Question: Operation Managements, Flexsim modeling, Flexsim With regard to each problem set within CDVD enterprise, answer the following questions:Theoretical: What are the problem sets and how
Operation Managements, Flexsim modeling, Flexsim
With regard to each problem set within CDVD enterprise, answer the following questions:Theoretical: What are the problem sets and how are they interrelated? Which is the most severe problem? What are the decision variables for each problem set? Flexsim model: How is the due date set? Change the relevant parameter(s) and analyze/interpret the changes in the costs (Global Table Performance). Describe how order release works within the provided Flexsim model. What is the cost performance of immediate release/backward infinite scheduling?

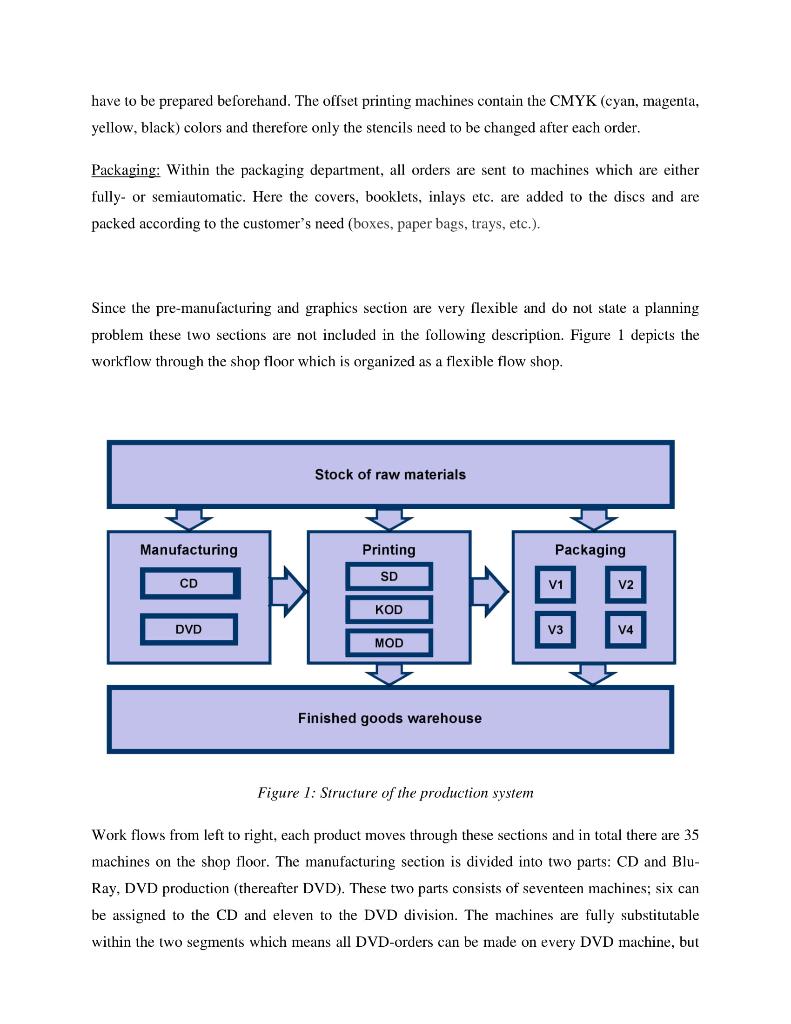

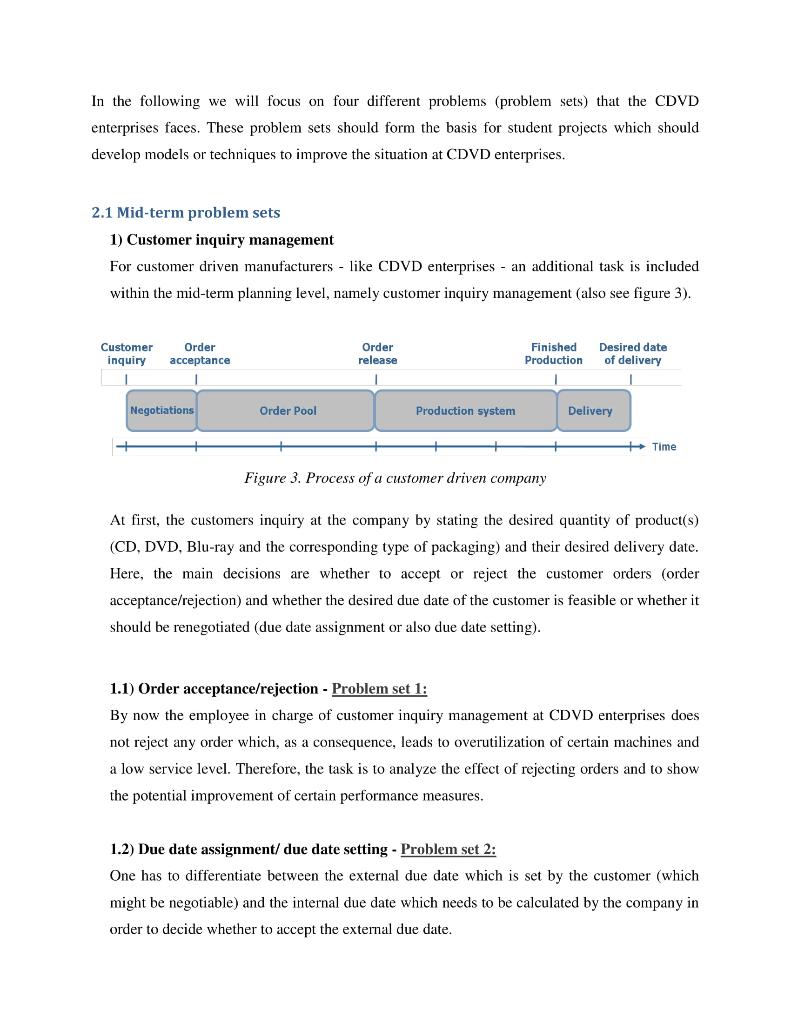


CDVD-Enterprises 1. Introduction "CDVD enterprises" is a customer driven optical storage media producer making about 90.000.000 CDs, Blu-rays and DVDs per year serving about 31.500 different customers. Production is divided into five sections: pre-manufacturing, manufacturing, graphics, printing and packaging. In general, the production can be described as follows: Pre-manufacturing: Each customer sends an email (or a CD) containing the data to be reproduced by CDVD enterprises. This data is written to a unique mould a so-called "stamper" which is used to make a disc ingot for further replication. The stamper consists of silicone or glass with a diameter of about 20 centimeters. The data is written to silicone- glassmaster with a laser beam that "records" the information that is going to be replicated. The information is recorded to the disc by producing tiny indentations to the polycarbonate known as "pits" and "lands". Manufacturing: After the stamper is made the disc replication starts by using molding machines. Here a syringe injects a heated liquid polycarbonate (approx. 360 degrees Celsius) producing the disc which already contains digital information, but cannot be scanned since at this stage the disc is completely transparent. After a short cooling of the disc, one side of the disc (containing the information) is covered with a silver, aluminum or gold layer and thereafter is covered with lacquer which reflects the laser beam in order to read the information from the disc. After a quality inspection the discs are collected on a spindle. Graphics: Within the graphics department the covers of the discs are produced according to the customer's provided graphic design. Here print stencils are made for the different printing technologies (serigraphy or offset printing). Printing: Depending on the quality requirements (high quality offset) the discs are printed at a serigraphy- or an offset machine. The difference between these two techniques is mainly that for the serigraphy printing machines the mesh has to be cleaned after each order and that the colors have to be prepared beforehand. The offset printing machines contain the CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, black) colors and therefore only the stencils need to be changed after each order. Packaging: Within the packaging department, all orders are sent to machines which are either fully- or semiautomatic. Here the covers, booklets, inlays etc. are added to the discs and are packed according to the customer's need (boxes, paper bags, trays, etc.). Since the pre-manufacturing and graphics section are very flexible and do not state a planning problem these two sections are not included in the following