Question: Operating system Homework, please help me solve it, thank you in advance Designing a Virtual Memory Manager This project consists of writing a program that

Operating system Homework, please help me solve it, thank you in advance
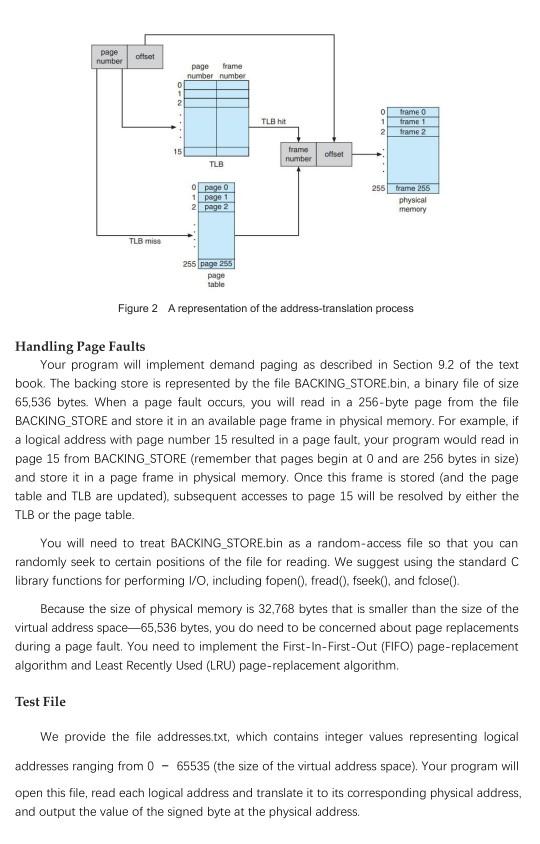
Designing a Virtual Memory Manager This project consists of writing a program that translates logical to physical addresses for a virtual address space of size 2" = 65,536 bytes. Your program will read from a file containing logical addresses and, using a TLB as well as a page table, will translate each logical address to its corresponding physical address and output the value of the byte stored at the translated physical address. The goal behind this project is to simulate the steps involved in translating logical to physical addresses. Specifics Your program will read a file containing several 32-bit integer numbers that represent logical addresses. However, you need only be concerned with 16-bit addresses, so you must mask the rightmost 16 bits of each logical address. These 16 bits are divided into (1) an 8-bit page number and (2) 8-bit page offset. Hence, the addresses are structured as shown in Figure 1. Other specifics include the following: 1) 2 entries in the page table 2) Page size of 2' bytes 3) 16 entries in the TLB 4) Frame size of 2 bytes 5) 128 frames 6) Physical memory of 32,768 bytes (128 frames 256-byte frame size) offset page number 1615 87 31 Figure 1 Address structure Additionally, your program need only be concerned with reading logical addresses and translating them to their corresponding physical addresses. You do not need to support writing to the logical address space. Address Translation Your program will translate logical to physical addresses using a TLB and page table as outlined in Section 8.5 of the text book. First, the page number is extracted from the logical address, and the TLB is consulted. In the case of a TLB-hit, the frame number is obtained from the TLB. In the case of a TLB-miss, the page table must be consulted. In the latter case, either the frame number is obtained from the page table or a page fault occurs. A visual representation of the address-translation process appears in Figure 2. page number otset frame page number number 0 TL hit frame trame frame 2 15 frame number oliset TLD opage 1 page 1 2 page 2 256 Frame 255 physical memory TLB misa 255 page 25 page table Figure 2 A representation of the address-translation process Handling Page Faults Your program will implement demand paging as described in Section 9.2 of the text book. The backing store is represented by the file BACKING_STORE.bin, a binary file of size 65,536 bytes. When a page fault occurs, you will read in a 256-byte page from the file BACKING_STORE and store it in an available page frame in physical memory. For example, if a logical address with page number 15 resulted in a page fault, your program would read in page 15 from BACKING_STORE (remember that pages begin at O and are 256 bytes in size) and store it in a page frame in physical memory. Once this frame is stored and the page table and TLB are updated), subsequent accesses to page 15 will be resolved by either the TLB or the page table. You will need to treat BACKING_STORE.bin as a random-access file so that you can randomly seek to certain positions of the file for reading. We suggest using the standard C library functions for performing I/O, including fopen(), fread(), fseek(), and fclose(). Because the size of physical memory is 32,768 bytes that is smaller than the size of the virtual address space-65,536 bytes, you do need to be concerned about page replacements during a page fault. You need to implement the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) page-replacement algorithm and Least Recently Used (LRU) page-replacement algorithm Test File We provide the file addresses.txt, which contains integer values representing logical addresses ranging from 0 - 65535 (the size of the virtual address space). Your program will open this file, read each logical address and translate it to its corresponding physical address, and output the value of the signed byte at the physical address
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


