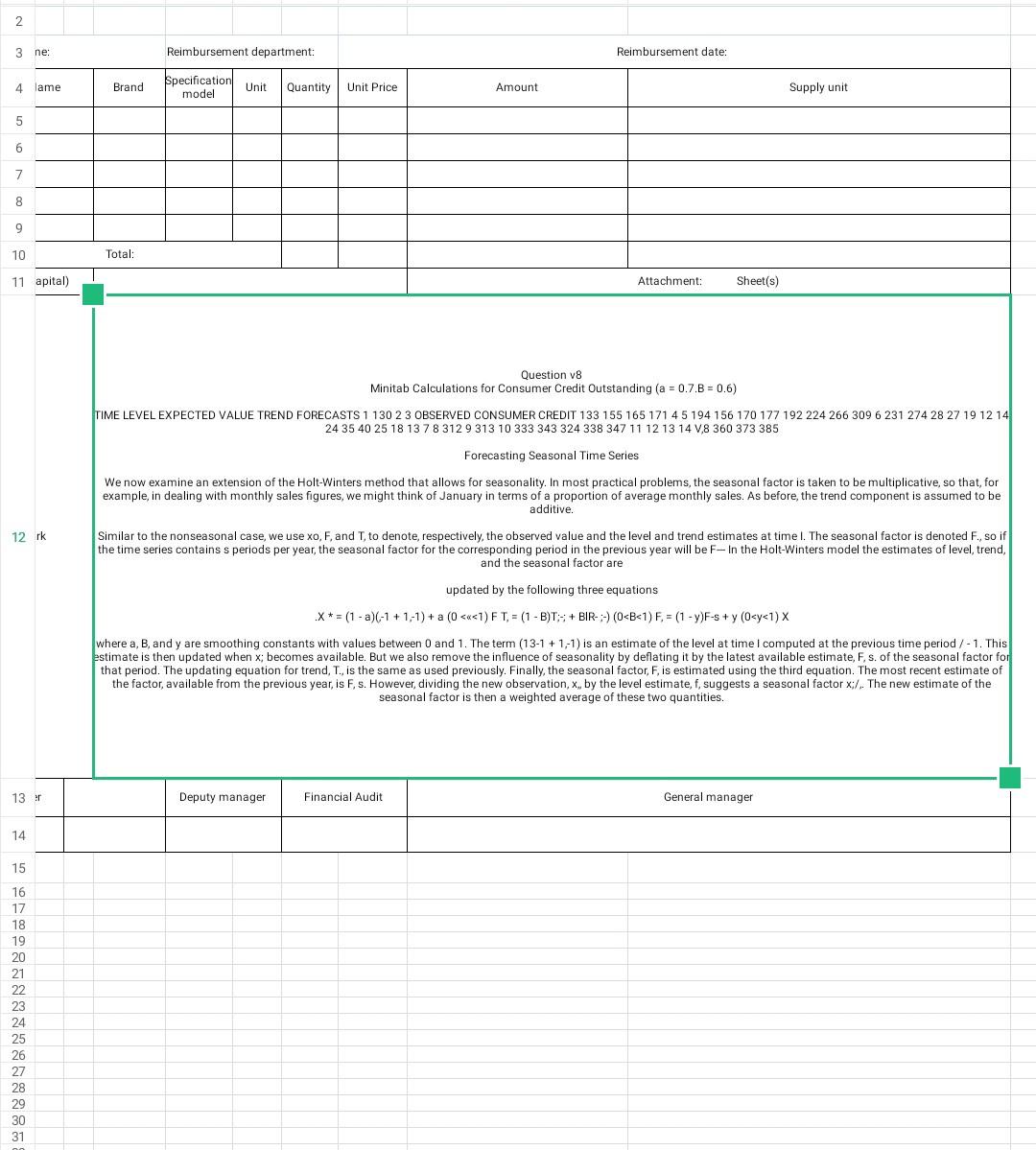
2 3 ne : Reimbursement department: Reimbursement date: 4 lame Bran Brand Specification model Unit Quantity Unit Price Amount Supply unit 5 6 7 8 9 10 Total: 11 apital) Attachment: Sheet(s) Question v8 Minitab Calculations for Consumer Credit Outstanding (a = 0.7.B = 0.6) TIME LEVEL EXPECTED VALUE TREND FORECASTS 1 130 2 3 OBSERVED CONSUMER CREDIT 133 155 165 171 45 194 156 170 177 192 224 266 309 6 231 274 28 27 19 12 14 24 35 40 25 18 13 7 8 312 9 313 10 333 343 324 338 347 11 12 13 14 V,8 360 373 385 Forecasting Seasonal Time Series We now examine an extension of the Holt-Winters method that allows for seasonality. In most practical problems, the seasonal factor is taken to be multiplicative, so that, for example, in dealing with monthly sales figures, we might think of January in terms of a proportion of average monthly sales. As before, the trend component is assumed to be additive. 12 rk Similar to the nonseasonal case, we use xo, F, and T, to denote, respectively, the observed value and the level and trend estimates at time I. The seasonal factor is denoted F., so if the time series contains s periods per year, the seasonal factor for the corresponding period in the previous year will be F- In the Holt-Winters model the estimates of level, trend, and the seasonal factor are updated by the following three equations X* = (1-a)(-1 +1:1)+ a (0Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


