Question: *ONLY NEED HELP WITH PHASE II, QUESTIONS G-I.* Here are the answers I have so far: Start-up costs: 1) The Boulevard Mall charges you $2,500
*ONLY NEED HELP WITH PHASE II, QUESTIONS G-I.*





Here are the answers I have so far:
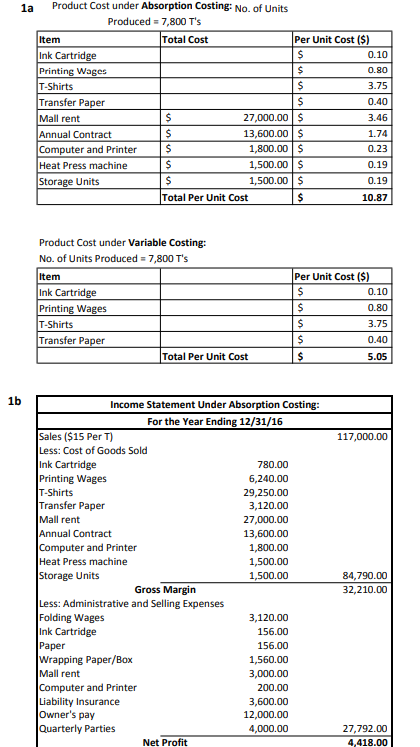
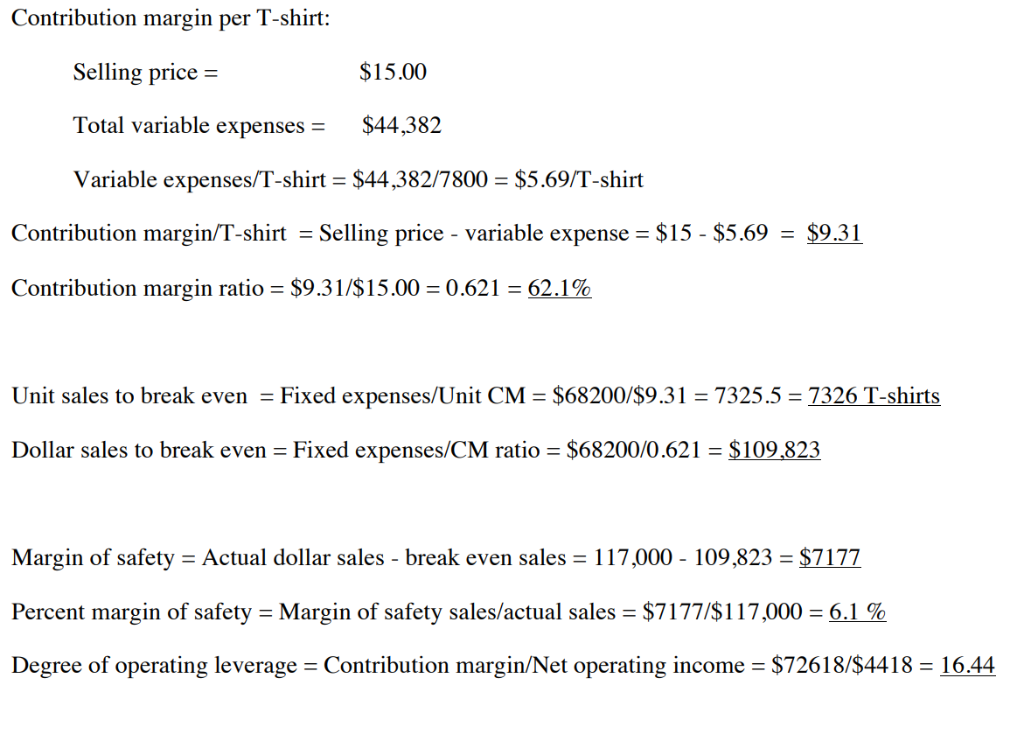
Start-up costs: 1) The Boulevard Mall charges you $2,500 rent per month, which includes utilities, telephone, cleaning, and maintenance. You estimated that 90% of the rent was related to factory operations and 10% was related to selling and administrative activities. 2) You order white, cotton t-shirts from a T-shirt wholesaler. Each T-shirt costs (including taxes, shipping, and handling) $3.75 to purchase. To store T-shirts that were bought, but not yet imprinted, you rent a storage unit. The storage unit costs you $125 per month. 3) 4) You agree to pay your artist friend a $10,000 annual contract fee plus a $300 design fee for each of the 12 T-shirt pictures designed. This same term is renewable for the next 3 years. Each T-shirt picture will only be used for one year. Therefore, in the second year, 12 new pictures will be designed at $300 each and another $10,000 annual contract fee will be charged You buy several items before that start of your business: 5) a] A computer and a printer: You pay $6,000 (including taxes, shipping and handling) to buy a computer and a printer. You expect both to last about 3 years without salvage value. You will use the straight-line method for depreciation. You estimate that about 90% of the computer and printer will be used for factory operations and 10% will be for selling and administrative activities. [b] A heat press machine: You pay $4,500 (including taxes, shipping and handling) for a heat press machine. The machine is used for imprinting t-shirts only and is expected to last 3 years without salvage value. [C] Transfer paper: Each case of transfer paper costs $400 and contains 1,000 sheets of 8.5011 transfer paper. You expect to use one transfer paper to print one T-shirt. [d] Ink-jet carges: On average, each cartridge costs $50 and can make 500 prints. Each T- shirt requires one print. You also need to print flyers, etc. for selling and administrative purposes. For this non-manufacturing printing, you will print about one page for every 5 T- shirts sold. el Laser paper: You will buy several reams of laser paper to print promotion fiyers, etc. Each ream costs $20 and contains 200 sheets of 8.5011 laser paper. Wrapping paper and box: Each T-shirt costs about $0.20 to wrap and box. Wrapping and boxing are not considered manufacturing. 6) 7) You hire three fellow students as part-time workers. They not only help you operate the machine, but also help fold, wrap and box T-shirts. Sometimes, three of them work at the same time. But, sometimes they don't because of their different class schedules. On average, printing 10 shirts will take one labor hour. Folding and packaging 20 shirts also will take about one labor hour. You pay each of your workers $8 per hour (I really need to adjust this for recent inflation!). Folding and wrapping are not considered manufacturing. 