Question: One theme from the the first two weeks is that there are some important similarities between managerial and financial accounting. While managerial and financial accounting
One theme from the the first two weeks is that there are some important similarities between managerial and financial accounting. While managerial and financial accounting are designed to provide information to different types of users, the tools that are used are often the same. This is because, ultimately, external users would like to know as much about an organization as possible to better inform their decisions. So, some of the information that managers use to run the organization is passed on to external users for decision making purposes.
This raises an interesting point: Why do we bother with preparing different types of accounting information for internal and external users? External and internal users have different motives, so they require different types of information. However, assuming that external users of information are competent, it seems reasonable that they could make more informed decisions if given free access to an organization's internal accounting information (as opposed to the summary data contained in external financial reports). Thus, there must be some reason why companies choose to keep their accounting details hidden from the public.
We will only really scratch the surface of the principal-agent problem, but I do want to touch on a few issues. First, what is one reason that company managers (i.e. "agents") would want to avoid disclosing private accounting information of the company? Second, as an owner (i.e. "principal"), would you be concerned that there might be important information about the company that the managers are not disclosing in the financial statements. Finally, what might be a way that owners can ensure that managers are faithfully representing the financial position of the company without forcing them to disclose private company information?
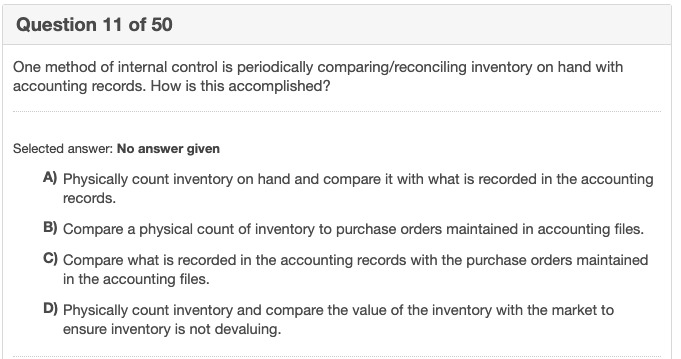
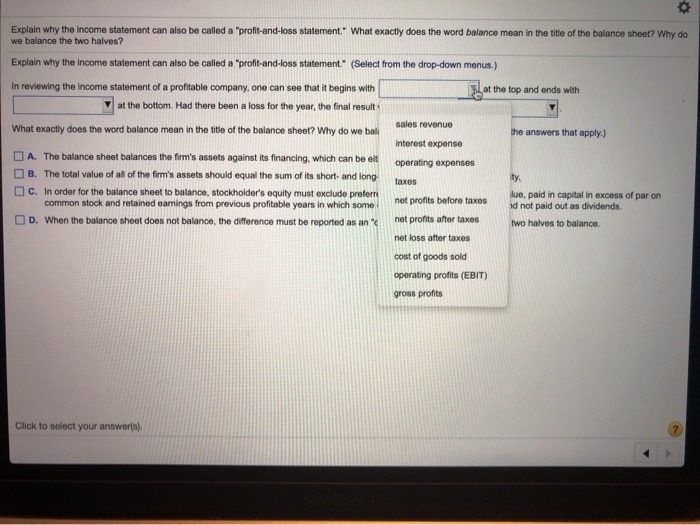
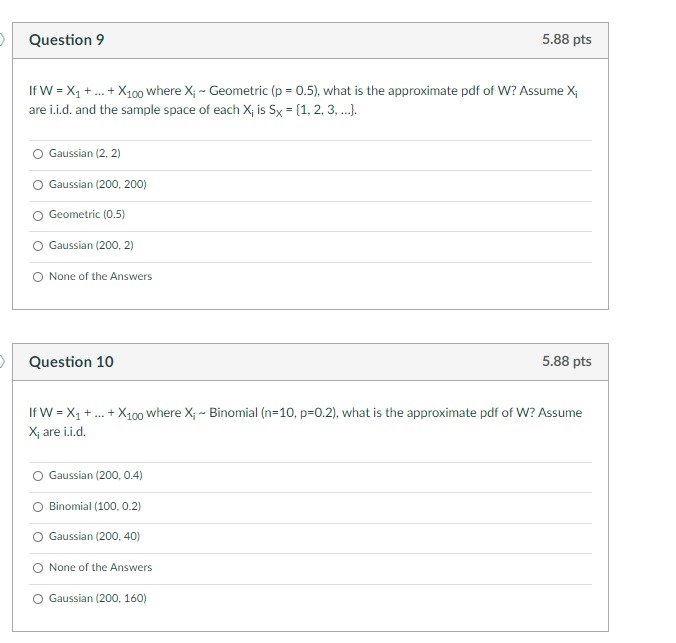
Question 11 of 50 One method of internal control is periodically comparing/reconciling inventory on hand with accounting records. How is this accomplished? Selected answer: No answer given A) Physically count inventory on hand and compare it with what is recorded in the accounting records. B) Compare a physical count of inventory to purchase orders maintained in accounting files. C) Compare what is recorded in the accounting records with the purchase orders maintained in the accounting files. D) Physically count inventory and compare the value of the inventory with the market to ensure inventory is not devaluing.Explain why the income statement can also be called a "profit-and-loss statement. " What exactly does the word balance mean in the title of the balance sheet? Why do we balance the two halves? Explain why the income statement can also be called a "profit-and-loss statement." (Select from the drop-down menus.) In reviewing the income statement of a profitable company. one can see that it begins with That the top and ends with at the bottom. Had there been a loss for the year, the final result : sales revenue What exactly does the word balance mean in the title of the balance sheet? Why do we ball the answers that apply.) interest expense A. The balance sheet balances the firm's assets against its financing, which can be elt operating expenses ()B. The total value of all of the firm's assets should equal the sum of its short- and long- ity. C. In order for the balance sheet to balance, stockholder's equity must exclude prefer lue, paid in capital in excess of par on common stock and retained earnings from previous profitable years in which some not profits before taxes id not paid out as dividends. D. When the balance sheet does not balance, the difference must be reported as an 'c net profits after taxes two halves to balance. net loss after taxes cost of goods sold operating profits (EBIT) gross profits Click to select your answerto).Question 9 5.88 pts If W = X1 + ... + X10o where X; - Geometric (p = 0.5), what is the approximate pdf of W? Assume X; are i.i.d. and the sample space of each X; is 5x = [1, 2, 3, ...]. O Gaussian (2, 2) O Gaussian (200, 200) O Geometric (0.5) O Gaussian (200, 2) O None of the Answers Question 10 5.88 pts If W = X1 + ... + X100 where X; ~ Binomial (n=10, p=0.2), what is the approximate pdf of W? Assume X; are i.i.d. O Gaussian (200, 0.4) O Binomial (100. 0.2) O Gaussian (200, 40) O None of the Answers O Gaussian (200, 160)