description. Figure 1 depicts the workflow through the shop floor which is organized as a flexible flow shop. Stock of raw materials Manufacturing Printing Packaging SD CD V2 KOD DVD V3 V4 MOD Finished goods warehouse Figure 1: Structure of the production system Work flows from left to right, each product moves through these sections and in total there are 35 machines on the shop floor. The manufacturing section is divided into two parts: CD and Blu- Ray, DVD production (thereafter DVD). These two parts consists of seventeen machines; six can be assigned to the CD and eleven to the DVD division. The machines are fully substitutable within the two segments which means all DVD-orders can be made on every DVD machine, but an DVD-order cannot be transferred to the CD part. The printing section is structured into three parts since three technologies are available to print the media: serigraphy division (SD), kammann- (KOD) and metronic offset division (MOD). These three parts consists of ten machines, six of them are serigraphy, three are kammann offset and one is a metronic offset machine. The SD machines are partly substitutable and the KOD machines are fully substitutable. The packaging section is structured into four parts, the VI (CD boxes), V2 (shrinking), V3 (DVD boxes) and V4 (paper, cardboard and plastic bags) packaging and consists of 8 machines (2 for each part) whereas the machines in Vi. V3 and V4 are partly substitutable and V2 machines are fully substitutable. The production operates 16 hours per day, seven days a week in two shifts, bottlenecks work stations are in the printing and packaging section due to the varying product mix. The next section describes the production) planning tasks and problems at CDVD enterprises. 2. Production planning and control tasks and problems at CDVD enterprises In general, production planning and control at CDVD enterprises follows a hierarchical approach. Figure 2 shows the hierarchical structure and the planning tasks at the company. procurement production distribution sales long-term materials program supplier selection - cooperations plant location . production system physical distribution structure . product program strategic sales planning Master Planning ---- mid-term personnel planning master production - material requirements planning planning capacity planning contracts distribution planning mid-term sales planning short-term personnel planning ordering materials lot-sizing machine scheduling shop floor control Warehouse replenishment - transport planning short-term sales planning flow of goods information flows 1 Figure 2. Planning tasks as described in Fleischmann et al. (2008) In the following we will focus on four different problems (problem sets) that the CDVD enterprises faces. These problem sets should form the basis for student projects which should develop models or techniques to improve the situation at CDVD enterprises. 2.1 Mid-term problem sets 1) Customer inquiry management For customer driven manufacturers - like CDVD enterprises - an additional task is included within the mid-term planning level, namely customer inquiry management (also see figure 3). Customer inquiry Order acceptance Order release Finished Production Desired date of delivery Negotiations Order Pool Production system Delivery Time Figure 3. Process of a customer driven company At first, the customers inquiry at the company by stating the desired quantity of product(s) (CD, DVD, Blu-ray and the corresponding type of packaging) and their desired delivery date. Here, the main decisions are whether to accept or reject the customer orders (order acceptance/rejection) and whether the desired due date of the customer is feasible or whether it should be renegotiated (due date assignment or also due date setting). 