8) You (the owner) do all the selling and administrative work by yourself. You pay yourself a total of $12,000 per year. To protect your business from legal obligation, you purchase liability insurance that will cost $3,600 per year. 9) 10) You hold four end-of-quarter parties to promote sales of your t-shirts. Each party costs you about $1,000 Phase One Requirements: (1) Give your company an attractive name. (1) Give your company an attractive name. (2) What and how much of your costs are variable costs? List your manufacturing and non-manufacturing variable cost items and present each of them in cost per T-shirt basis. (3) What and how much of your costs are fixed costs? List your manufacturing and non- manufacturing fixed cost items and present each of them in total cost per year. 4) Write out your yearly cost formula in Ya bX format. Be sure to include both manufacturing costs and non-manufacturing costs in the cost formula. (5) Assume that you make and sell 7,800 t-shirts in the first year. Use your cost formula to calculate your first year's total cost. If you sell these t-shirts at $15 each, how much would net profit be in the first year? Year ending 12/31/2019. To Prepare Your Report: Submit all answers into the appropriate drop box within Blackboard by the assigned due date. Proper formatting of all formal financial statements is one element of grading. One example of an exemplary submission has been included for your review (the data and all calculations have been removed so that only a shell remains, but the formatting is in contact) Phase Two: 1. Now you have developed your cost estimates, let's do some evaluations on this proposed business a. Continue to assume that 7,800 t-shirts will be made and sold in the first year. What is your product cost per unit under absorption costing? What is your product cost per unit under variable costing? b. Based on the estimated sales level of 7,800 t-shirts for the first year, prepare your company's (forecasted) income statement for the year ended on 12/31/2019 using both (1) the traditional format based on the absorption costing and (2) the contribution format based on the variable costing. c. Calculate contribution margin per T-shirt and contribution margin ratio. d. Calculate how many T-shirts you need to sell in order to break-even. Calculate how much sales in dollars you need to make in order to break-even. (Use break-even formulas.) e. Calculate how many T-shirts you need to sell in order to make $10,000 target profit for the year f Continue to assume that 7,800 T-shirts will be made and sold during the first year. Calculate your (1) margin of safety and (2) degree of operating leverage (DOL) for your business. What do these figures tell you about how risky your business is? g. lf sales could increase by 1,560 shirts (i.e. a 20% increase), by how much in dollars would net operating income increase? By what percentage would net operating income increase? Prepare a contribution format income statement assuming a sales increase by 20% to 9,360 shirts. Compare your new net operating income with your answer in Question "b" and prove mathematically that your answers to the two questions in Question "g" are correct. Ignore Questions "g" and "h". If the cost per plain t-shirt is expected to increase by 20% and sales (in number of T-shirts) are expected to be 5% less, how much is your projected net operating income (or loss)? i Phase Three: 1. Calculate the total amount of cash you will need to have before the launching day of your business, in order to buy all necessary equipment and machines, to purchase all materials and supplies needed for the first three months' operations, and to pay your employees' first three months salaries. Assume that your parents have agreed to loan you this amount, interest free The following is information regarding the cash payment needs for your variable costs and fixed costs