Question: only part d, e and f for upvote else will downvote. Problem 30-1E. The photocatalytic tubular reactor shown in Figure 301E is used to decompose
only part d, e and f for upvote else will downvote.
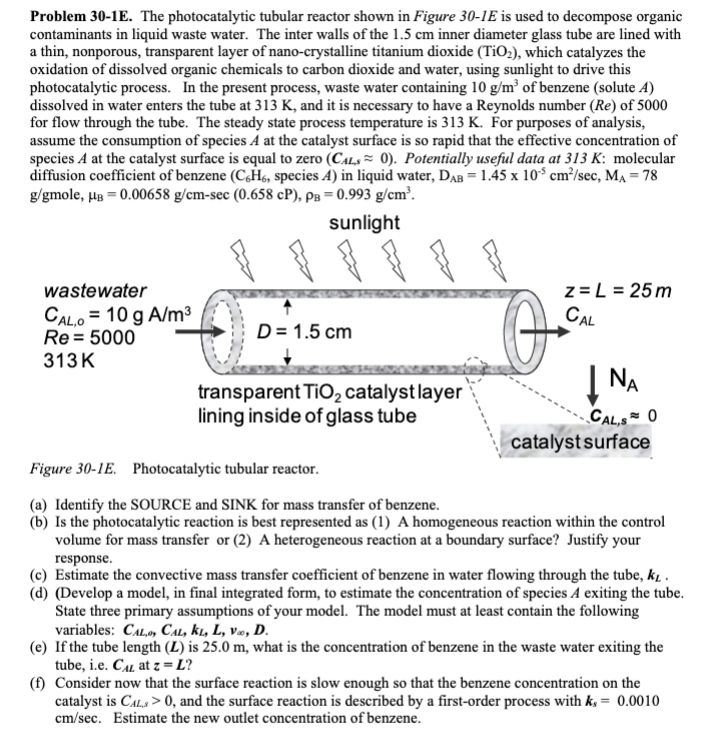
Problem 30-1E. The photocatalytic tubular reactor shown in Figure 301E is used to decompose organic contaminants in liquid waste water. The inter walls of the 1.5cm inner diameter glass tube are lined with a thin, nonporous, transparent layer of nano-crystalline titanium dioxide (TiO2), which catalyzes the oxidation of dissolved organic chemicals to carbon dioxide and water, using sunlight to drive this photocatalytic process. In the present process, waste water containing 10g/m3 of benzene (solute A ) dissolved in water enters the tube at 313K, and it is necessary to have a Reynolds number (Re) of 5000 for flow through the tube. The steady state process temperature is 313K. For purposes of analysis, assume the consumption of species A at the catalyst surface is so rapid that the effective concentration of species A at the catalyst surface is equal to zero (CALs0). Potentially useful data at 313K : molecular diffusion coefficient of benzene (C6H6, species A) in liquid water, DAB=1.45105cm2/sec,MA=78 g/gmole,B=0.00658g/cmsec(0.658cP),B=0.993g/cm3. (a) Identify the SOURCE and SINK for mass transfer of benzene. (b) Is the photocatalytic reaction is best represented as (1) A homogeneous reaction within the control volume for mass transfer or (2) A heterogeneous reaction at a boundary surface? Justify your response. (c) Estimate the convective mass transfer coefficient of benzene in water flowing through the tube, kL. (d) (Develop a model, in final integrated form, to estimate the concentration of species A exiting the tube. State three primary assumptions of your model. The model must at least contain the following variables: CAL,,CAL,kL,L,v,D. (e) If the tube length ( L ) is 25.0m, what is the concentration of benzene in the waste water exiting the tube, i.e. CAL at z=L ? (f) Consider now that the surface reaction is slow enough so that the benzene concentration on the catalyst is CAL,s>0, and the surface reaction is described by a first-order process with ks=0.0010 cm/sec. Estimate the new outlet concentration of benzene
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