1.1) Order acceptance/rejection - Problem set 1: By now the employee in charge of customer inquiry management at CDVD enterprises does not reject any order which, as a consequence, leads to overutilization of certain machines and a low service level. Therefore, the task is to analyze the effect of rejecting orders and to show the potential improvement of certain performance measures. 1.2) Due date assignment/ due date setting - Problem set 2: One has to differentiate between the external due date which is set by the customer (which might be negotiable) and the internal due date which needs to be calculated by the company in order to decide whether to accept the external due date. By now, CDVD enterprises uses forward scheduling to set the internal due date. Starting with the expected date that the customer places the order (Email with the data for the CD/DVD/Blu ray production) they add a fixed planned lead time of 6 days (3 days production, printing and packaging, 2 days transport and 1 day buffer) and thereafter accept or renegotiate the due date with the customer. A major weakness of this approach is that the capacities of the production departments are not taken into account and thus the 6 days (fixed) lead time are mostly a bad estimation of the actual lead times. 2.2 Short-term problem sets 2) Shop floor control: order release - Problem set 3: After order acceptance and due date setting all accepted) orders are collected in an order pool (see figure 3 above). This order pool is a (digital list) of orders provided to the production planner who decides (each day) which orders to release to the shop floor. At CDVD enterprises orders are automatically released by an infinite backward scheduling approach. Thus, the release date is calculated by subtracting a fixed lead time of 3 days from the given (external) due date of an order. Capacities of the machines are not considered which leads to time-varying loading and thus to changing utilization levels at the machines and as a consequence to shifting bottlenecks. Thus, high WIP levels and therefore long lead times are observed which, as a consequence, lead to a poor service level. The management seeks for an improved order release mechanism; they are especially fond of an order release mechanism based on workload control. 3) Machine scheduling - Problem set 4: On the shop floor, supervisors need to decide on the schedule of orders on specific machines that is - allocating orders to resources at a specific time. Especially at the printing department, scheduling of orders to the nine different printing machines is important. By now, supervisors make scheduling decisions using a rule of thumb. Thus the managers and the supervisors request a decision support tool for detailed scheduling at least for the six serigraphy machines. Extra problem set - supply of polycarbonate: In order to guarantee a smooth production, polycarbonate needs to be on stock when needed, acquired in time and in good quality. Currently, the responsible employee forecasts the demand for polycarbonate over a planning horizon of 14 days. Therefore, she looks at the order book, the stock of the material and uses historical data (simple average) in order to anticipate the demand. The company looks for an inventory control policy that determines a reorder point and quantity (the mean lead time of the supplier is 3 days)