a. Variable Costs and Expenses For every variable cost item, you decide to buy sufficient quantity for making the first 2,000 T-shirts. You also want to prepare sufficient amount of cash to pay for the labor costs needed for making, folding, and wrapping the first 2,000 T-shirts. Assume that you can pay your workers for a fraction of an hour. However, you cannot purchase a fraction of an ink-jet cartridge or a partial case or ream of paper b. Fixed Costs and Expenses: In addition to covering variable costs for the first 2,000 T-shirts, your initial amount of cash should be sufficient to pay for the first quarter's cash needs for your fixed costs Prepare a cash budget for your company's first year of operations. (NOT the first three months or the first 2,000 T-shirts!. Continue to assume that the selling price is $15 and that 7,800 t shirts will be made and sold in the first vear. Assume all sales are cash sales and that all costs and expenses are paid in cash. Prepare cash budget for the entire year, do not separate the budget into four quarters. Your initial cash balance is the amount you reported in Item 1 above You decide to keep a cash balance of $20,000 at December 31, 2019 and use the extra cash, if there is any, to pay back part of the loan you borrowed from your parents 2. 3. Calculate the first year's estimated "Simple Rate of Return" (i.e. accounting rate of return) of your business. Use the net income under the absorption costing. For simplicity, use the amount of money you originally borrowed from your parents as the amount of "initial investment" for this calculation Product Cost under Absorption Costing: No. of Units 1a Produced = 7,800 T's Per Unit Cost (S) Item Ink Cartridge Printing Wages T-Shirts Transfer Paper Mall rent Annual Contract Computer and Printer Heat Press machine Storage Units Total Cost 0.10 0.80 3.75 0.40 3.46 1.74 0.23 0.19 0.19 10.87 27,000.00 $ 13,600.00 $ 1,800.00S 1,500.00 $ 1,500.00 $ Total Per Unit Cost Product Cost under Variable Costing: No. of Units Produced 7,800 T's Item Ink Cartridge Printing Wages T-Shirts Transfer Paper Per Unit Cost (S) 0.10 0.80 3.75 0.40 5.05 Total Per Unit Cost 1b Income Statement Under Absorption Costing For the Year Ending 12/31/16 Sales ($15 Per T) Less: Cost of Goods Sold Ink Cartridge Printing Wages T-Shirts Transfer Paper Mall rent Annual Contract Computer and Printer Heat Press machine Storage Units 117,000.00 780.00 6,240.00 29,250.00 3,120.00 27,000.00 13,600.00 1,800.00 1,500.00 1,500.00 84,790.00 32,210.00 Gross Margin Less: Administrative and Selling Expenses Folding Wages Ink Cartridge Paper Wrapping Paper/Box Mall rent Computer and Printer Liability Insurance Owner's pay Quarterly Parties 3,120.00 156.00 156.00 1,560.00 3,000.00 200.00 3,600.00 12,000.00 4,000.00 27,792.00 4,418.00 Net Profit Contribution margin per T-shirt: $15.00 Selling price Total variable expenses$44,382 Variable expenses/T-shirt $44,382/7800 $5.69/T-shirt Contribution margin/T-shirt Selling price variable expense $15-$5.69 $9.31 Contribution margin ratio-$9.31/$15.00-0.621-62.1% Unit sales to break even Fixed expenses/Unit CM $68200/s9.31 7325.5 7326 T-shirts Dollar sales to break even Fixed expenses/CM ratio $68200/0.621 S109,823 Margin of safety Actual dollar sales break even sales 117,000 - 109,823 $7177 Percent margin of safety-Margin of safety sales/actual sales-$7177/$17,000-6.1 % Degree of operating leverage Contribution margin/Net operating income $72618/S4418 1644
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


