Question: Operating Leverage Operating leverage is the use of fixed costs to increase the percentage change in profits as sales activity changes. Typically a company has
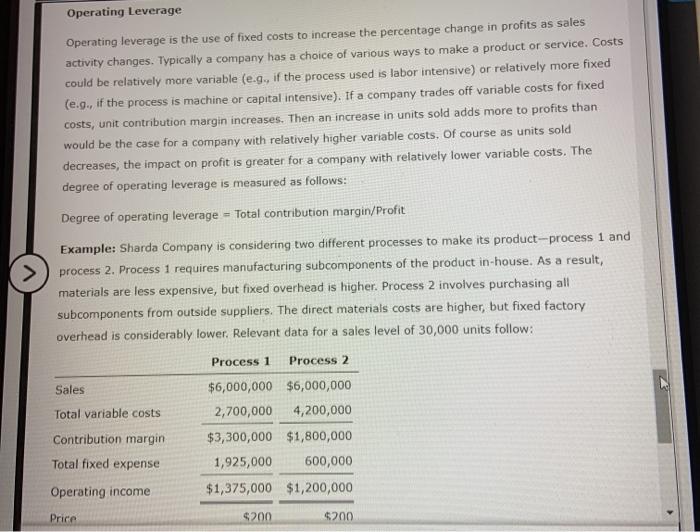
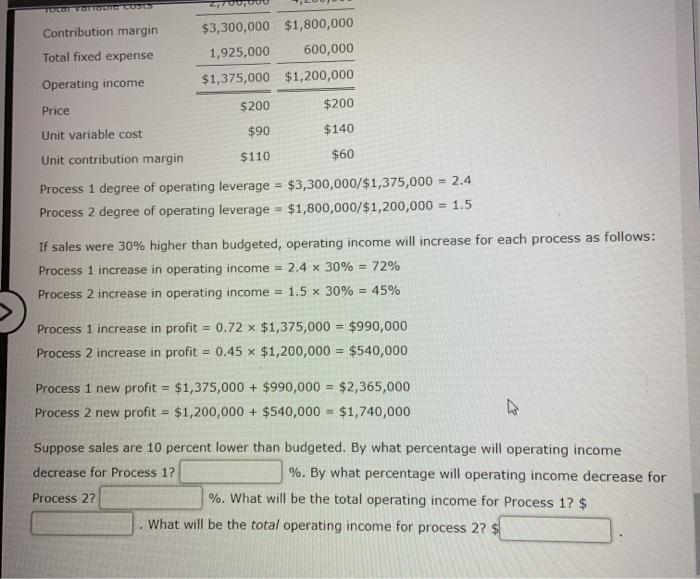
Operating Leverage Operating leverage is the use of fixed costs to increase the percentage change in profits as sales activity changes. Typically a company has a choice of various ways to make a product or service. Costs could be relatively more variable (e.g., if the process used is labor intensive) or relatively more fixed (e.g., if the process is machine or capital intensive). If a company trades off variable costs for fixed costs, unit contribution margin increases. Then an increase in units sold adds more to profits than would be the case for a company with relatively higher variable costs. Of course as units sold decreases, the impact on profit is greater for a company with relatively lower variable costs. The degree of operating leverage is measured as follows: Degree of operating leverage - Total contribution margin/Profit > Example: Sharda Company is considering two different processes to make its product-process 1 and process 2. Process 1 requires manufacturing subcomponents of the product in-house. As a result, materials are less expensive, but fixed overhead is higher. Process 2 involves purchasing all subcomponents from outside suppliers. The direct materials costs are higher, but fixed factory overhead is considerably lower. Relevant data for a sales level of 30,000 units follow: Process 1 Process 2 Sales Total variable costs Contribution margin Total fixed expense $6,000,000 $6,000,000 2,700,000 4,200,000 $3,300,000 $1,800,000 1,925,000 600,000 $1,375,000 $1,200,000 Operating income Price $200 $200 TUTTGOTG CONES Contribution margin Total fixed expense $3,300,000 $1,800,000 1,925,000 600,000 $1,375,000 $1,200,000 $200 $200 Operating income Price Unit variable cost $90 $140 Unit contribution margin $110 $60 Process 1 degree of operating leverage = $3,300,000/$1,375,000 = 2.4 Process 2 degree of operating leverage = $1,800,000/$1,200,000 = 1.5 If sales were 30% higher than budgeted, operating income will increase for each process as follows: Process 1 increase in operating income = 2.4 x 30% = 72% Process 2 increase in operating income = 1.5 x 30% = 45% Process 1 increase in profit = 0.72 x $1,375,000 = $990,000 Process 2 increase in profit = 0.45 x $1,200,000 = $540,000 Process 1 new profit = $1,375,000 + $990,000 = $2,365,000 Process 2 new profit = $1,200,000 + $540,000 = $1,740,000 Suppose sales are 10 percent lower than budgeted. By what percentage will operating income decrease for Process 1? %. By what percentage will operating income decrease for Process 22 %. What will be the total operating income for Process 1? $ What will be the total operating income for process 2? $
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


