Question: Only need parts D,E,F,G Solved Problem The solution is available at www.mhhe.com/Hillierbe. 5.S1. Sensitivity Analysis at Stickley Furniture Stickley Furniture is a manufacturer of fine

 Only need parts D,E,F,G
Only need parts D,E,F,G
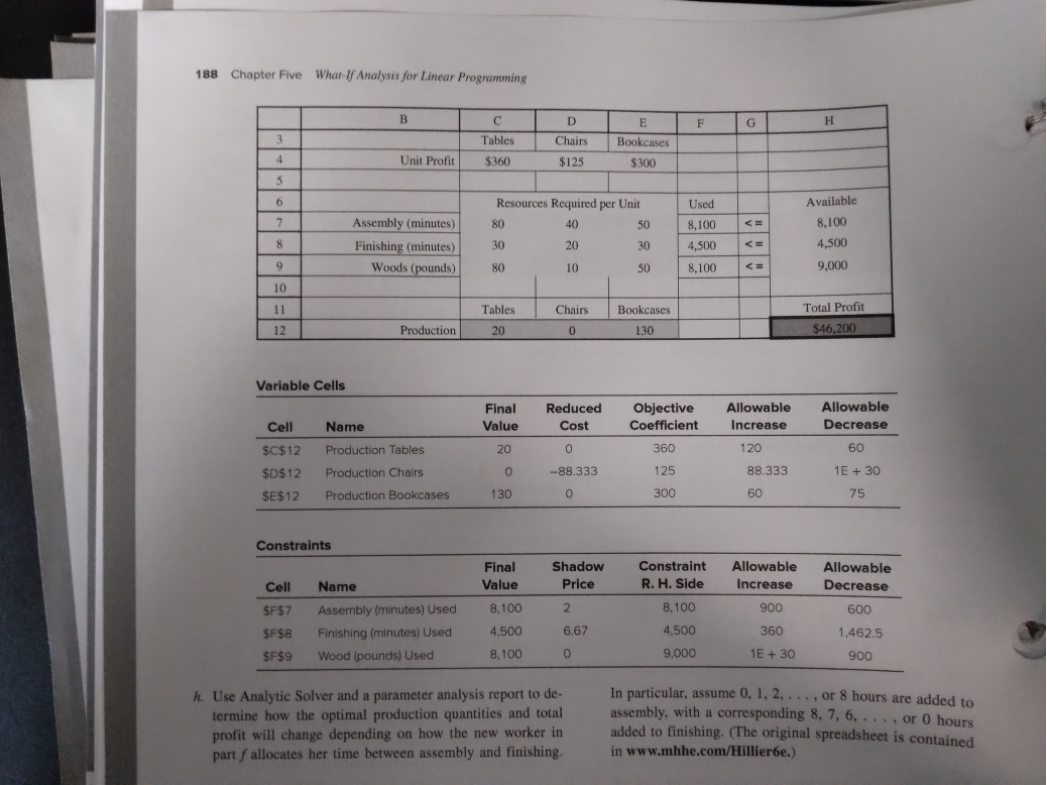
Solved Problem The solution is available at www.mhhe.com/Hillierbe. 5.S1. Sensitivity Analysis at Stickley Furniture Stickley Furniture is a manufacturer of fine hand-crafted fur- niture. During the next production period (the eight-hour shift tomorrow), management is considering producing dining room tables, dining room chairs, and/or bookcases. The time required for each item to go through the two stages of production (assem- bly and finishing), the amount of wood required (fine cherry wood), and the corresponding unit profits are given in the fol- lowing table, along with the amount of each resource available in the upcoming production period. Tables a. Suppose the profit per table increases by $100. Will this change the optimal production quantities? What can be said about the change in total profit? b. Suppose the profit per chair increases by $100. Will this change the optimal production quantities? What can be said about the change in total profit? c. Suppose the profit per table increases by $90 and the profit per bookcase decreases by $50. Will this change the optimal production quantities? What can be said about the change in total profit? d. Suppose a worker in the assembly department calls in sick, so eight fewer hours will be available tomorrow in the assembly department. How much would this affect total profit? Would it change the optimal production quantities? e. Explain why the shadow price for the wood constraint is zero. f. A new worker has been hired who is trained to do both as- sembly and finishing. She will split her time between the two areas, so there now are four additional hours available tomor- row in both assembly and finishing. How much would this affect total profit? Would this change the optimal production quantities? 8. Based on the sensitivity report given below, is it wise to have the new worker in part f split her time equally between assem- bly and finishing, or would some other plan be better? Chairs Bookcases Available 80 40 50 8,100 30 20 30 4,500 Assembly (minutes) Finishing) (minutes) Wood (pounds) Unit profit 10 80 50 9,000 $360 $125 $300 After formulating a linear programming model to determine the production levels that would maximize profit, the solved model and the corresponding sensitivity report are shown below. 188 Chapter Five What If Analysis for Linear Programming B D F G H 3 Tables $360 Chairs E Bookcases $300 4 Unit Profit $125 5 5 6 7 Assembly (minutes) Finishing (minutes) Woods (pounds) Resources Required per Unit 80 40 50 30 20 30 Used 8,100 4,500 AAAL U Available 8,100 4,500 9,000 9 80 10 50 8,100 10 11 Tables Chairs Bookcases 130 Total Profit $46,200 12 Production 20 0 Variable Cells Final Value Reduced Cost Objective Coefficient Allowable Increase Allowable Decrease Cell Name $C$12 Production Tables 20 0 360 120 60 Production Chairs O -88.333 125 88.333 1E + 30 $D$12 $E$12 Production Bookcases 130 0 300 60 75 Constraints Final Value Shadow Price Allowable Increase Constraint R. H. Side 8,100 Allowable Decrease Cell Name 2 900 $F$7 $F$8 $F$9 Assembly (minutes) Used Finishing (minutes) Used Wood (pounds) Used 8,100 4,500 600 1,462.5 6.67 4,500 360 8,100 0 9,000 1E + 30 900 h. Use Analytic Solver and a parameter analysis report to de- termine how the optimal production quantities and total profit will change depending on how the new worker in part allocates her time between assembly and finishing. In particular, assume 0, 1, 2, ..., or 8 hours are added to assembly, with a corresponding 8, 7, 6, .... or 0 hours added to finishing. (The original spreadsheet is contained in www.mhhe.com/Hillierbe.)

 Only need parts D,E,F,G
Only need parts D,E,F,G



