Question: Operating Systems Questions (Please help if you can) 5. The following state transition table is a simplied model of process management, with the labels representing
Operating Systems Questions (Please help if you can)
5. The following state transition table is a simplied model of process management, with
the labels representing transitions between states of READY, RUN, BLOCKED, and NONRESIDENT
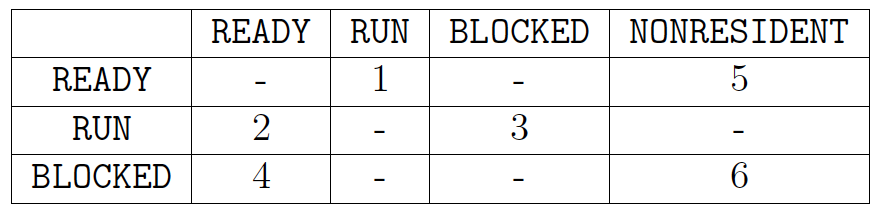
Interpret transition 2 as the fact that the process can change from RUN to READY. Give an
example of an event that can cause each of the above transitions. Draw a diagram if that
helps.
6. Consider the following program:
const int n = 50;
int tally;
void total()
{
for ( int count = 0; count
tally++;
}
void main()
{
tally = 0;
parbegin
total();
total();
parend;
write ( tally );
}
(a) Determine the proper lower bound and upper bound on the nal value of the shared
variable tally output by this concurrent program. Assume processes can execute at any
relative speed and that a value can only be incremented after it has been loaded into a
register by a separate machine instruction.
(b) Suppose that an arbitrary number of processes are permitted to execute in parallel under
the assumptions of part (a). What effect will this modifcation have on the range of final
value of tally?
READY RUN BLOCKED NONRESIDENT READY RUN BLOCKED 2 4 - - READY RUN BLOCKED NONRESIDENT READY RUN BLOCKED 2 4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


